Deposition Date
2025-04-18
Release Date
2025-10-22
Last Version Date
2025-10-29
Entry Detail
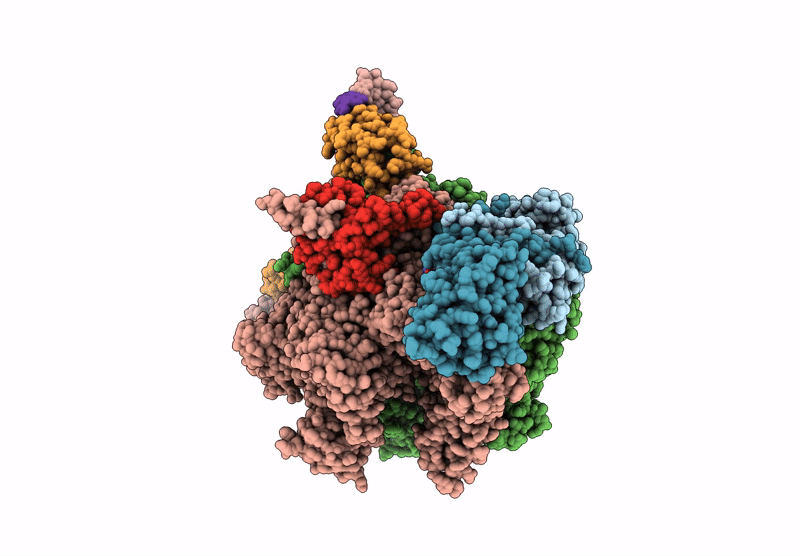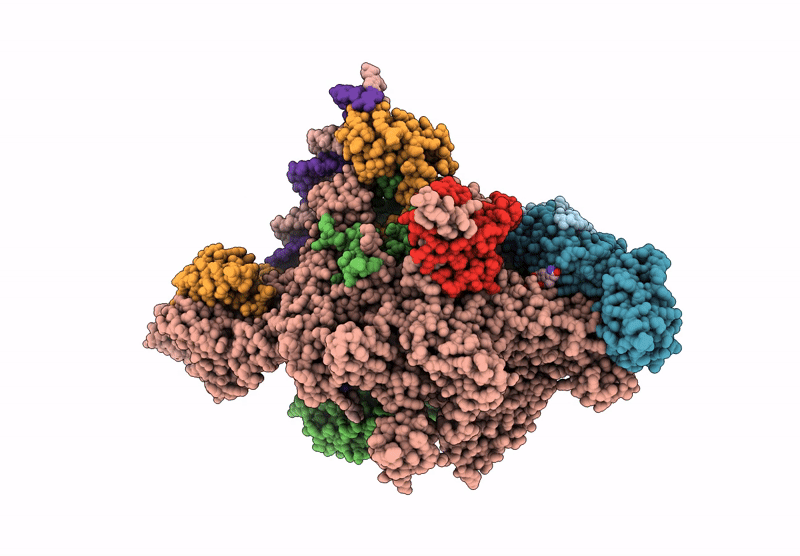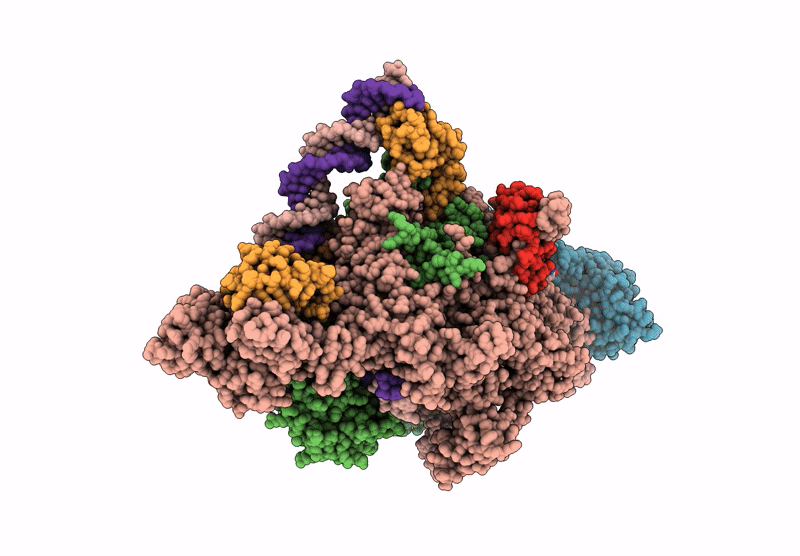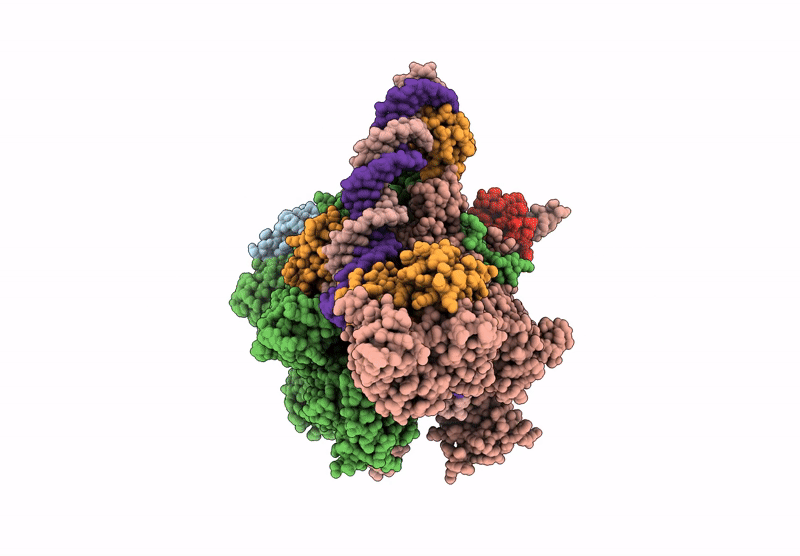
PDB ID:
9UKO
Keywords:
Title:
CryoEM structure of the T.thermophilus transcription initiation complex bound to Ap4A-C, -1 dA in the template DNA strand
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Thermus thermophilus HB8 (Taxon ID: 300852)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
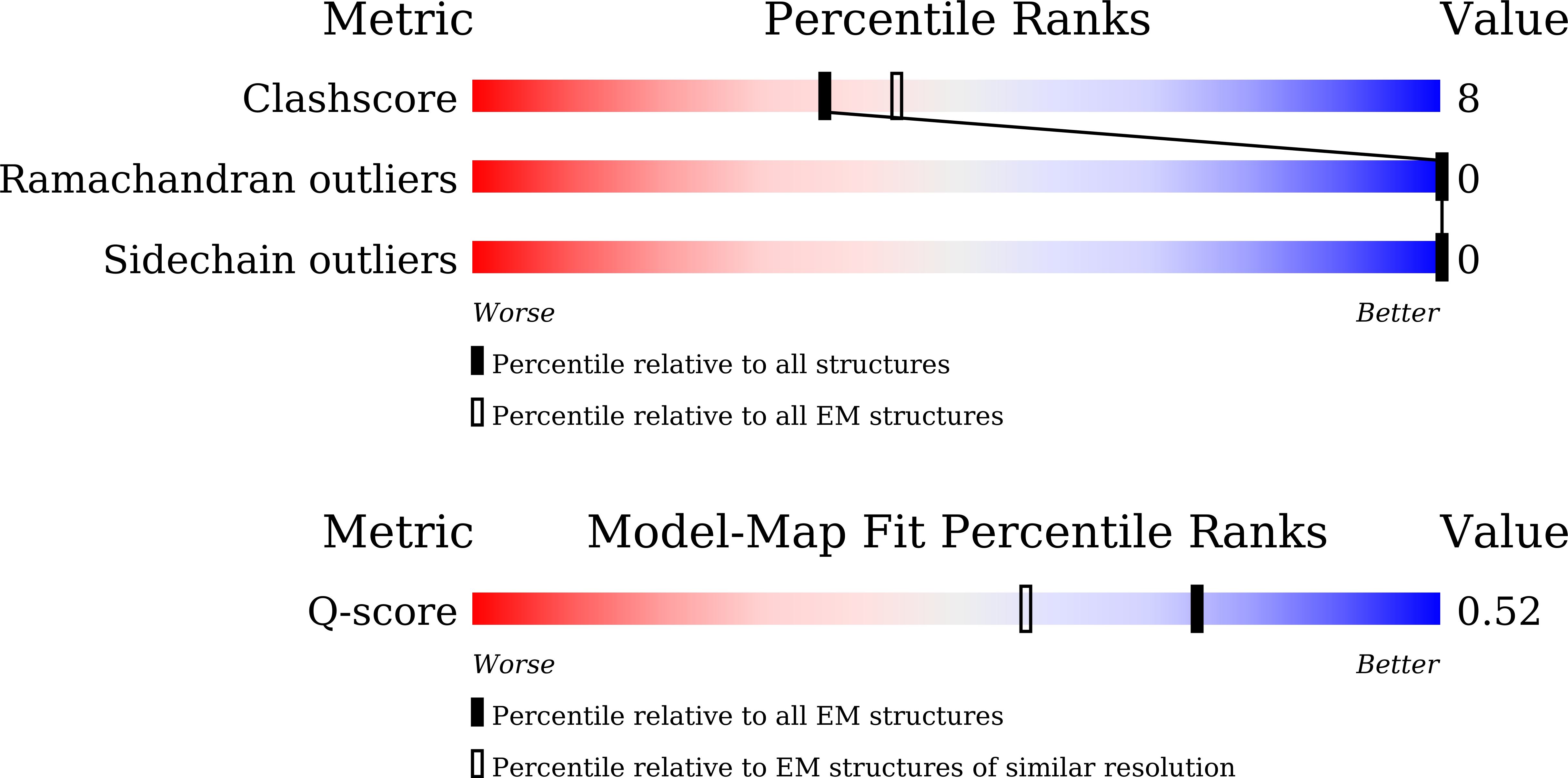
Resolution:
2.89 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE