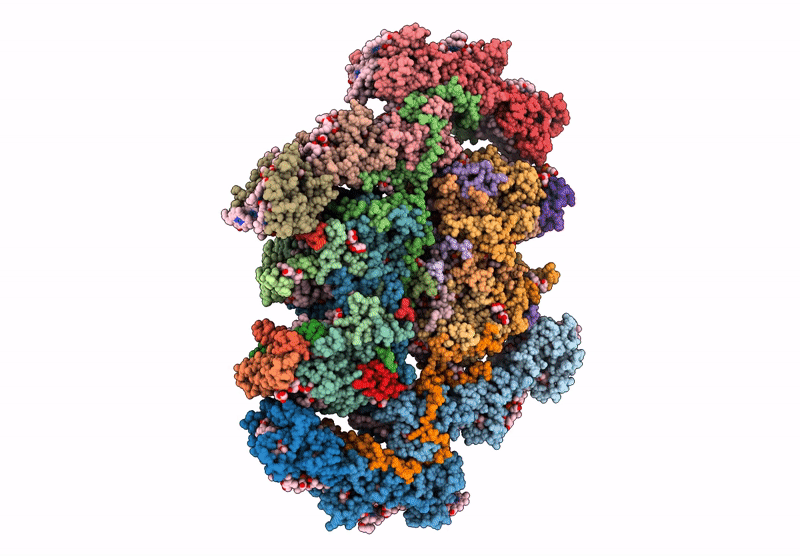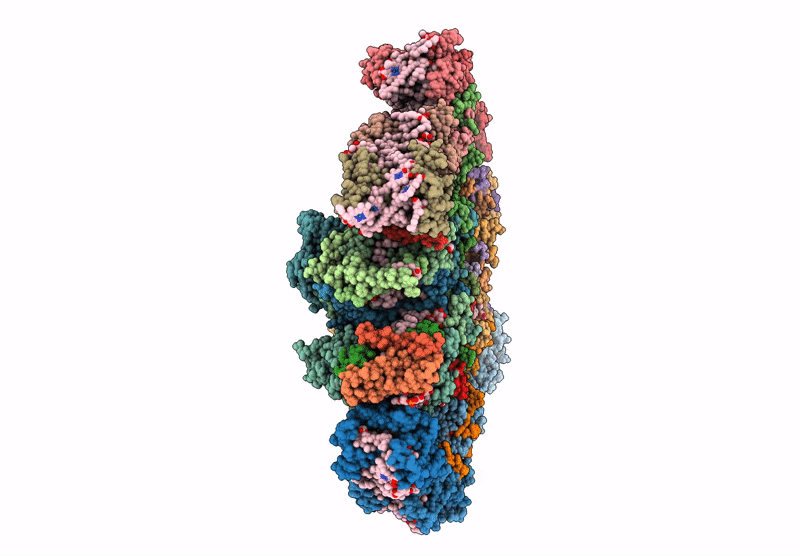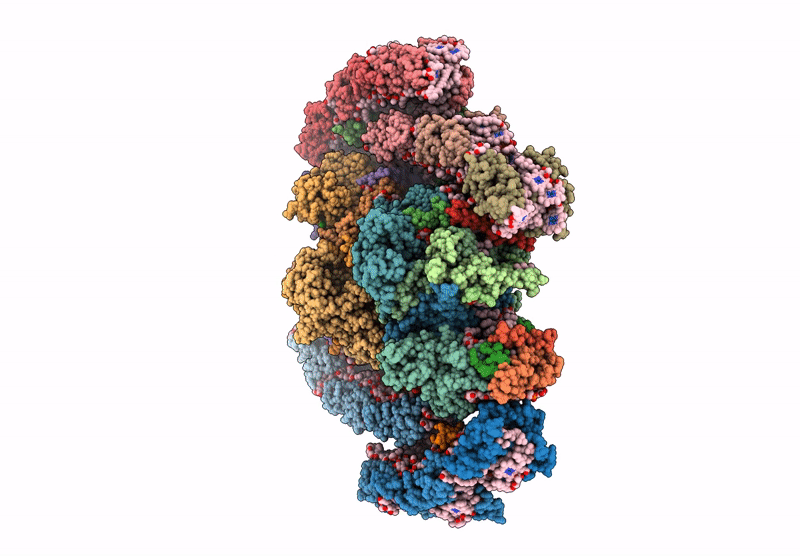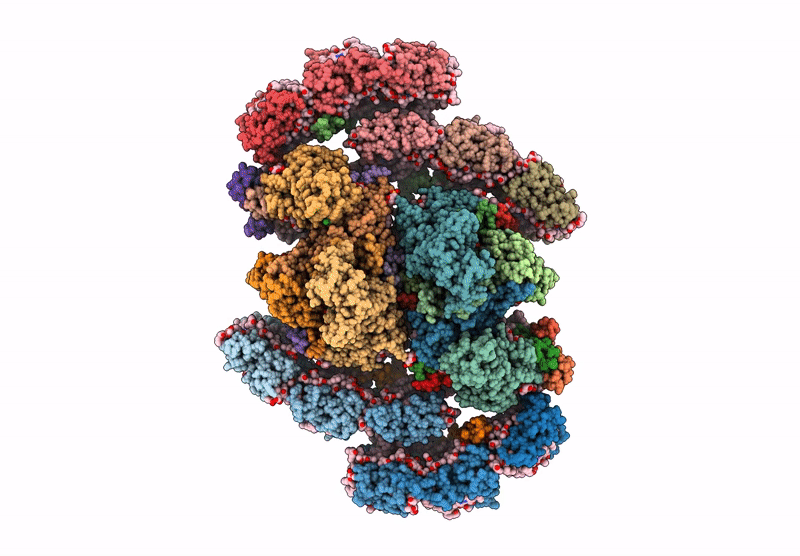
Deposition Date
2024-12-23
Release Date
2025-11-26
Last Version Date
2025-12-31
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9L5V
Keywords:
Title:
cryo-EM structure of PSII-ACPII from Rhodomonas sp. NIES-2332
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rhodomonas sp. NIES-2332 (Taxon ID: 2867507)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
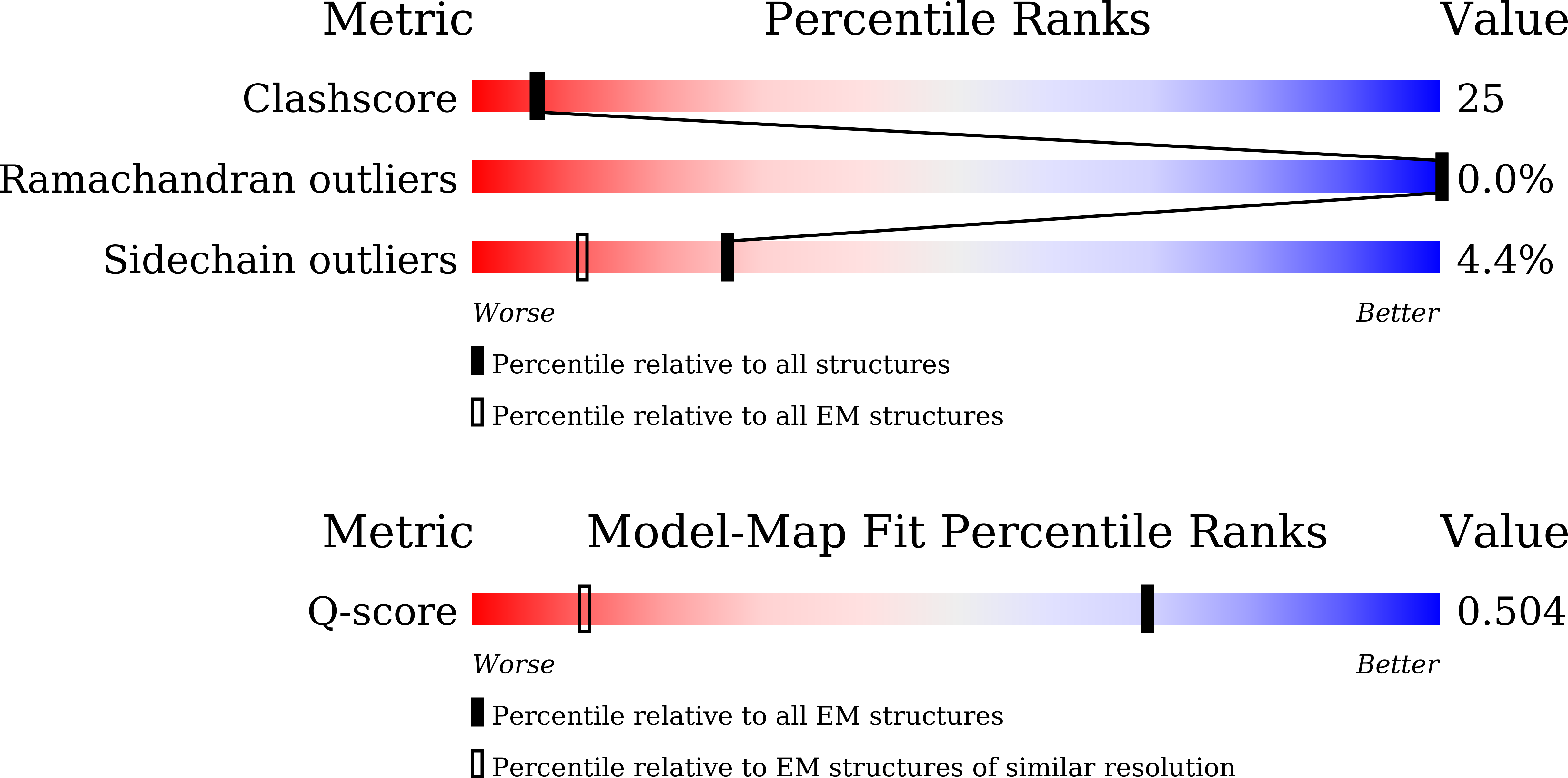
Resolution:
2.17 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE