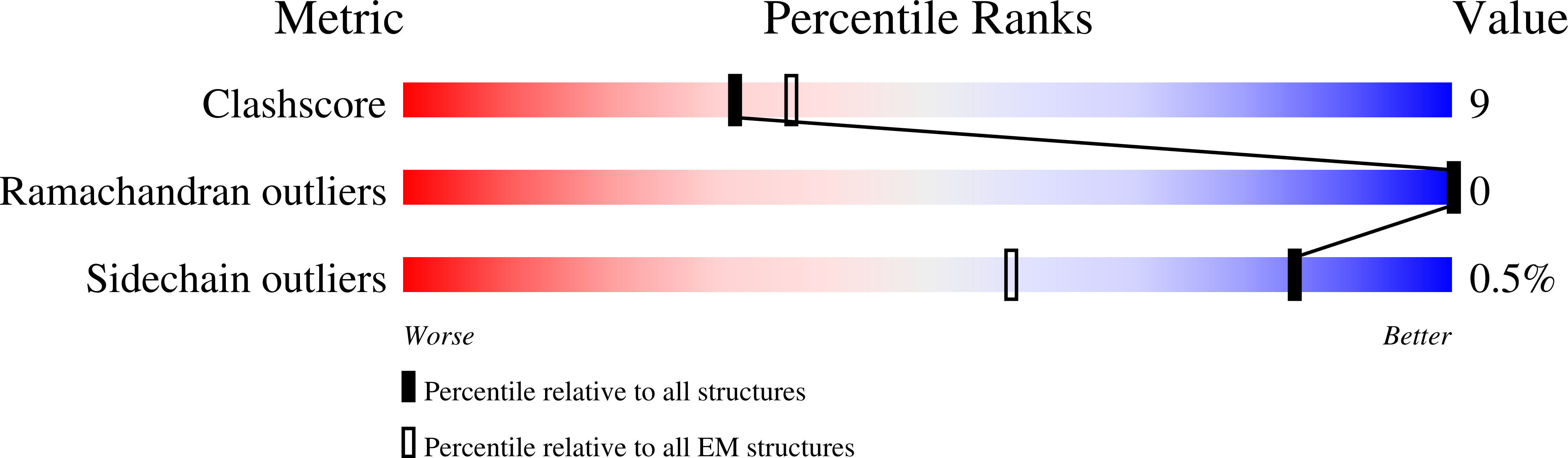
Deposition Date
2024-05-22
Release Date
2025-04-09
Last Version Date
2025-04-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9FF7
Keywords:
Title:
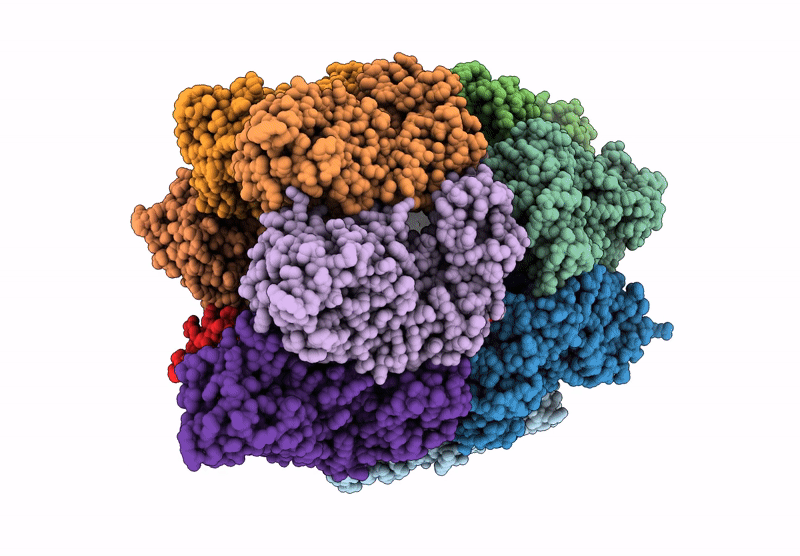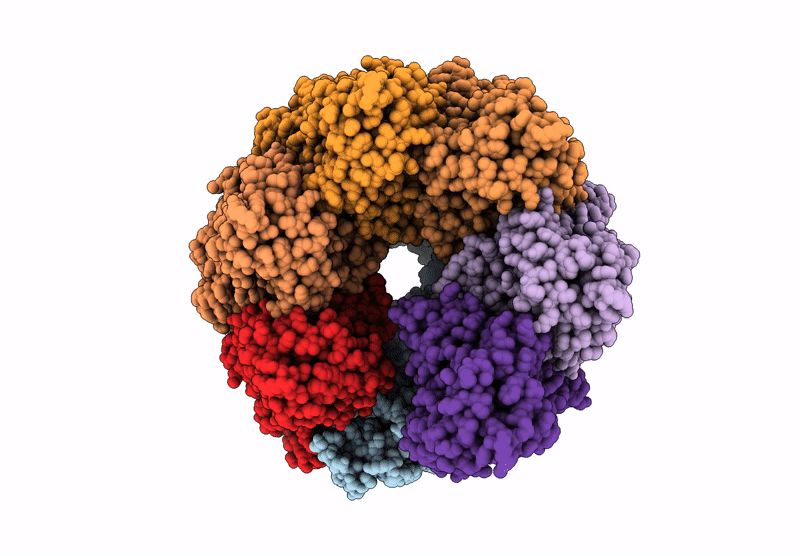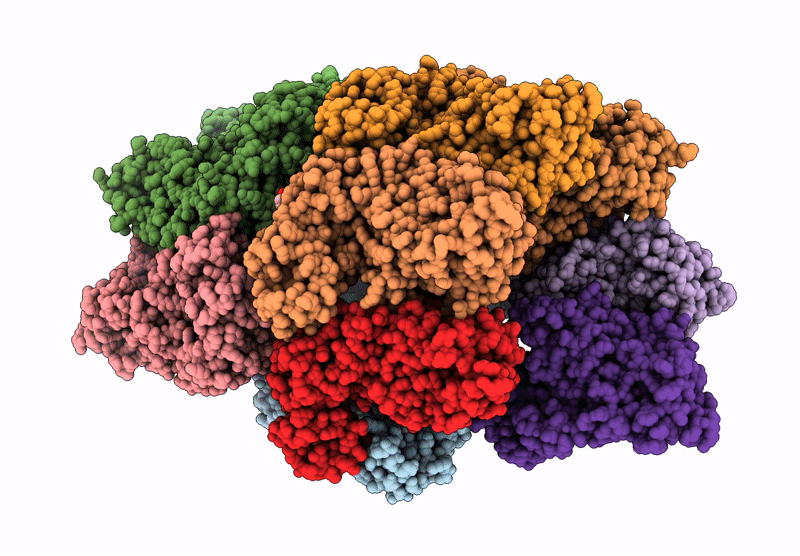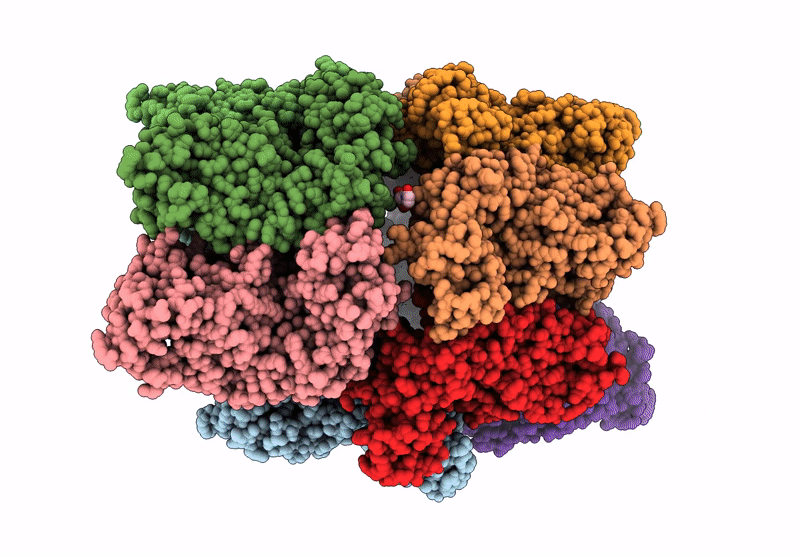
Structure of the BMOE-crosslinked transcription termination factor Rho in the presence of ppGpp; S84C/M405C double mutant
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.40 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE