Deposition Date
2025-03-14
Release Date
2025-07-02
Last Version Date
2025-09-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9NR6
Keywords:
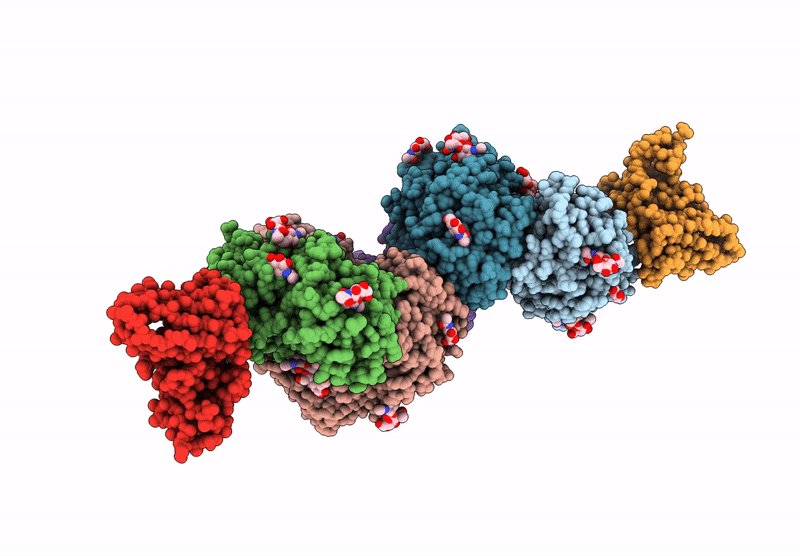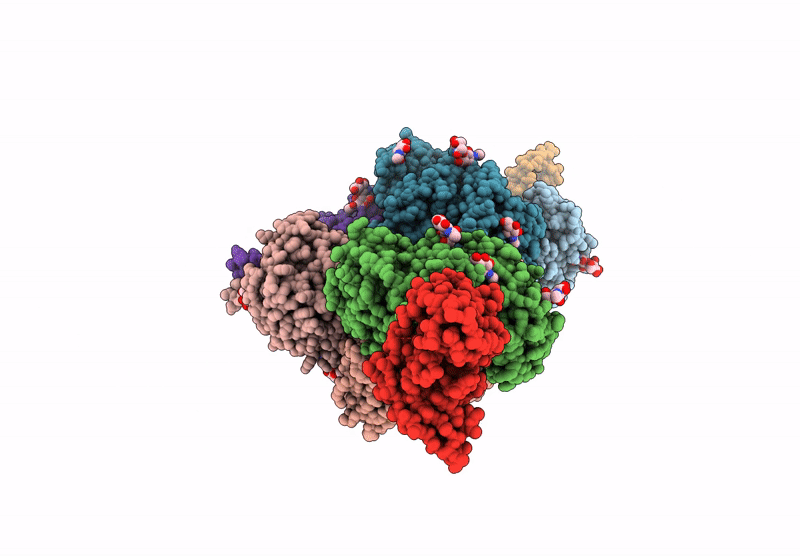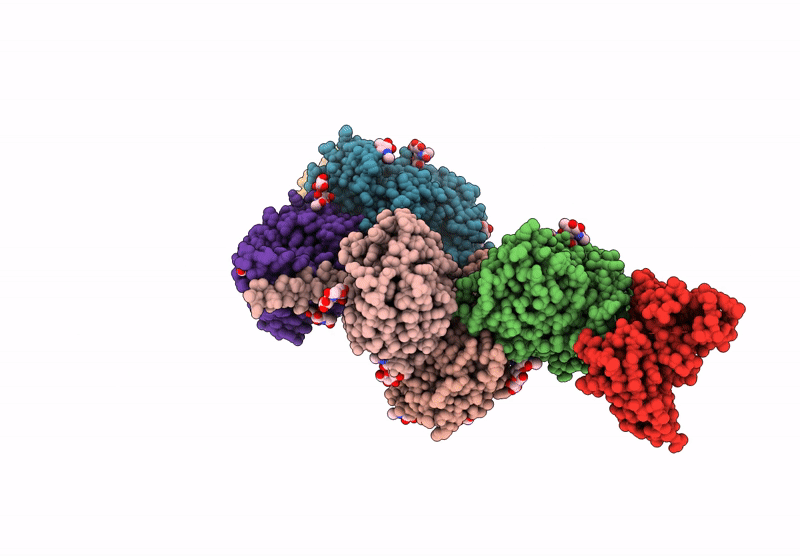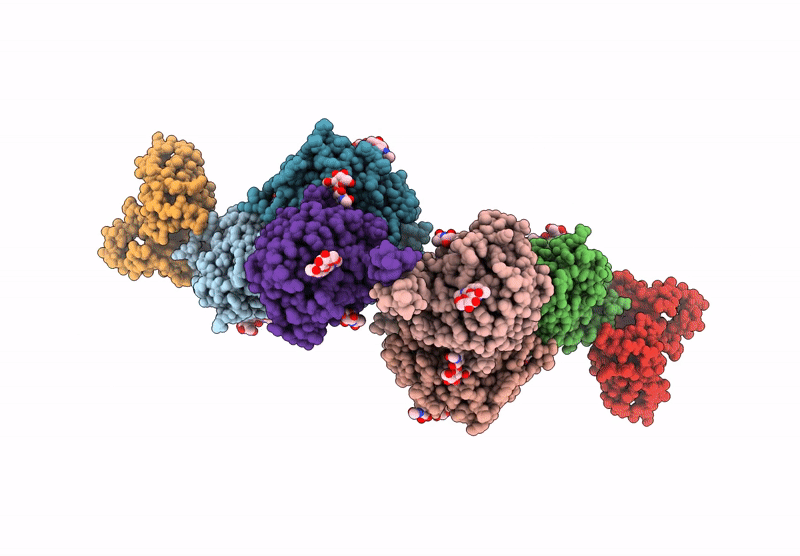
Title:
The structure of Noelin 1 with cerebellar GluA1/A4-ATD
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.26 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


