Deposition Date
2025-11-18
Release Date
2026-01-28
Last Version Date
2026-01-28
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9Z9H
Keywords:
Title:
Stable open state sheep connexin-50 in DMPC nanodiscs at low pH
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Ovis aries (Taxon ID: 9940)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
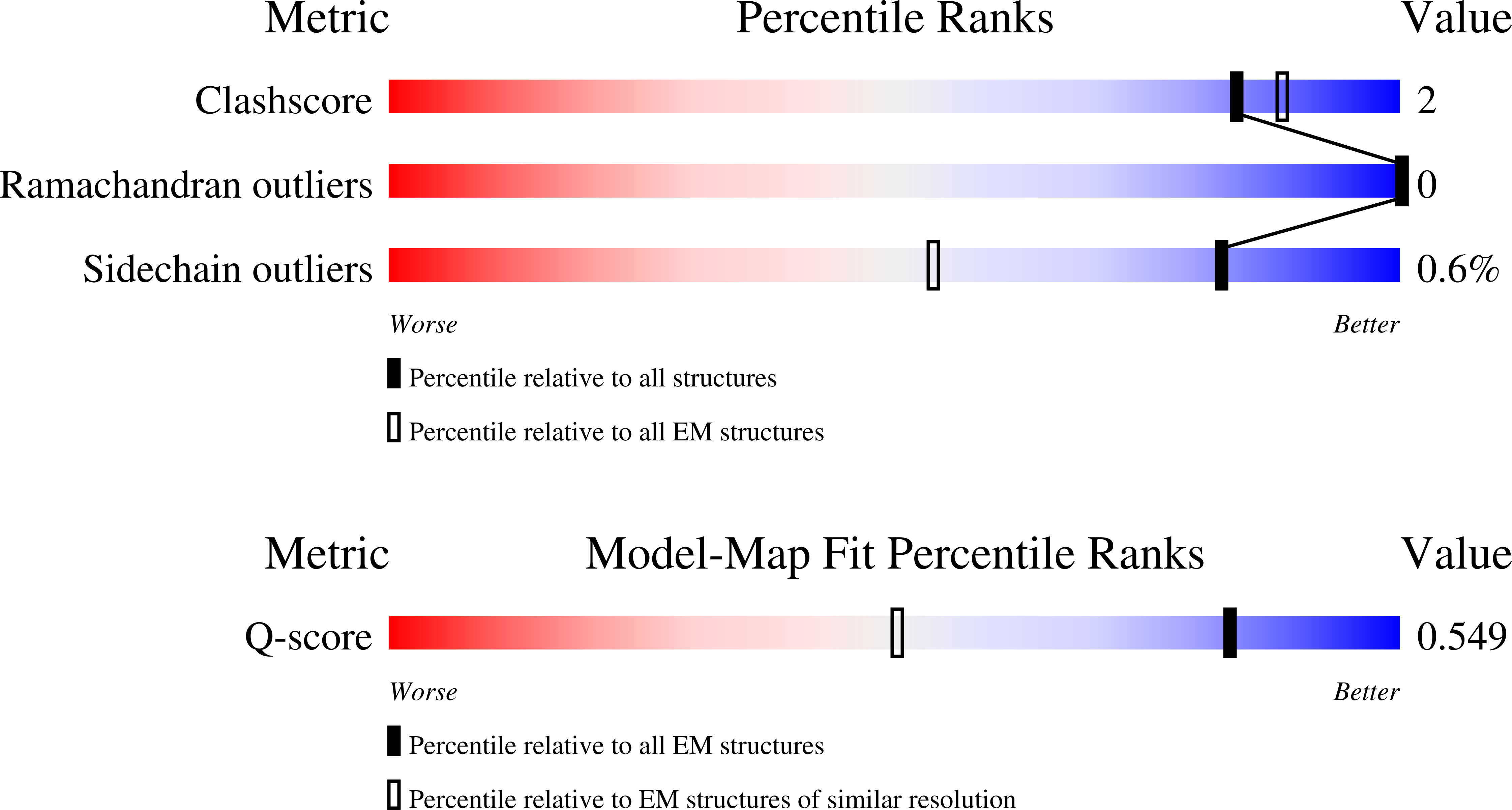
Resolution:
2.50 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE