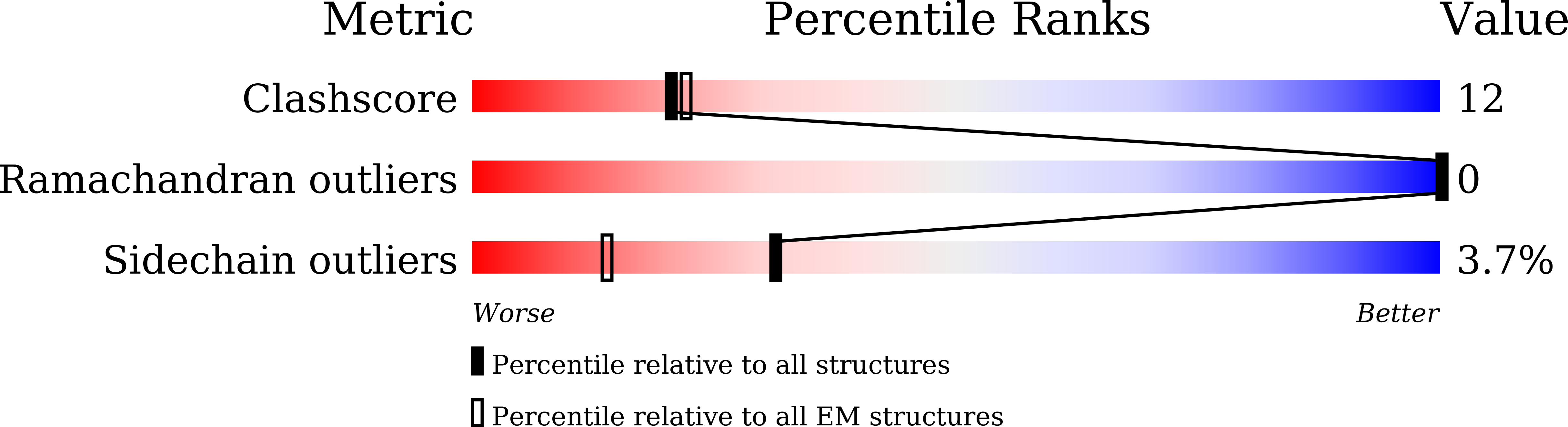
Deposition Date
2024-07-20
Release Date
2025-04-02
Last Version Date
2025-07-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9IUC
Keywords:
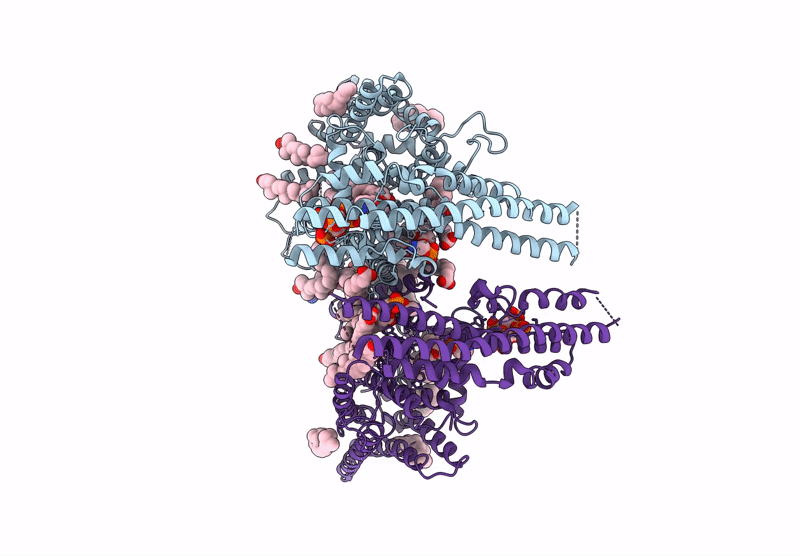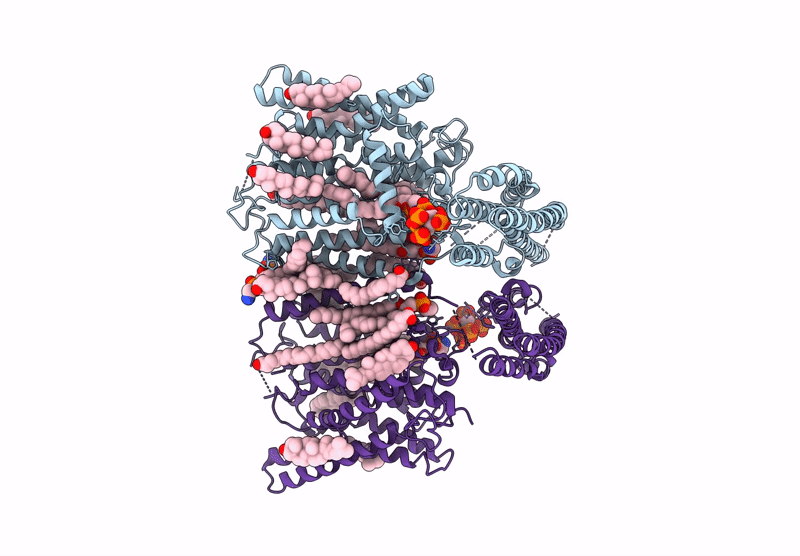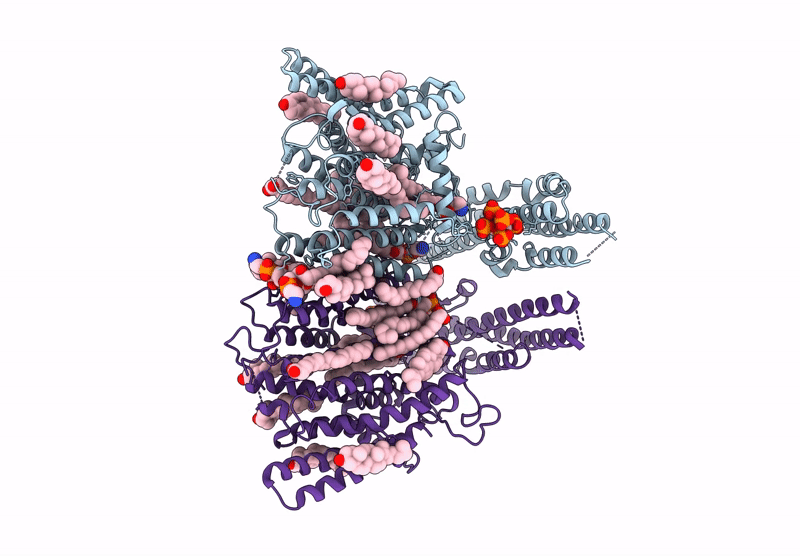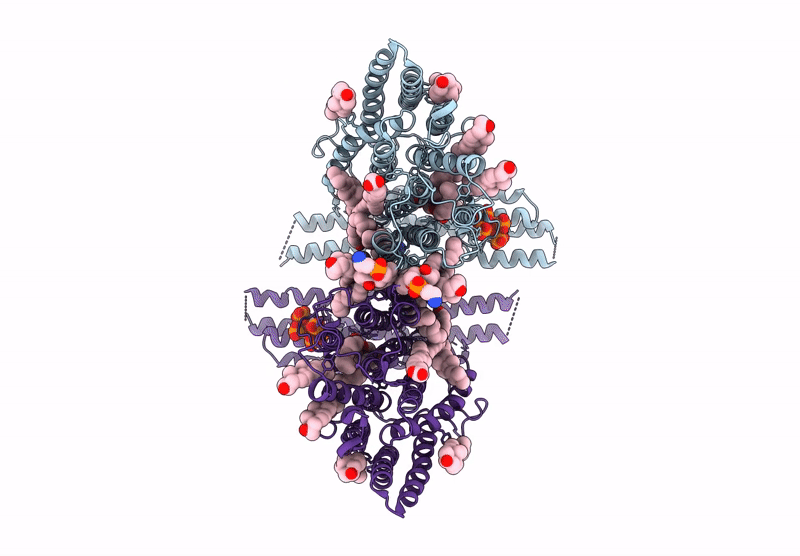
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of human XPR1 in complex with InsP6 in closed state - in the presence of KIDINS220-1-432 without substrate KH2PO4
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.80 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE