Deposition Date
2025-08-20
Release Date
2026-01-14
Last Version Date
2026-01-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9Q50
Keywords:
Title:
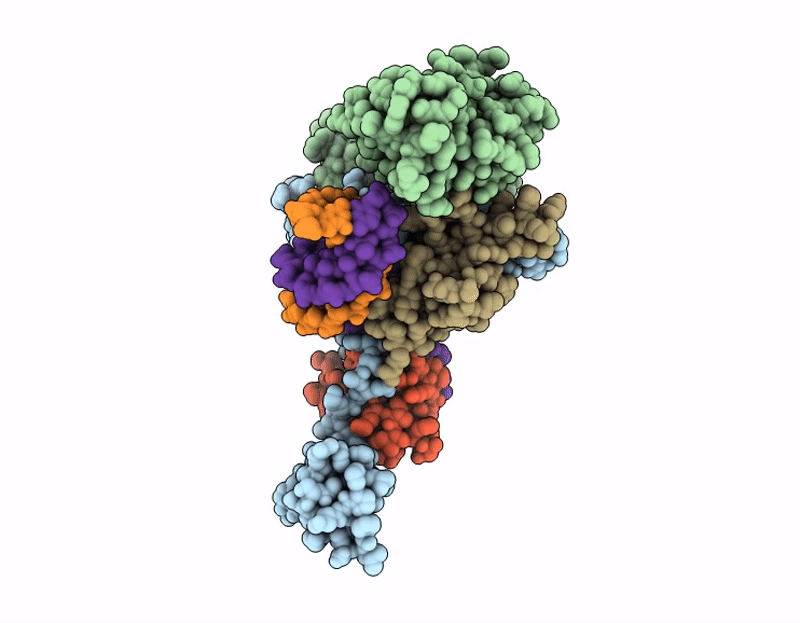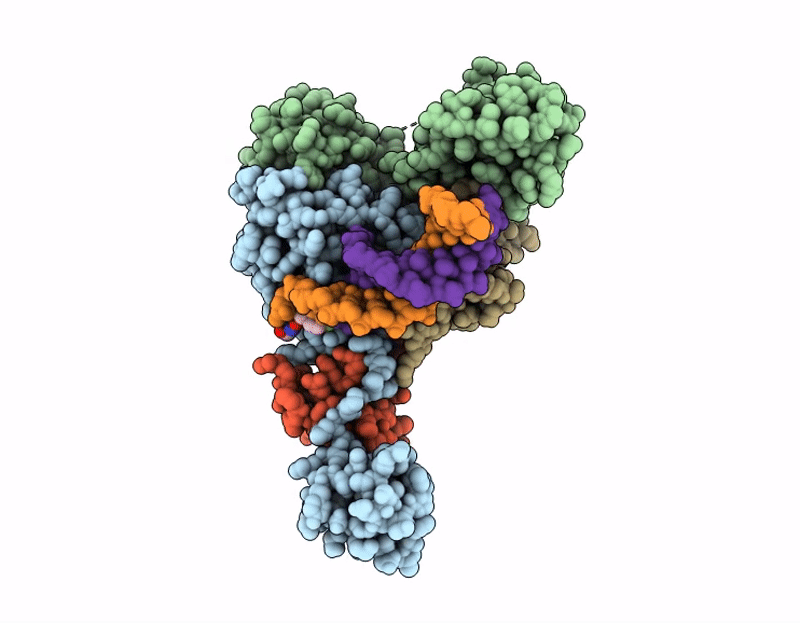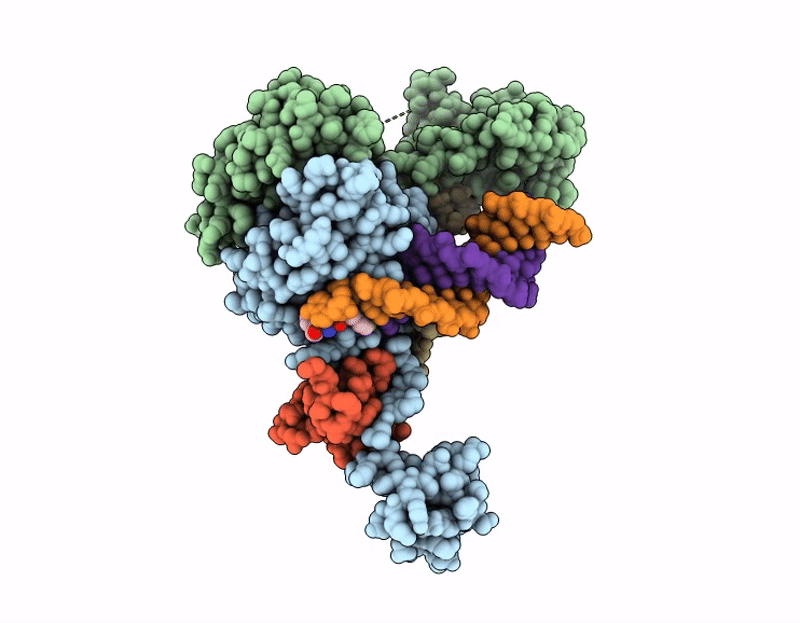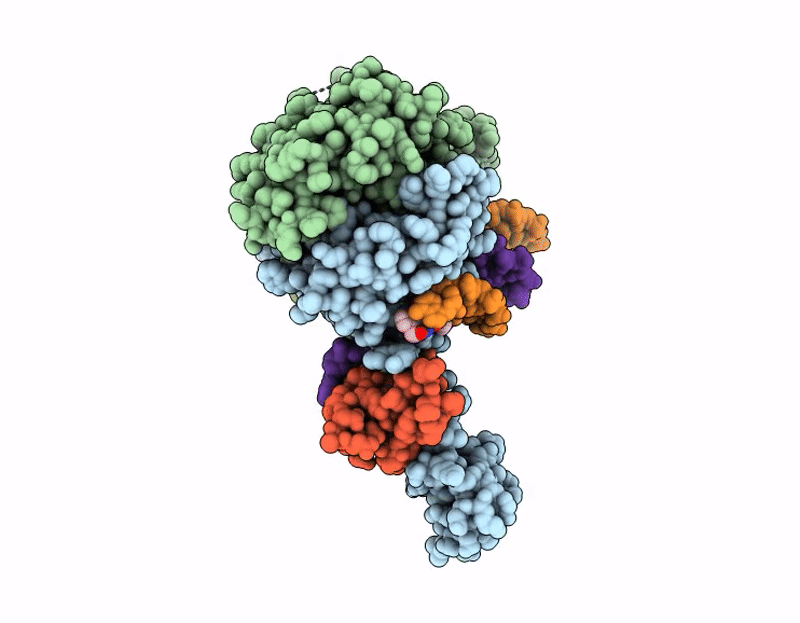
AK01 integrase inhibitor bound to Wild-type HIV-1 intasome
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
HIV-1 06TG.HT008 (Taxon ID: 587638)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
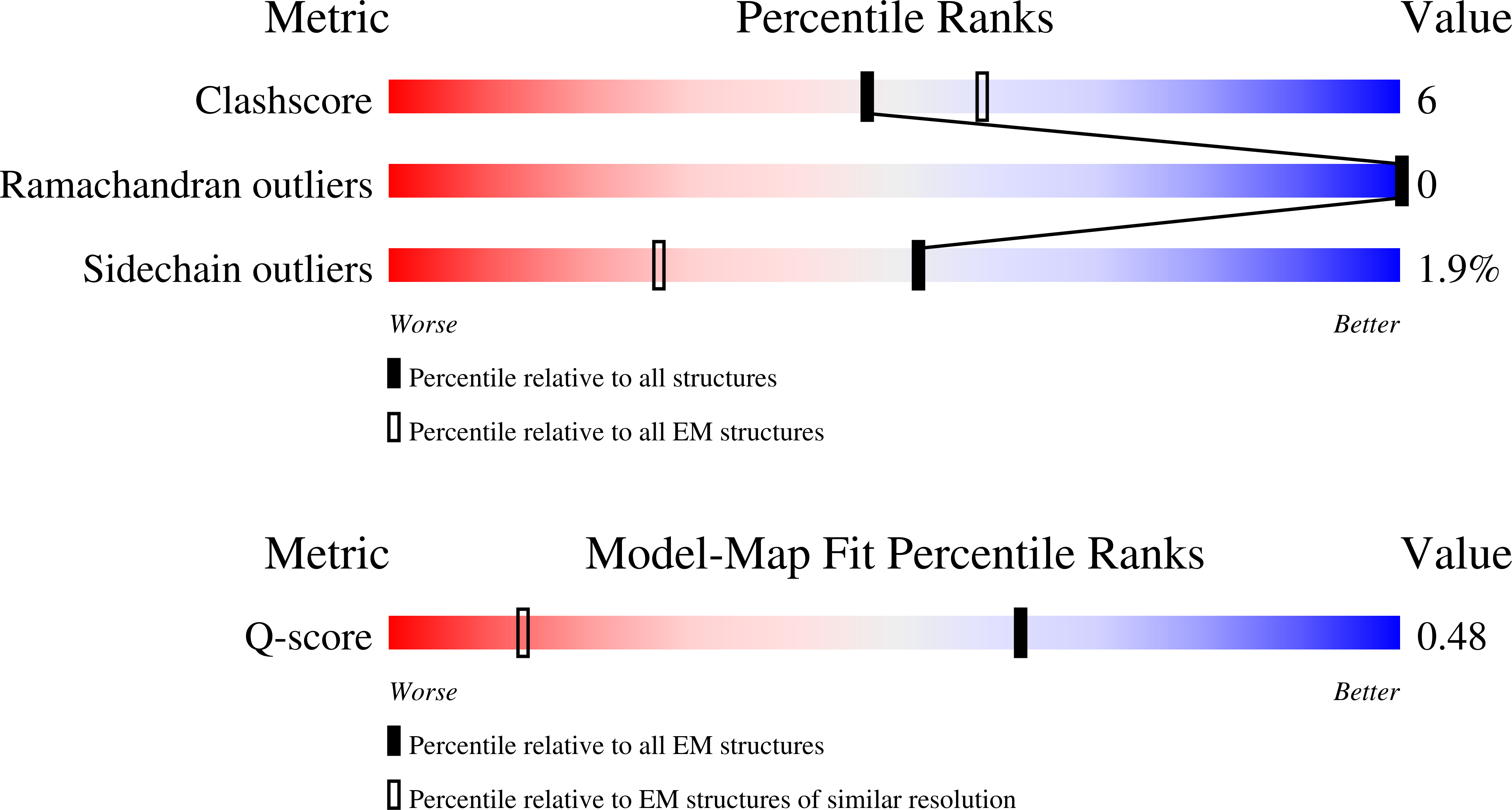
Resolution:
2.33 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE