Deposition Date
2025-04-09
Release Date
2025-12-24
Last Version Date
2026-01-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9QTP
Keywords:
Title:
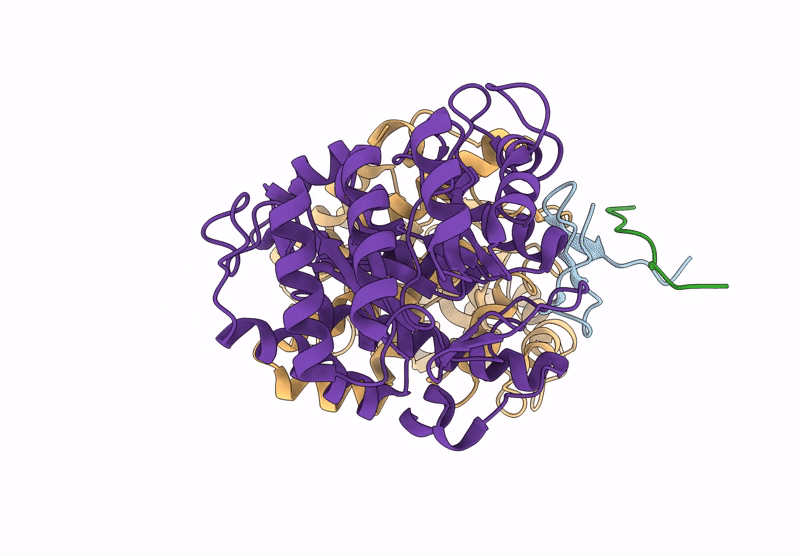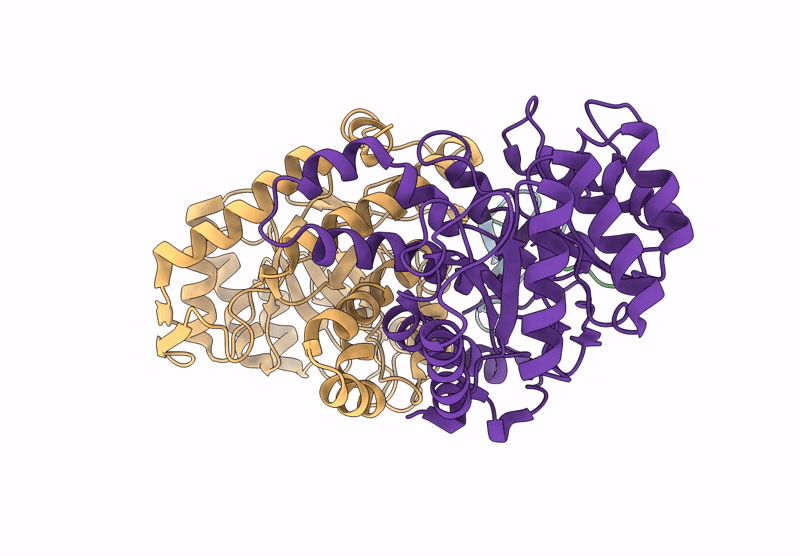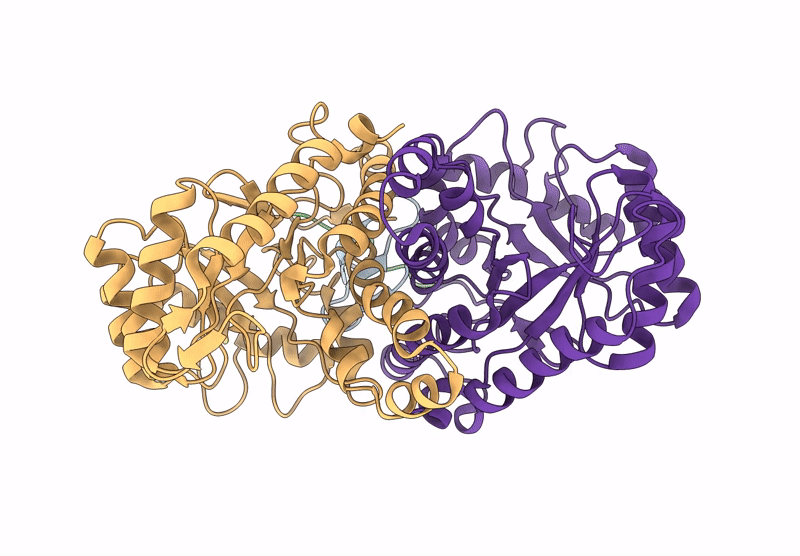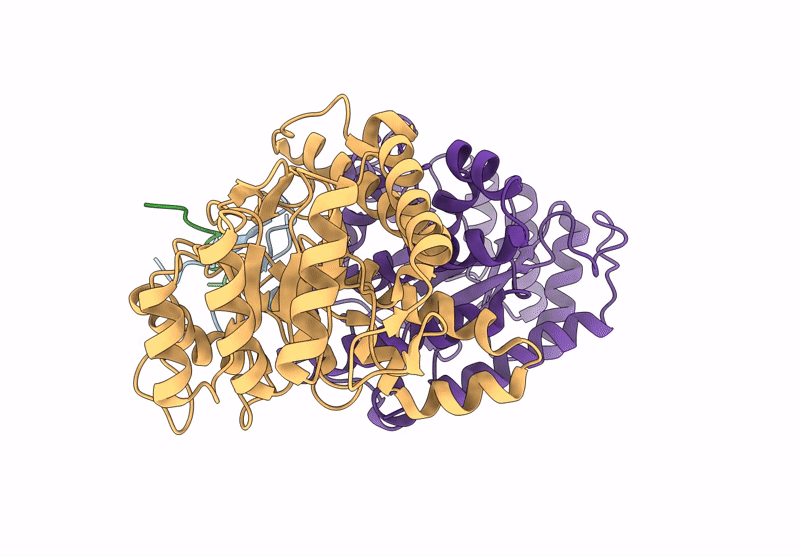
Structure of the energy converting methyltransferase (Mtr) of Methanosarcina mazei in complex with a novel protein binder
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Methanosarcina mazei Go1 (Taxon ID: 192952)
Method Details:
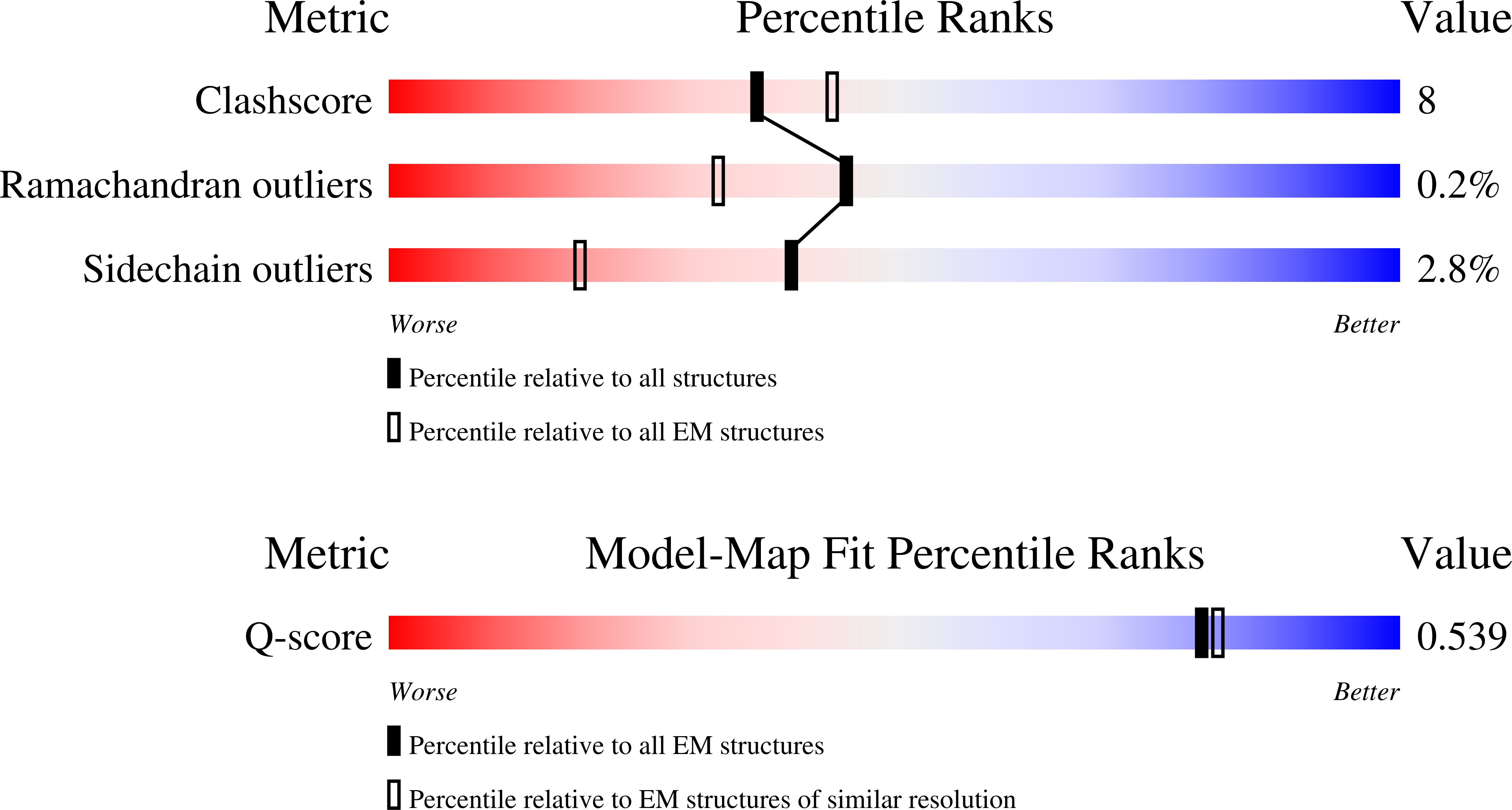
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.20 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE