Deposition Date
2024-08-05
Release Date
2025-02-05
Last Version Date
2025-02-05
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9J1W
Keywords:
Title:
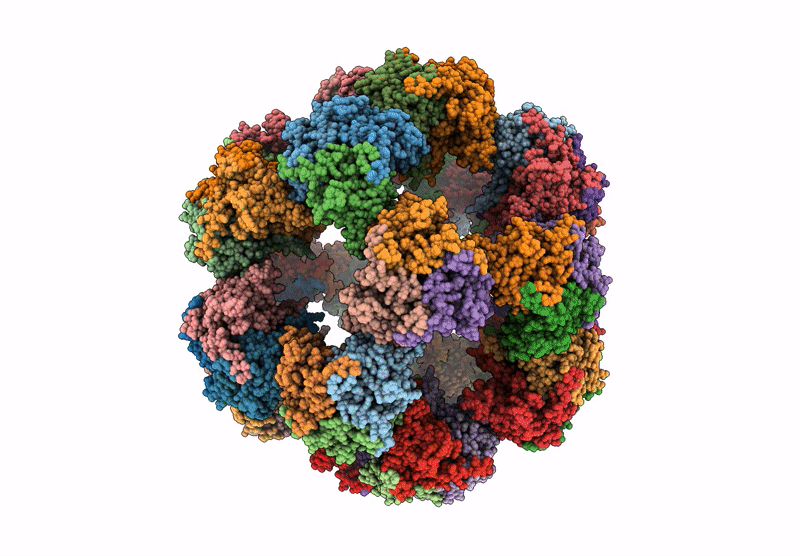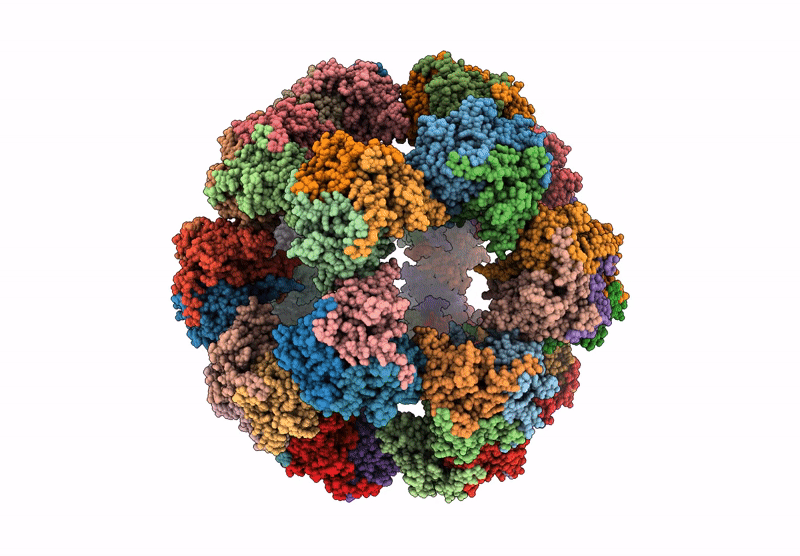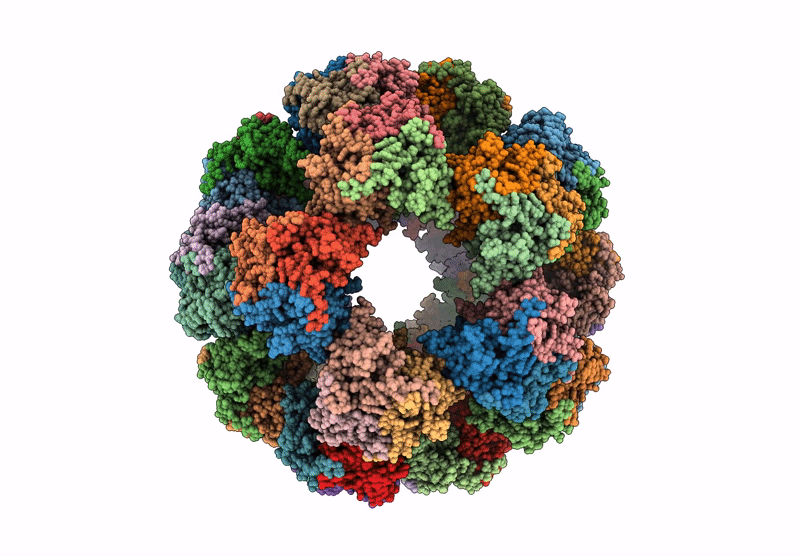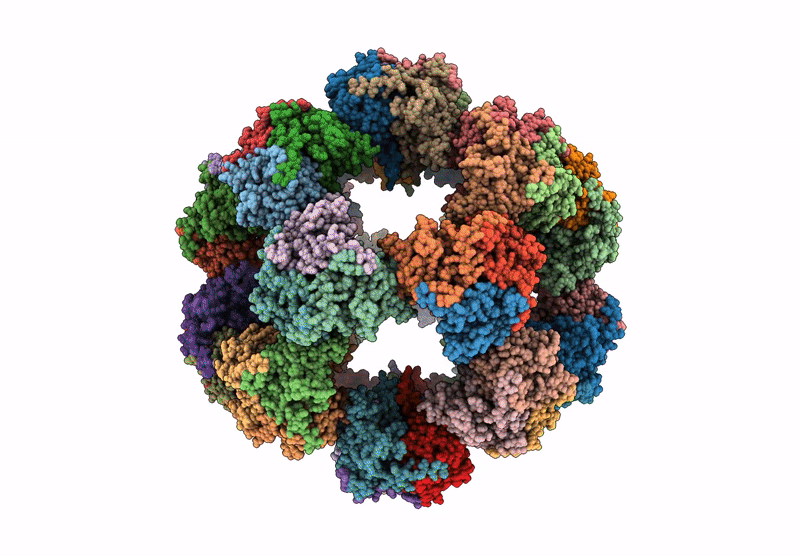
Endogenous dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) core of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from pig heart
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.20 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


