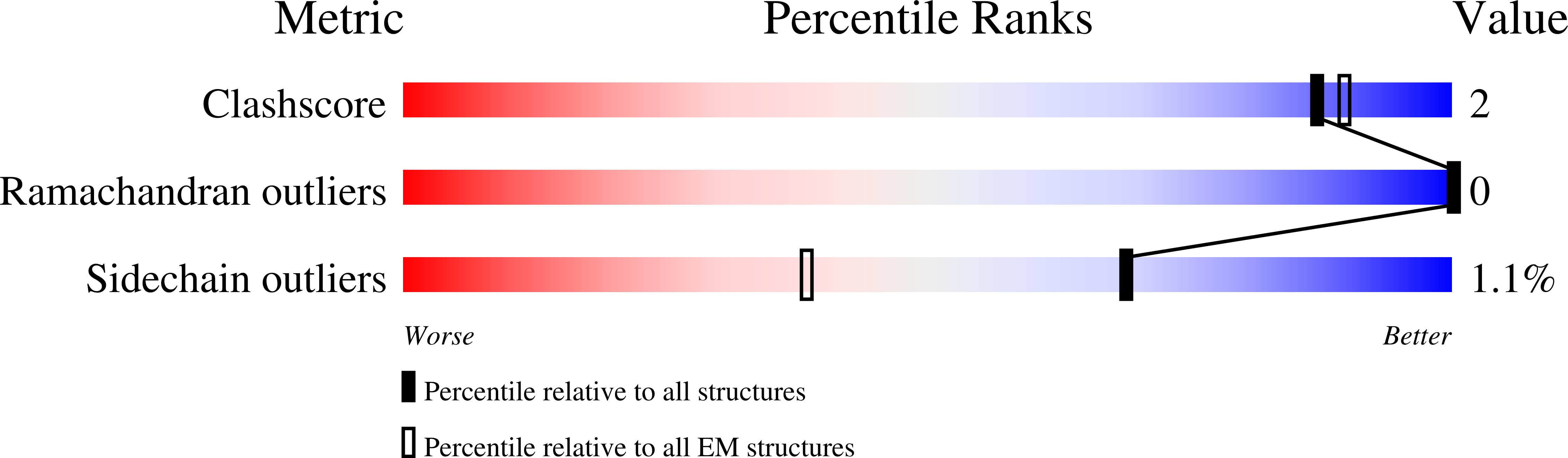Deposition Date
2025-01-15
Release Date
2025-03-26
Last Version Date
2025-04-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9I0K
Keywords:
Title:
Mycobacterium smegmatis inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) E-XMP* intermediate, compressed
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (Taxon ID: 246196)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.73 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE