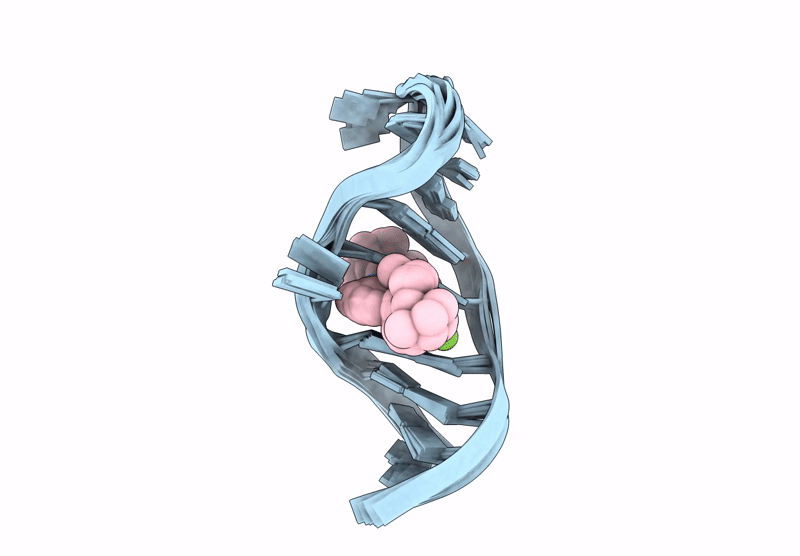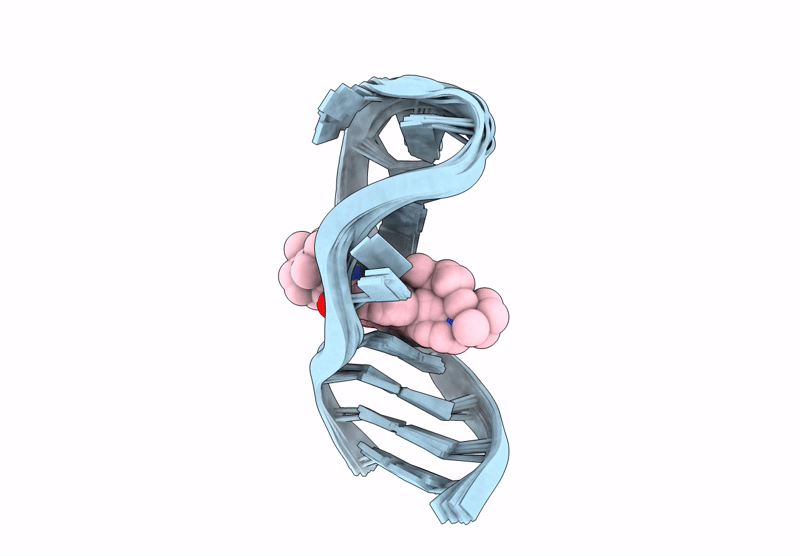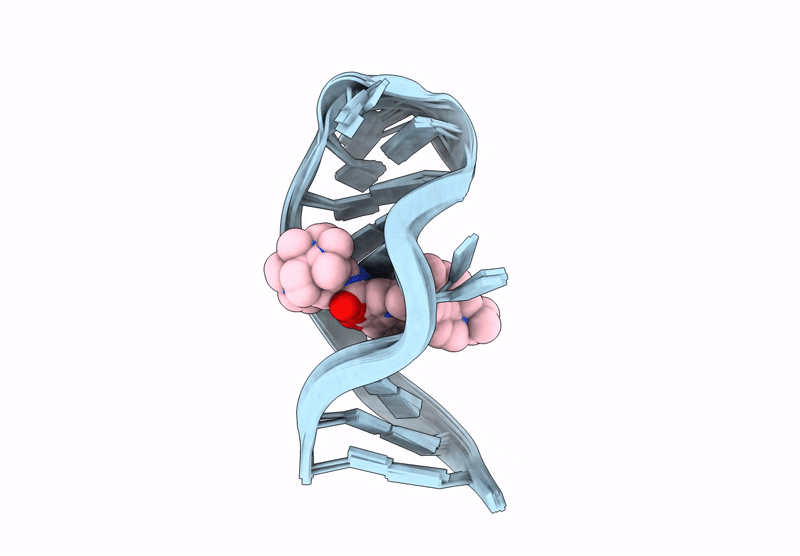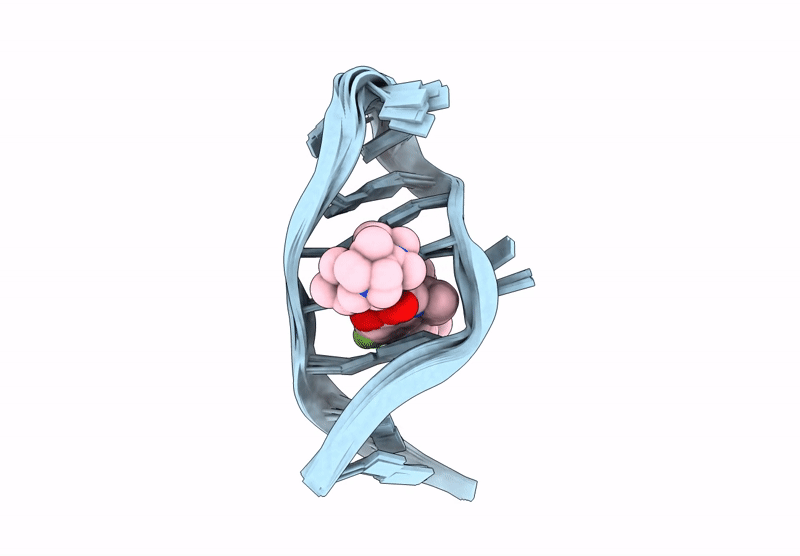
Deposition Date
2024-07-09
Release Date
2025-04-02
Last Version Date
2025-06-04
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9IOS
Keywords:
Title:
INTERACTION BETWEEN A FLUOROQUINOLONE DERIVATIVE KG022 AND RNAS: EFFECT OF BASE PAIRS 5' ADJACENT TO THE BULGE OUT ESIDUES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
11
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy


