Deposition Date
2025-07-30
Release Date
2025-08-20
Last Version Date
2025-10-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9S5X
Keywords:
Title:
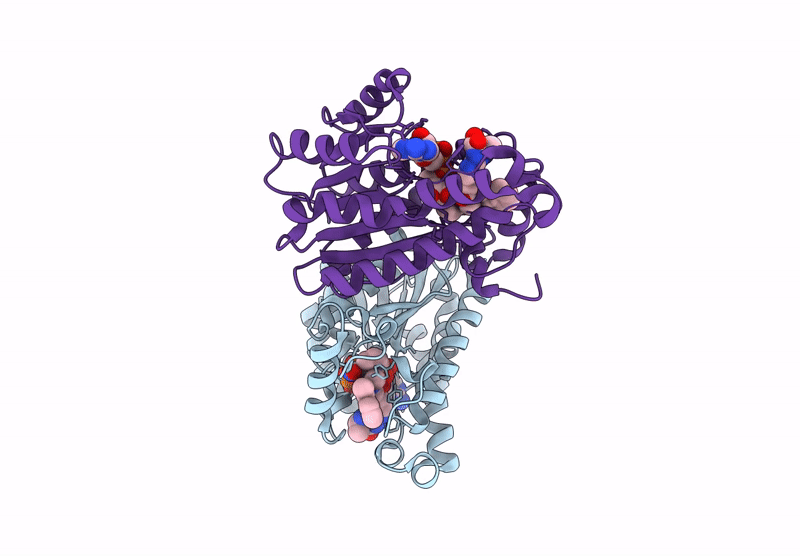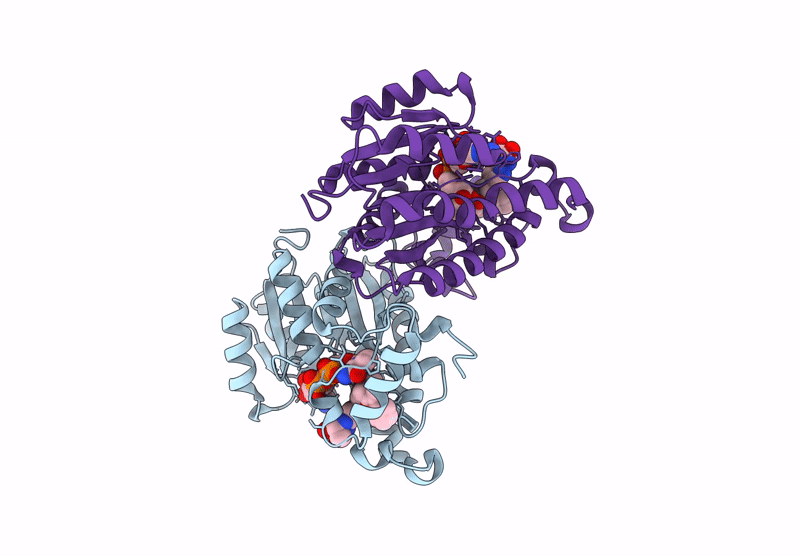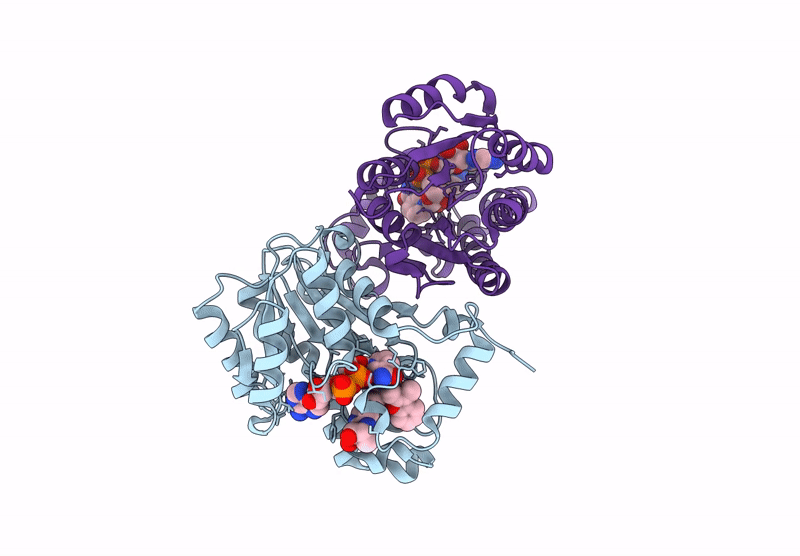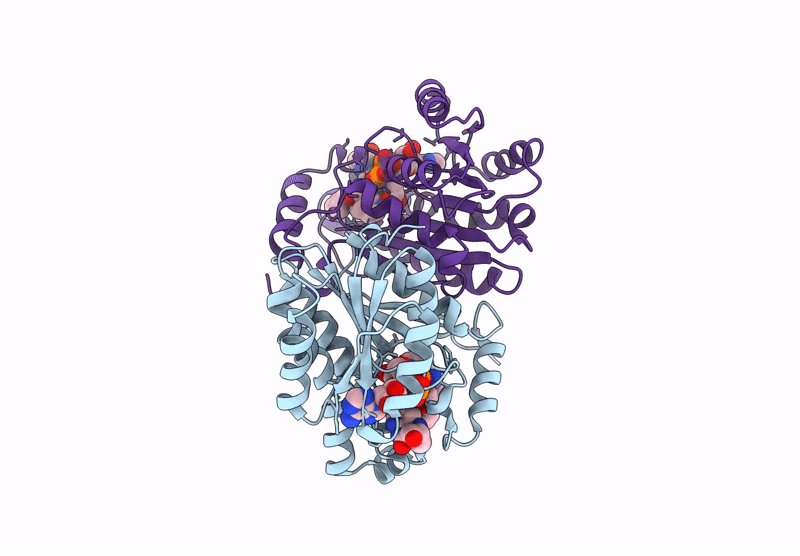
Crystal structure of Neisseria gonorrhoeae FabI in complex with NADH and (E)-3-((2R,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[2,3-b][1,4]diazepin-8-yl)-N-methyl-N-((3-methylbenzofuran-2-yl)methyl)acrylamide
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Taxon ID: 485)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
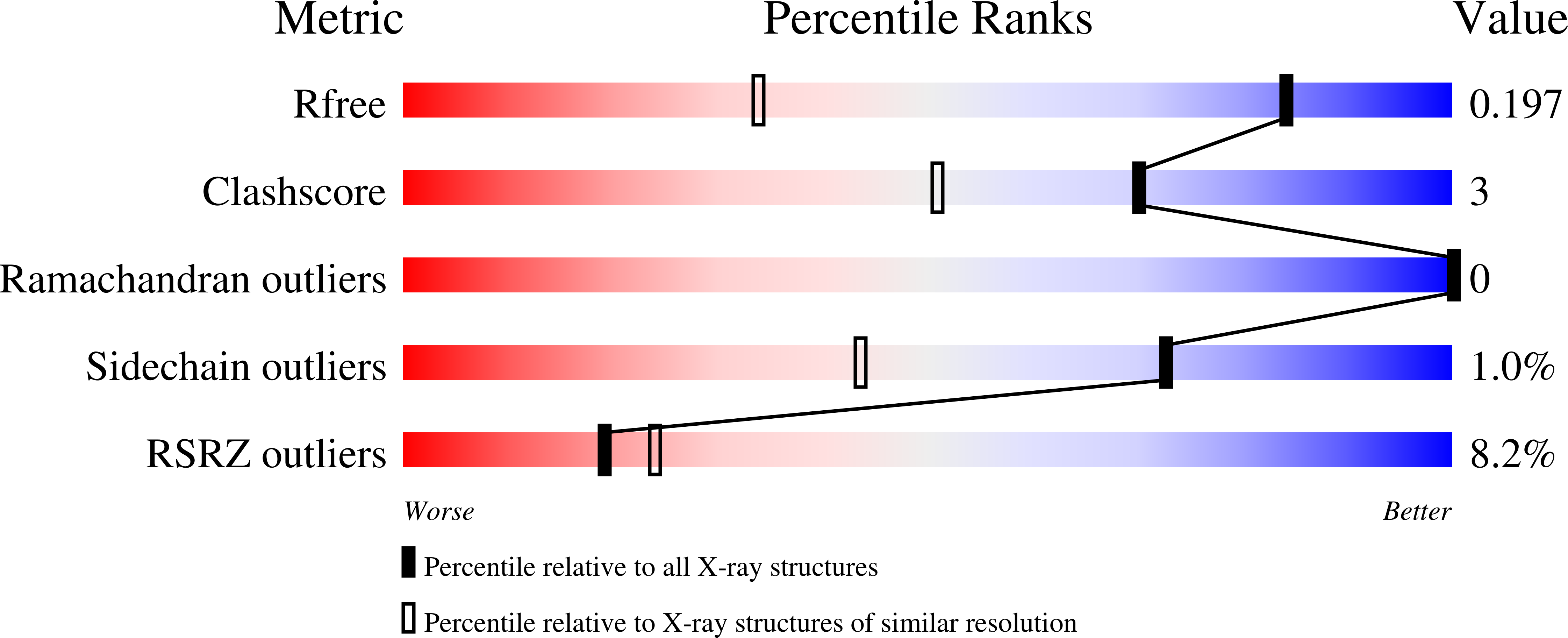
Resolution:
1.34 Å
R-Value Free:
0.19
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 61 2 2