Deposition Date
2025-01-14
Release Date
2025-04-16
Last Version Date
2025-06-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9MUO
Keywords:
Title:
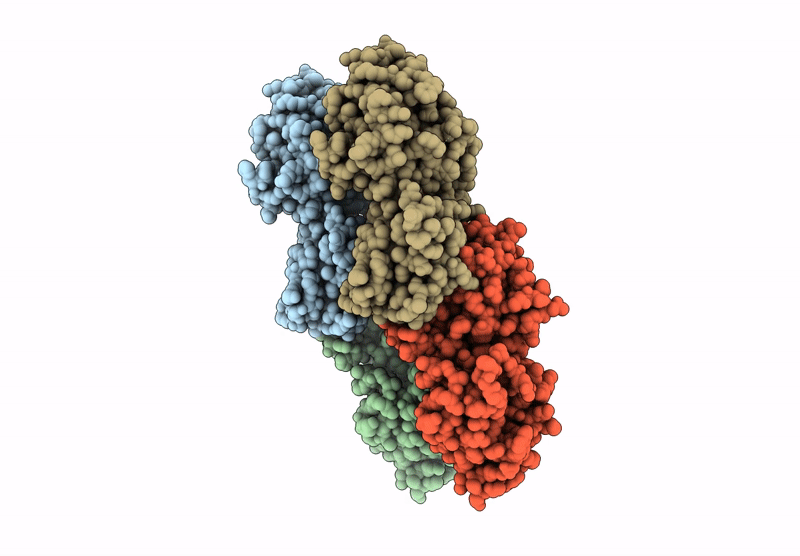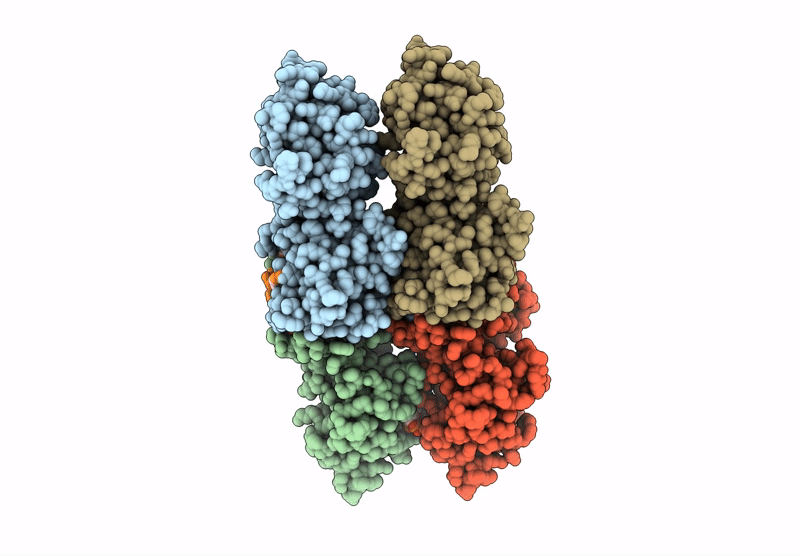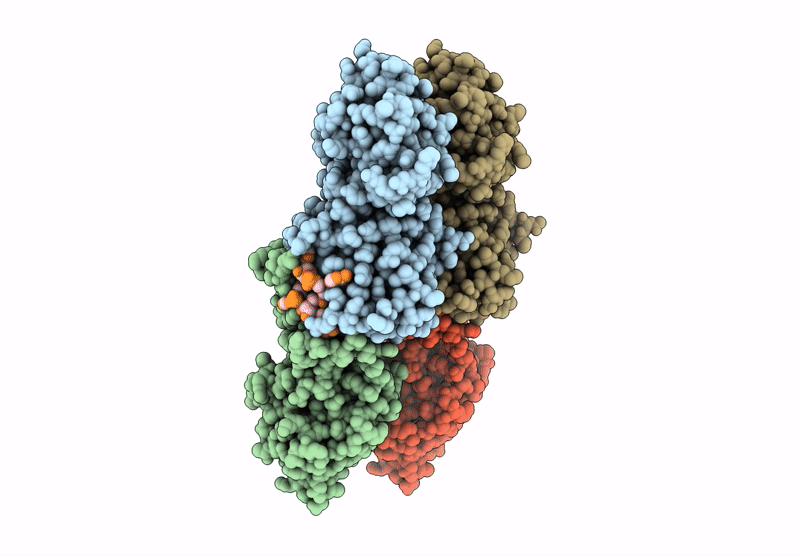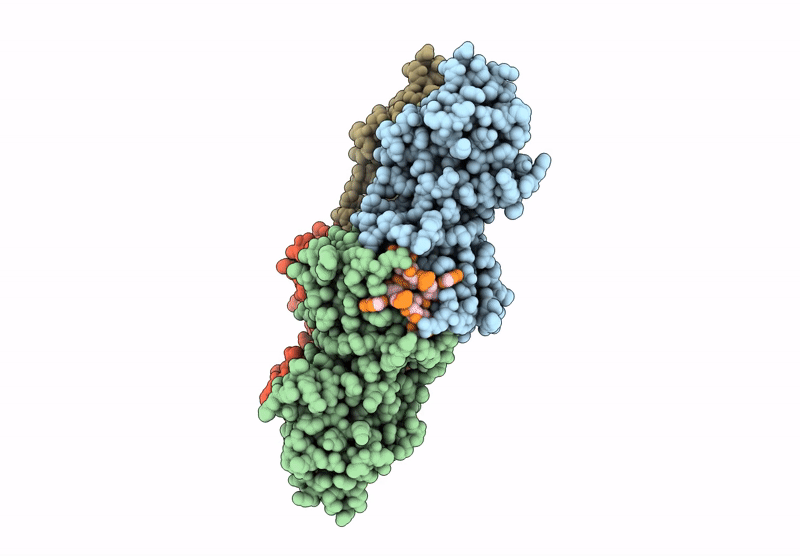
Cryo-EM structure of CRISPR-associated cA4 bound Cat1 Pentagonal filament assembly in the presence of NAD analog BAD
Biological Source:
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.30 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


