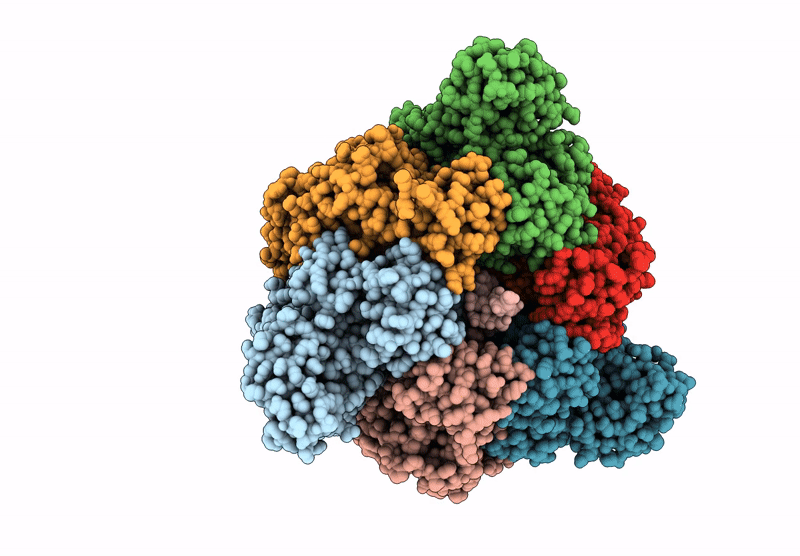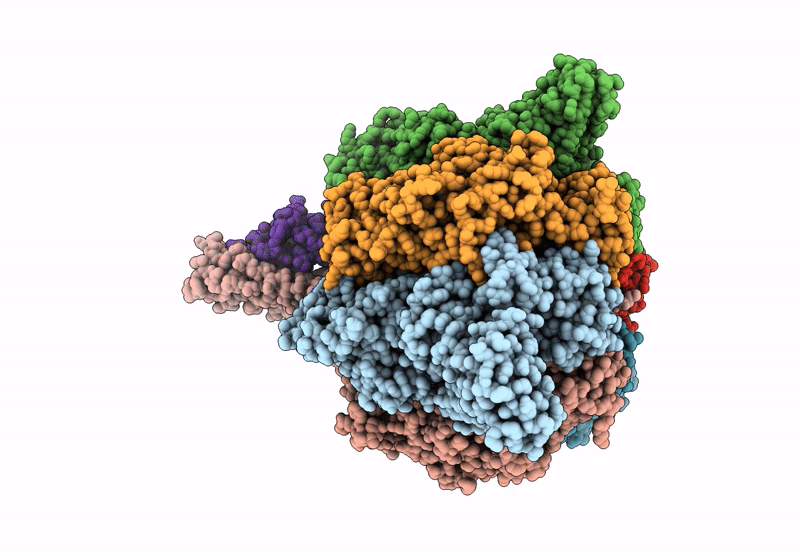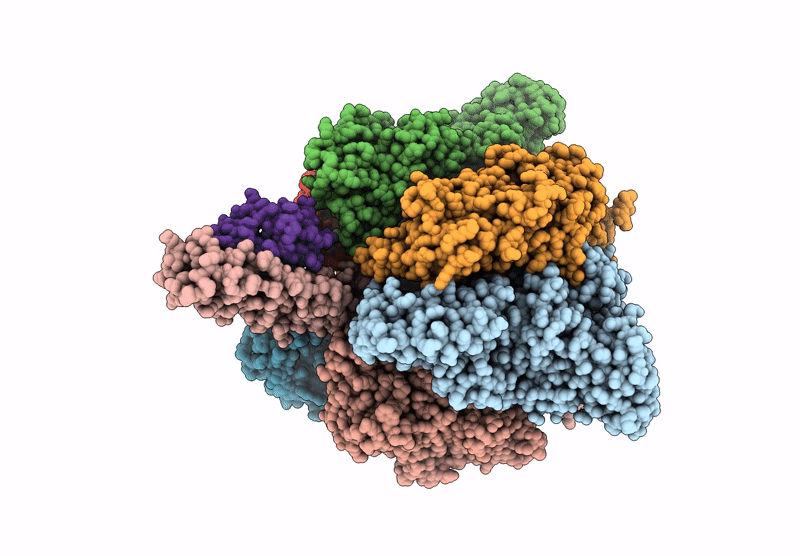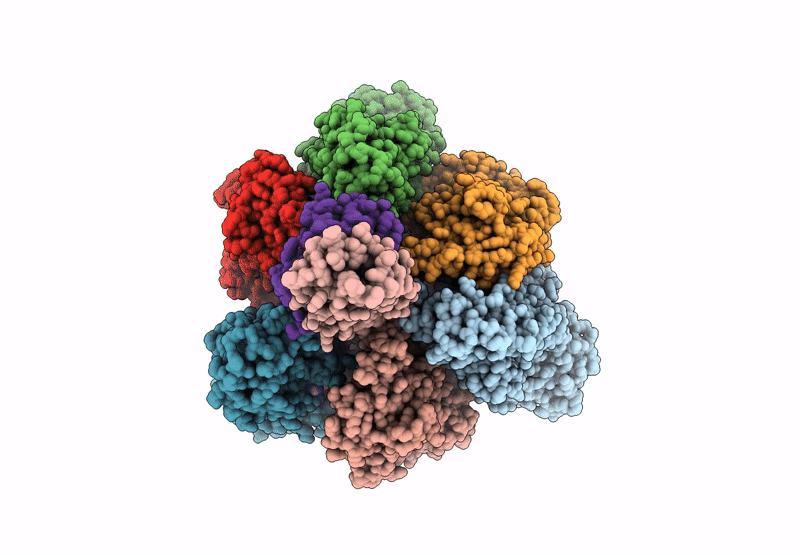
Deposition Date
2025-03-23
Release Date
2025-10-29
Last Version Date
2025-10-29
Entry Detail
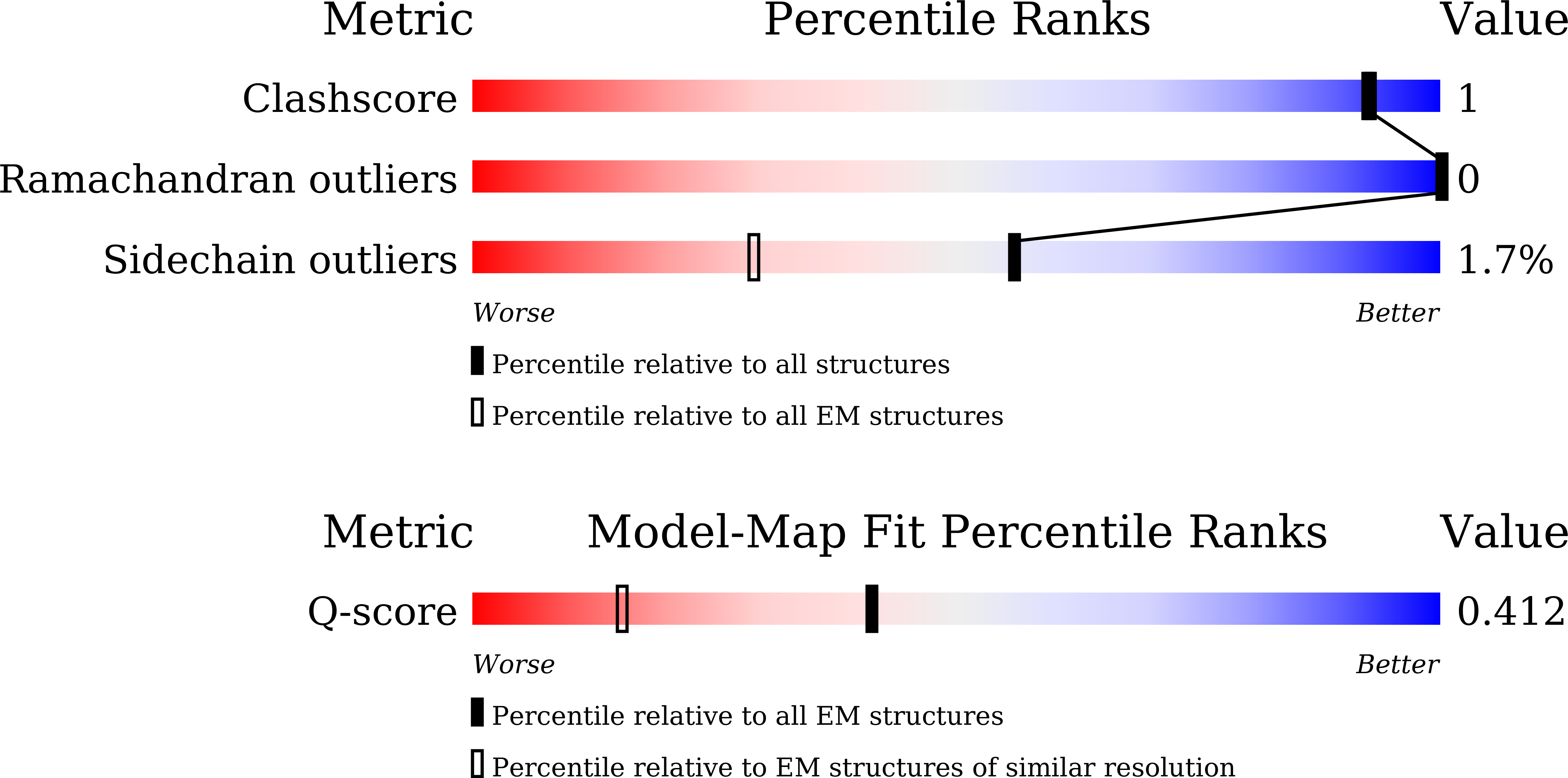
PDB ID:
9U6Y
Keywords:
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of the V1 domain of V/A-ATPase in liposomes under pmf condition, state3N
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermus thermophilus HB8 (Taxon ID: 300852)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.90 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE