Abstact
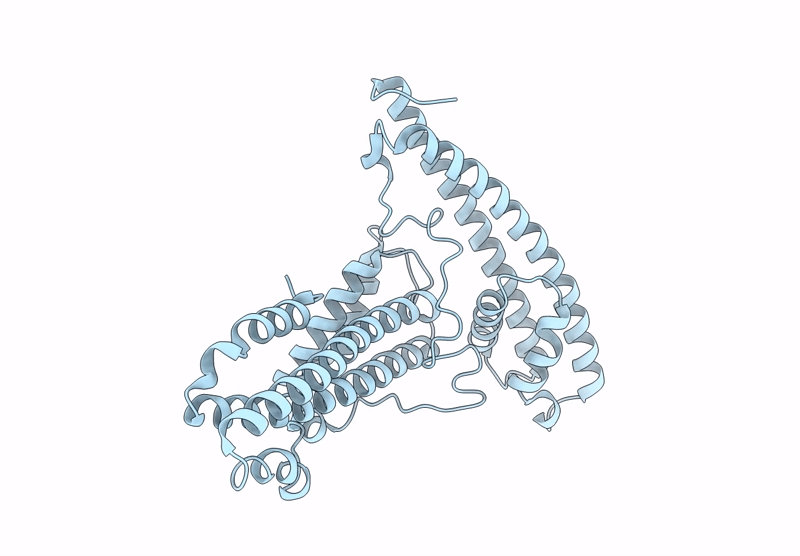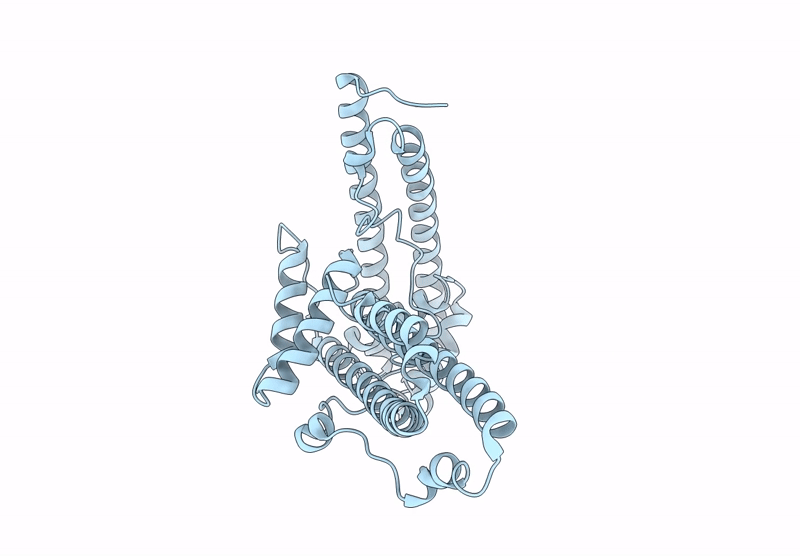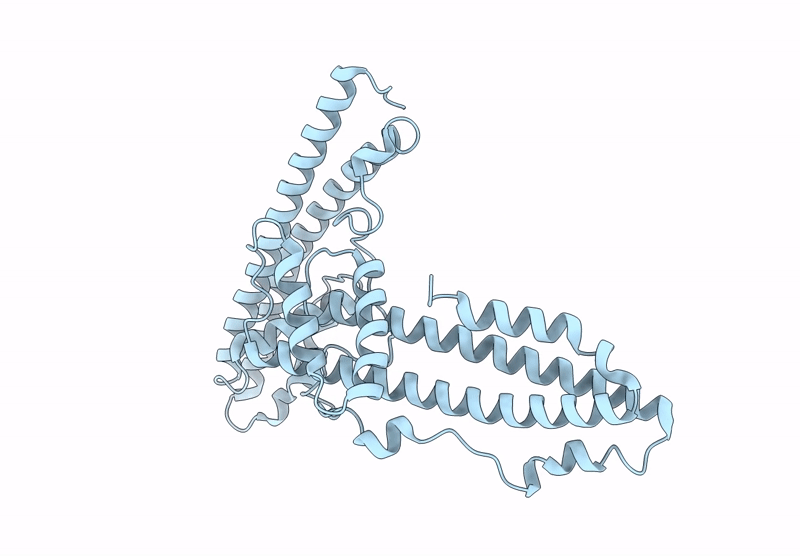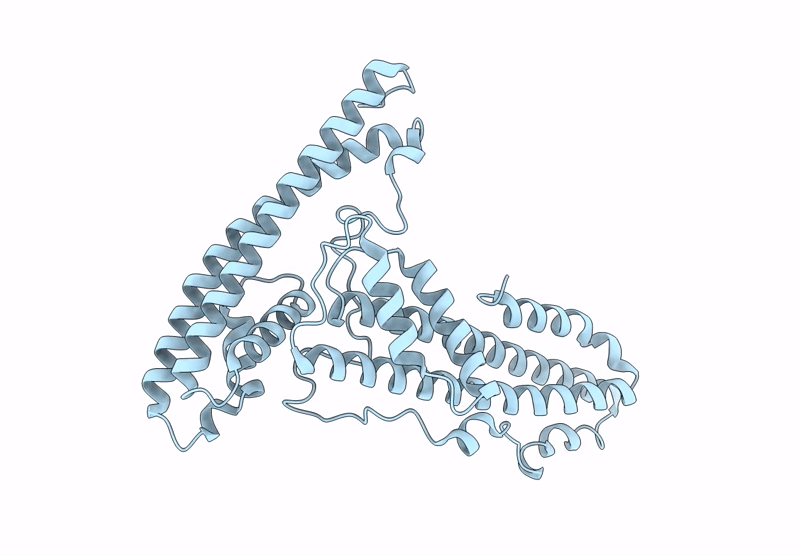
The surface protein P113 serves as a membrane-anchored protein that tethers the Plasmodium falciparum RH5 complex, including its associated partners CyRPA and RIPR, to the parasite surface. This anchoring mechanism ensures the proper localization and stabilization of RH5, facilitating its critical interaction with the host erythrocyte receptor basigin during erythrocyte invasion. Here, the helical-rich domain of P113 (residues 311-679) from a Plasmodium species was expressed, purified and crystallized to elucidate its structural and functional characteristics. The recombinant protein, with a molecular weight of approximately 44 kDa, was confirmed to be monomeric in solution. Crystallization in 0.5 mM MES pH 6.0, 22% PEG 3350 yielded high-quality crystals, enabling the determination of the structure of the apo form at 1.7 Å resolution. The structure revealed a predominant α-helical composition, with two distinct left-handed orthogonal four-helix bundles formed by helices α1-α4 and α6-α9 connected by a disordered region. Sequence analysis demonstrated high conservation of P113 across all human-infecting Plasmodium species, including P. vivax, P. malariae, P. falciparum and P. ovale, as well as in Plasmodium species infecting primates and rodents. Protein-protein interaction analysis using the STRING tool identified P113 as a hub protein that interacts with ten proteins, including small nuclear ribonucleoprotein, DNA polymerase delta small subunit and RIPR, which is part of the RH5-CyRPA-RIPR complex. AlphaFold predictions further elucidated the interaction patterns, revealing moderate to strong interaction scores (0.39-0.74) with key partners. Notably, the helical-rich domain of P113 was identified as the critical binding region for PF3D7_0308000, with key interaction sites mapped to residues Asp475, Arg381, Lys386, Asn390, Asp392 and Lys533. These findings provide critical insights into the structural and functional roles of P113 and its interaction network, advancing our understanding of its molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium biology.