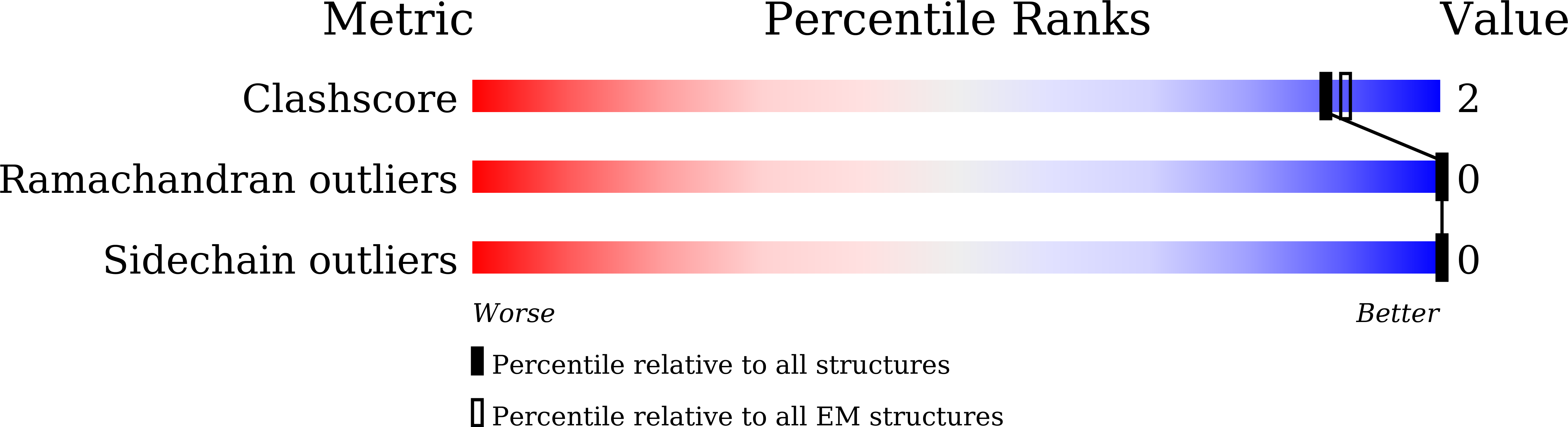
Deposition Date
2025-03-05
Release Date
2025-09-10
Last Version Date
2025-11-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9M5E
Keywords:
Title:
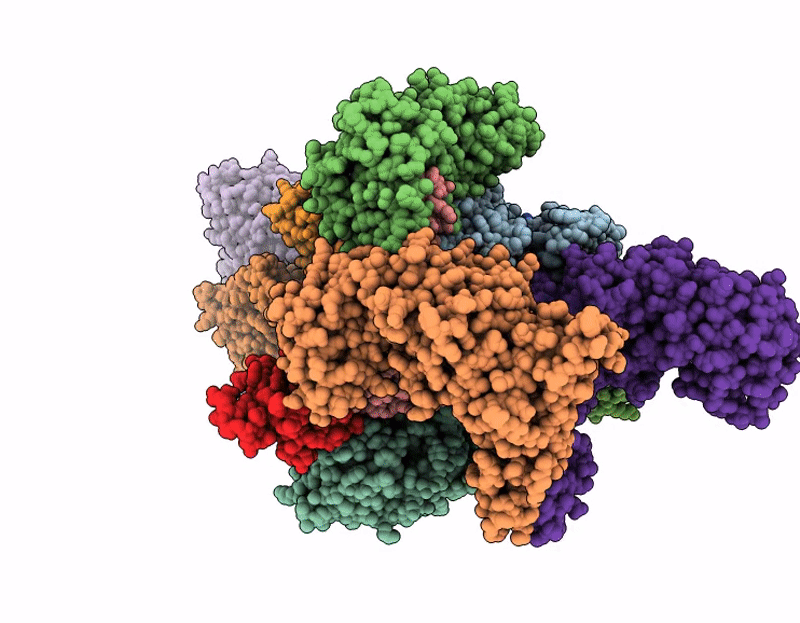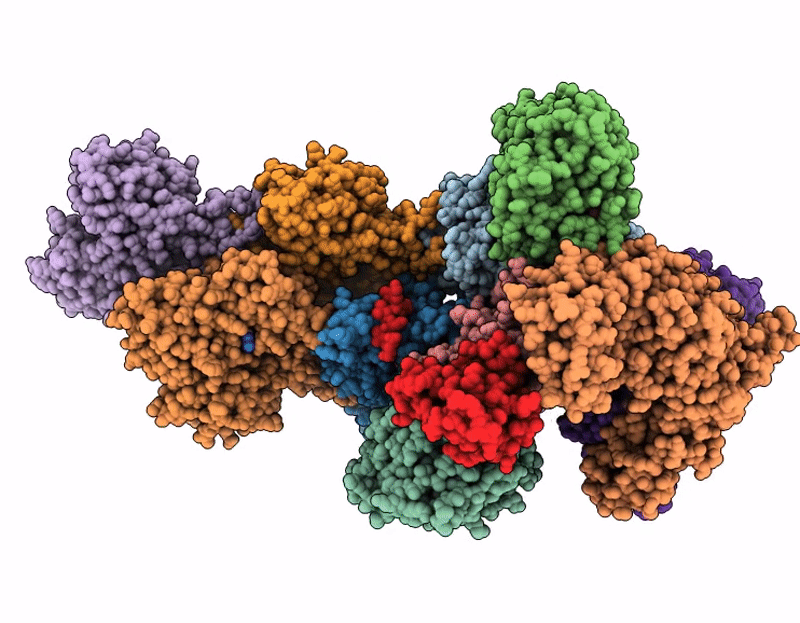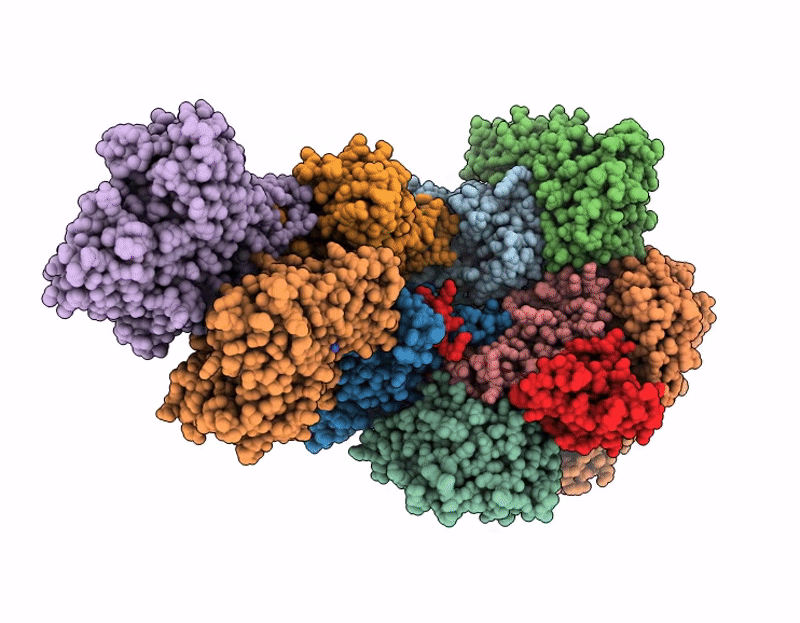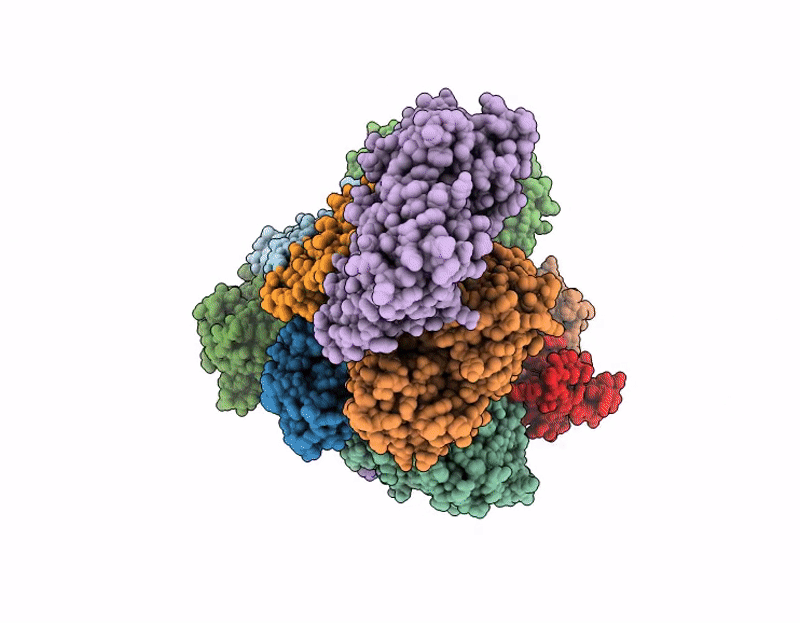
Structure of SPIN90 dimer-Arp2/3 complex-nucleated actin filament (singlet complex)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Gallus gallus (Taxon ID: 9031)
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Gallus gallus (Taxon ID: 9031)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.55 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE