Deposition Date
2025-01-08
Release Date
2025-10-08
Last Version Date
2025-10-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9MRQ
Keywords:
Title:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNA polymerase elongation complex bound to inhibitor N-aroyl-N-aryl-phenylalanine amide (AAP)-SO2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (Taxon ID: 83332)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Taxon ID: 1773)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Taxon ID: 1773)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
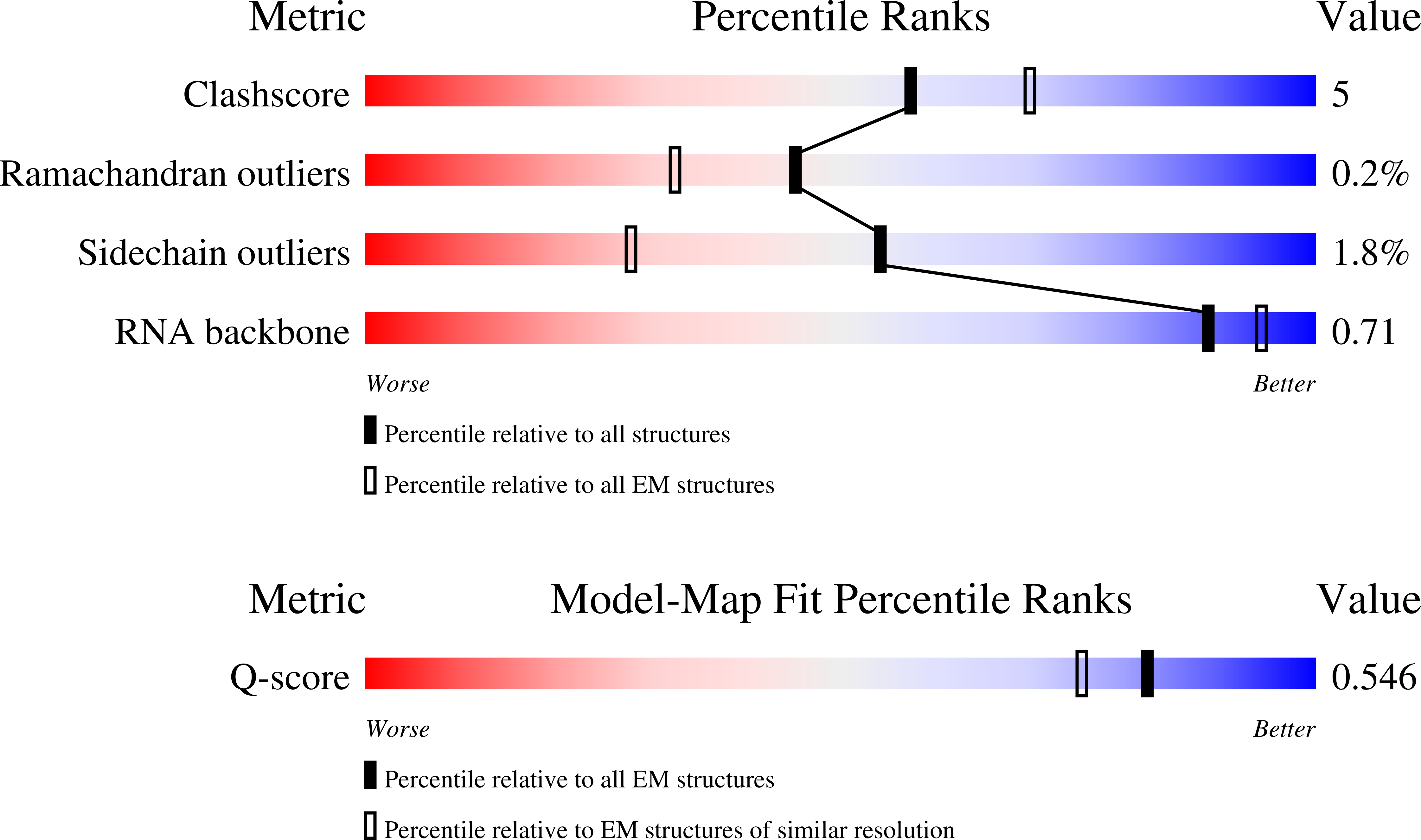
Resolution:
2.97 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE