Deposition Date
2024-08-22
Release Date
2025-03-05
Last Version Date
2025-03-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9GJU
Keywords:
Title:
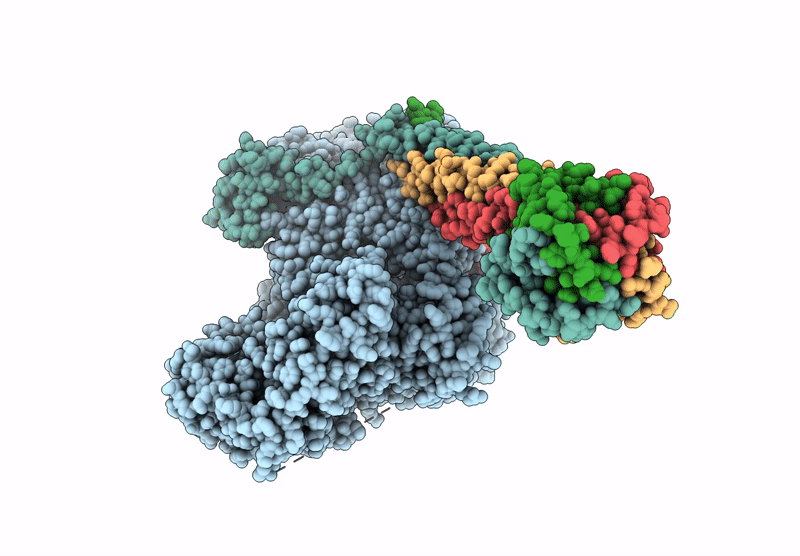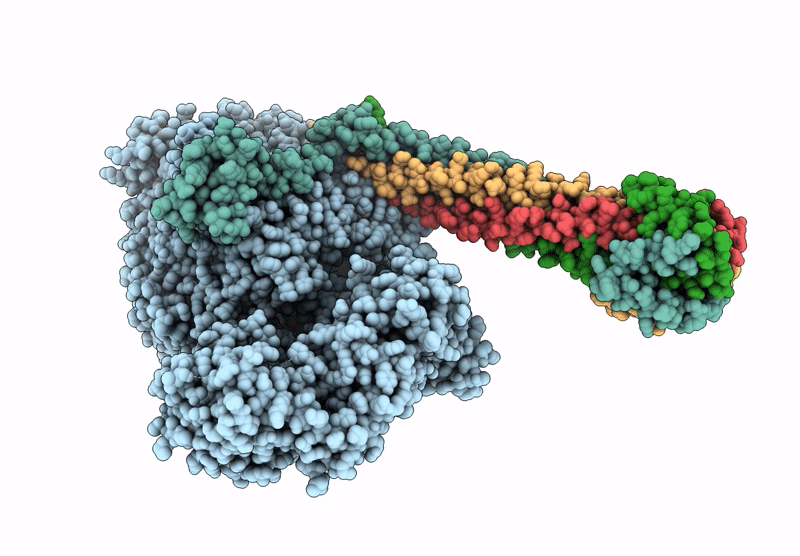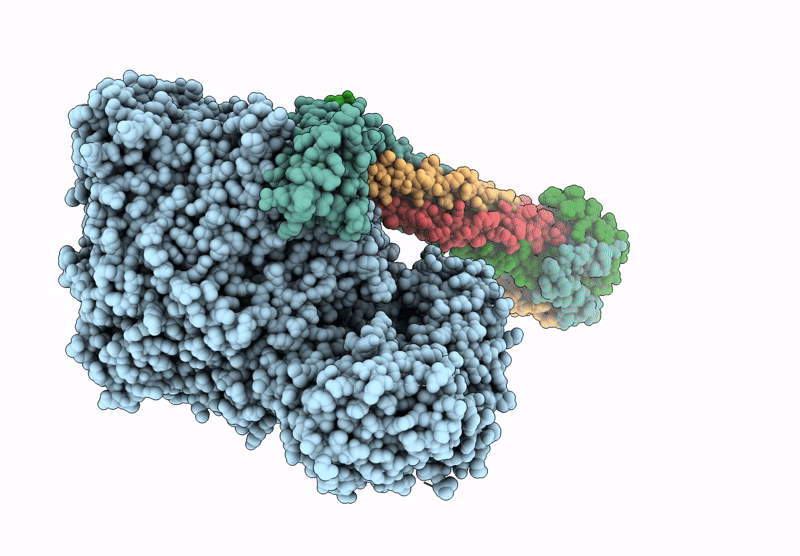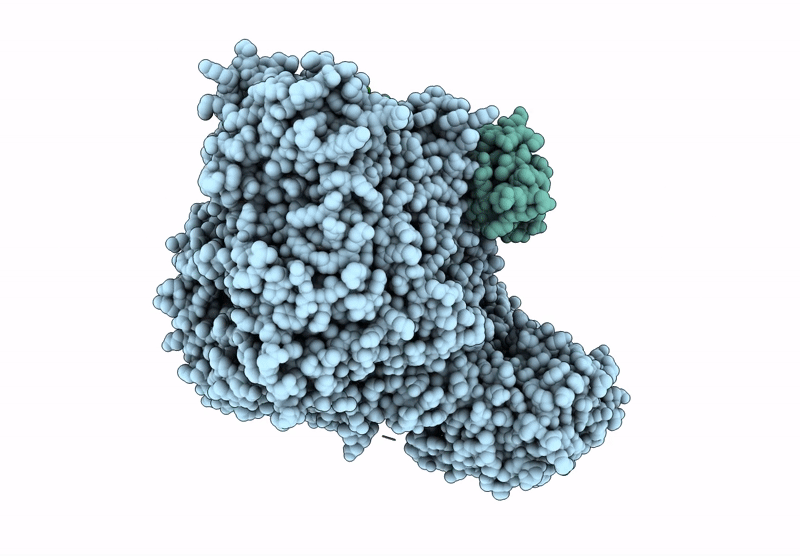
Structure of replicating Nipah Virus RNA Polymerase Complex - RNA-bound state
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Henipavirus nipahense (Taxon ID: 3052225)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.80 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE