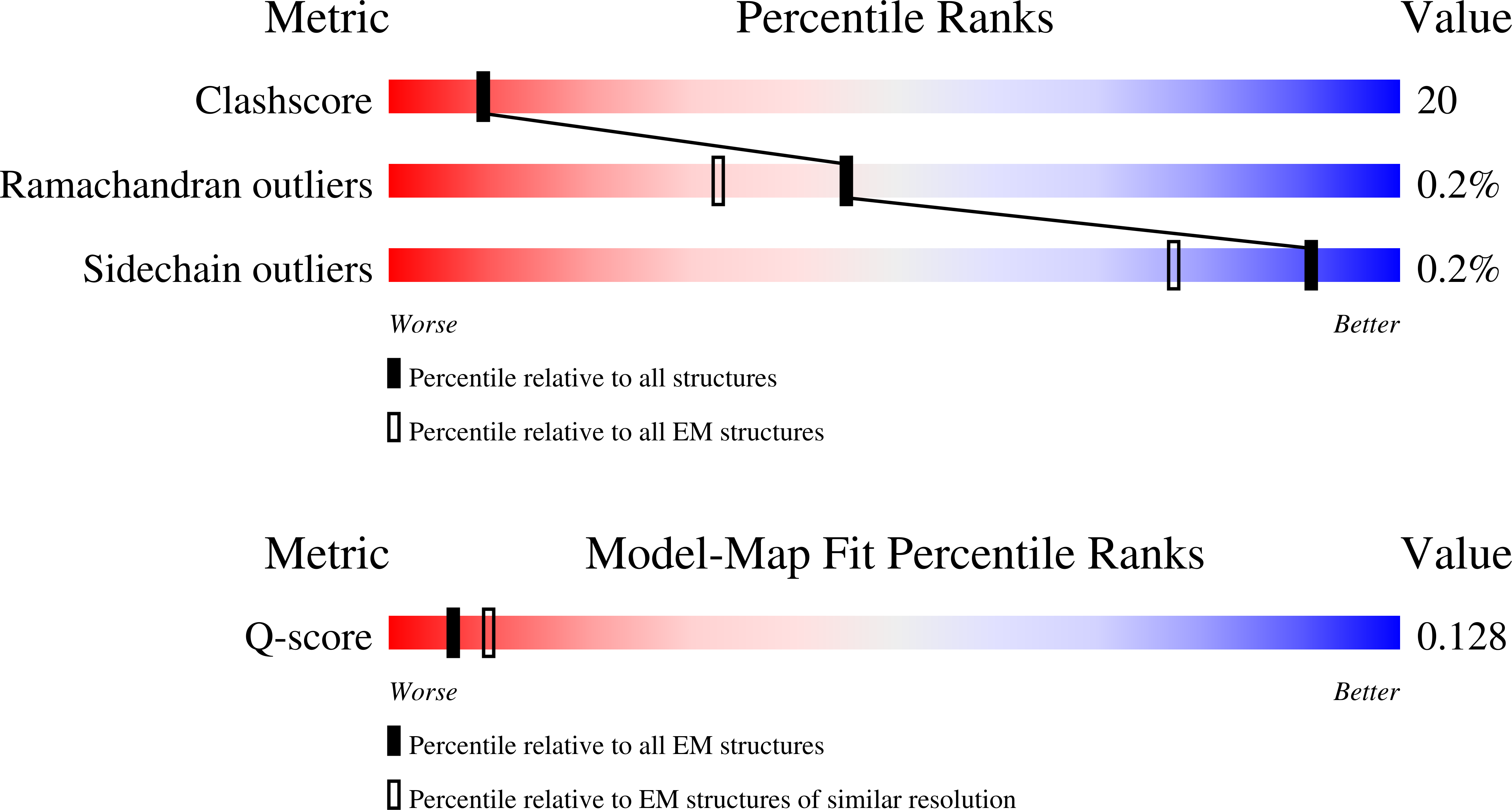
Deposition Date
2024-09-24
Release Date
2025-12-24
Last Version Date
2025-12-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9GVG
Keywords:
Title:
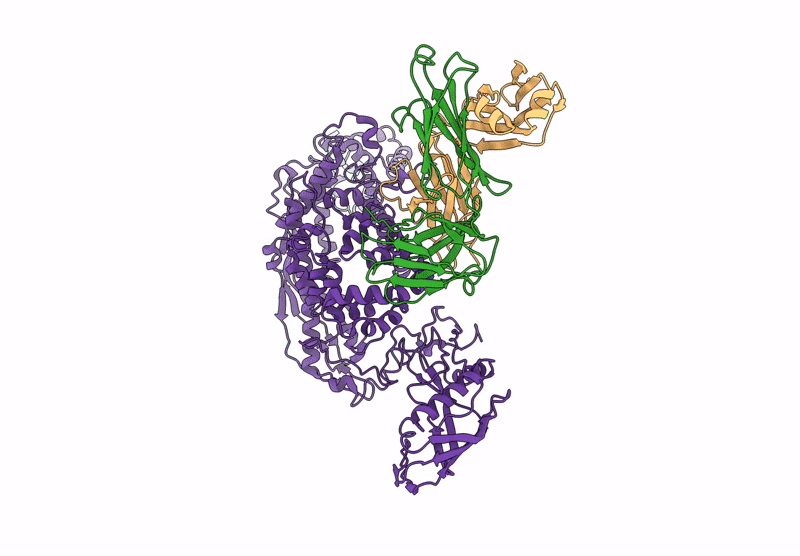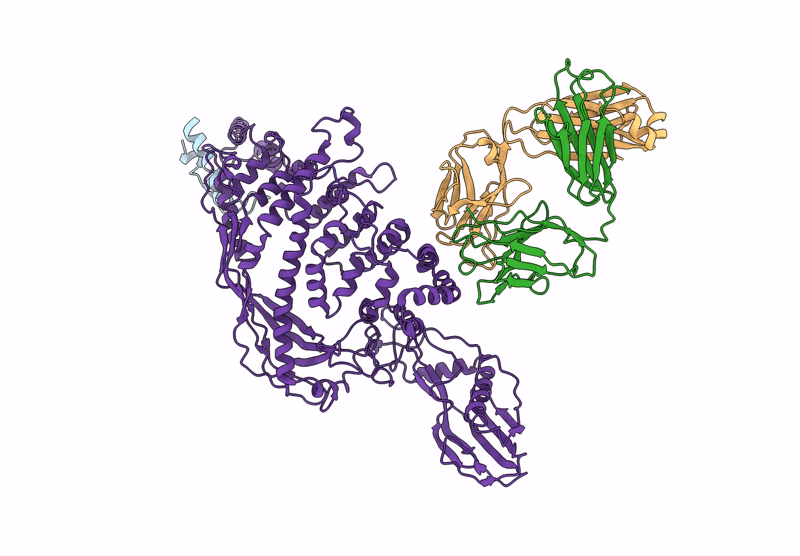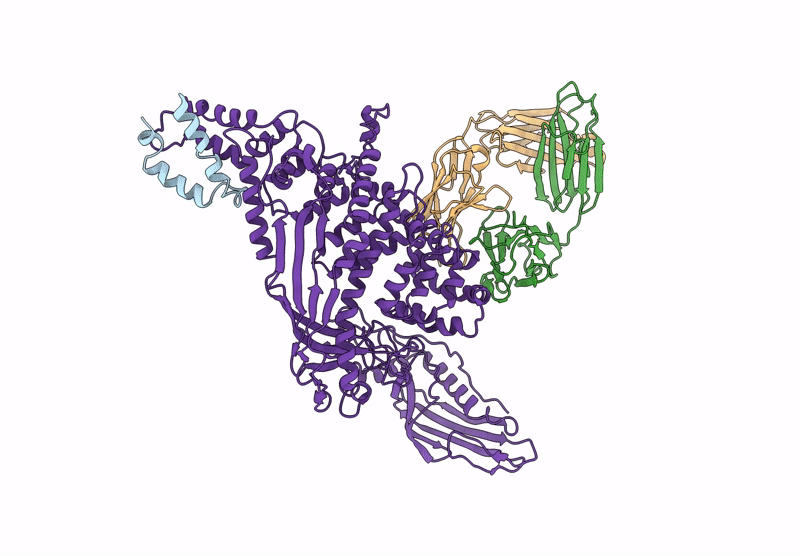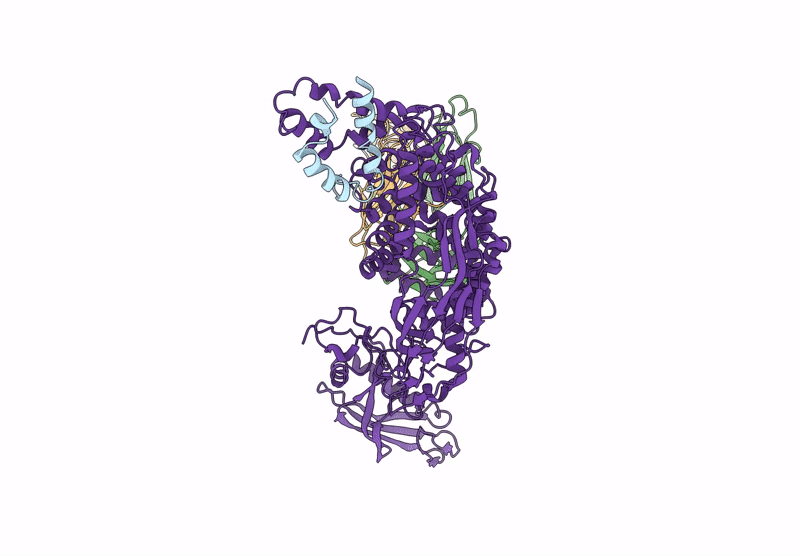
P116 from Mycoplasma pneumoniae in complex with mild growth suppressor monoclonal antibody
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (Taxon ID: 272634)
Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (Taxon ID: 272634)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
5.06 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE