Deposition Date
2025-05-15
Release Date
2025-11-19
Last Version Date
2025-12-03
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9UYN
Keywords:
Title:
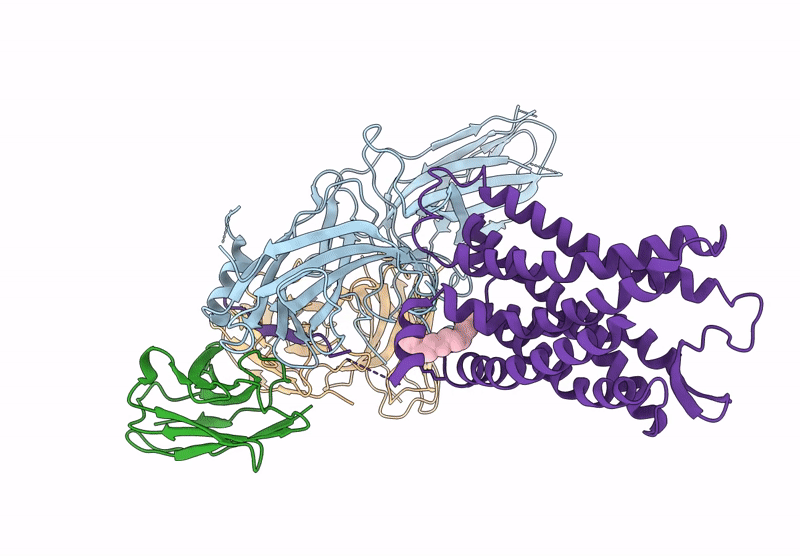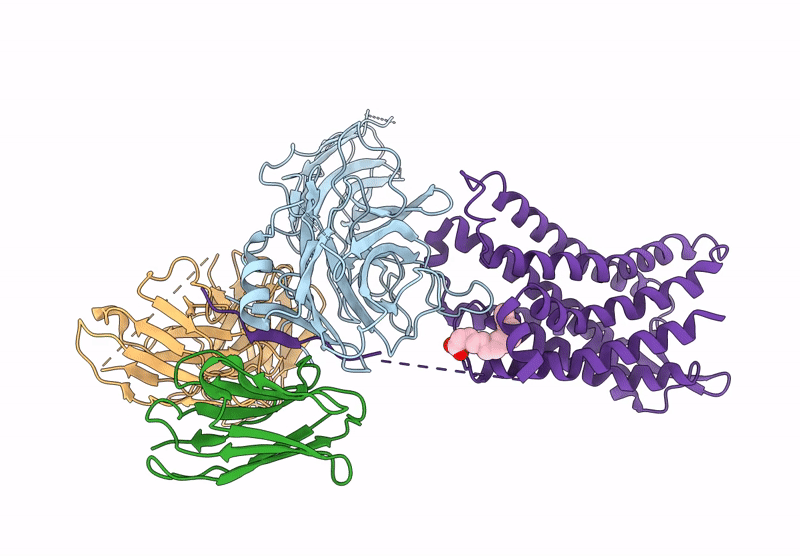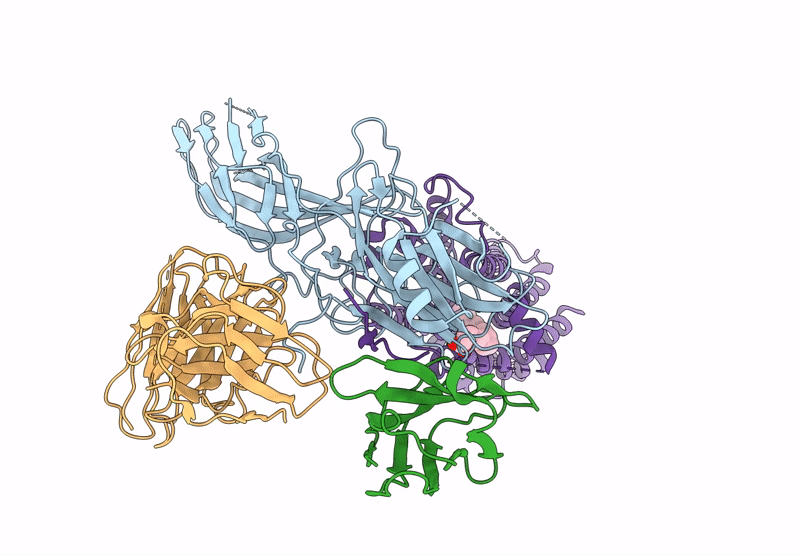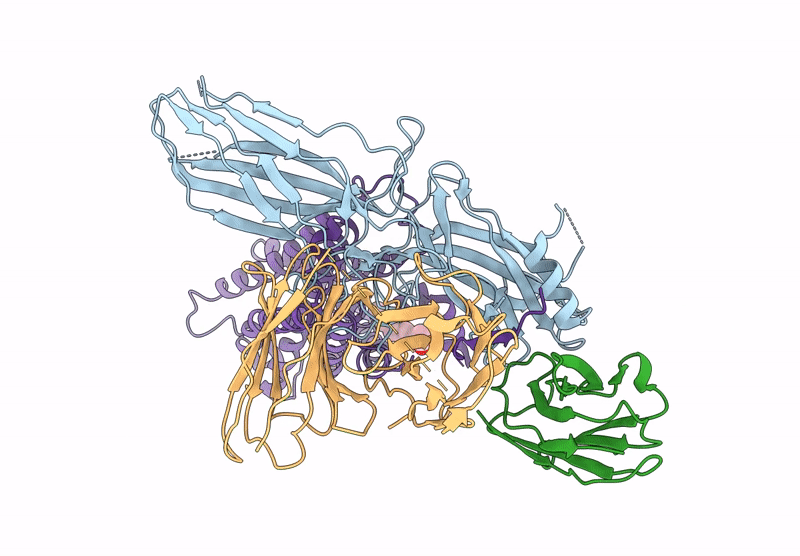
Cryo-EM structure of the G protein-coupled receptor 1 (GPR1) bound to beta-arrestin 1 in ligand-free state
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (Taxon ID: 2419741)
Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (Taxon ID: 2419741)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
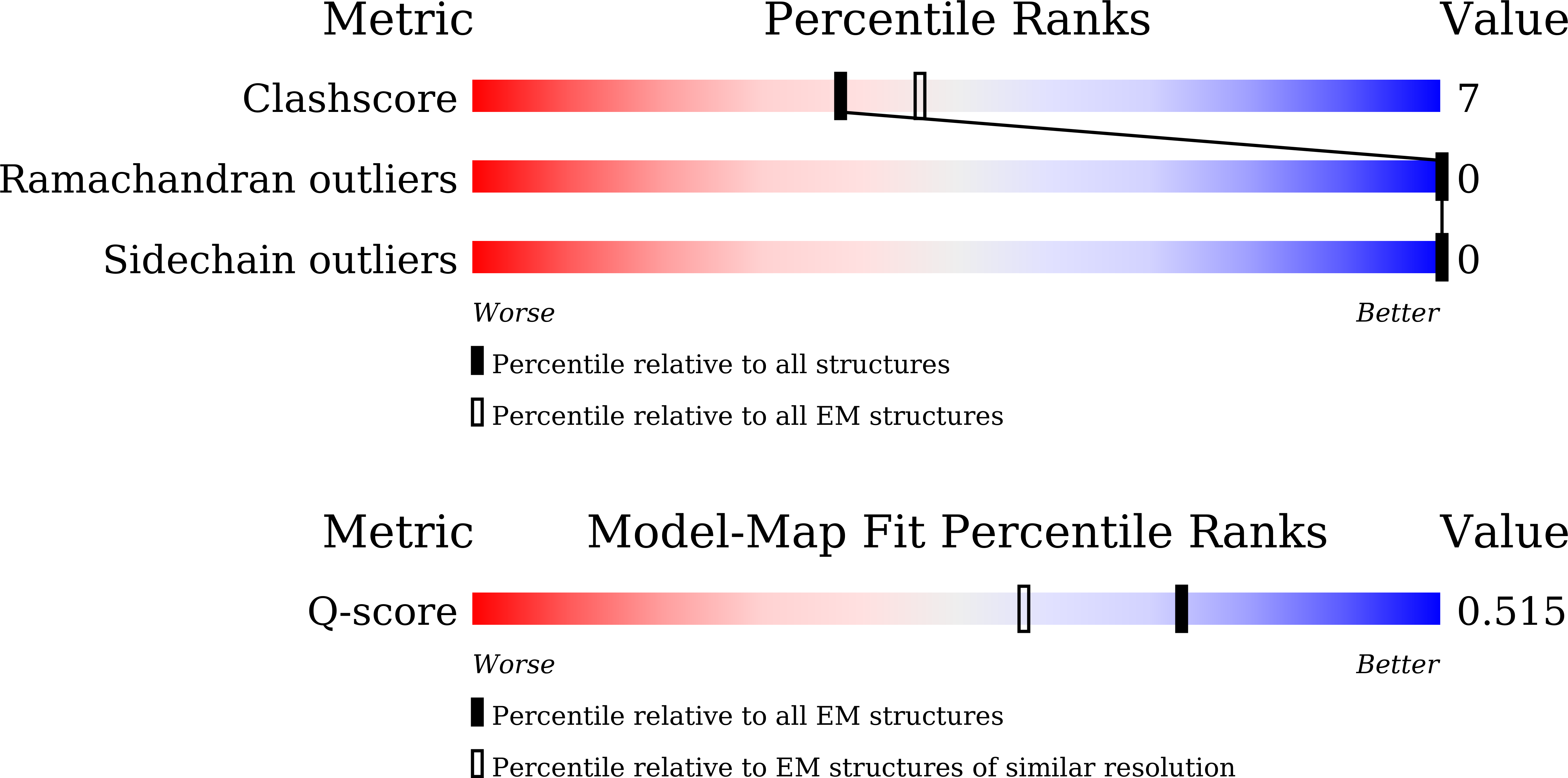
Resolution:
2.90 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE