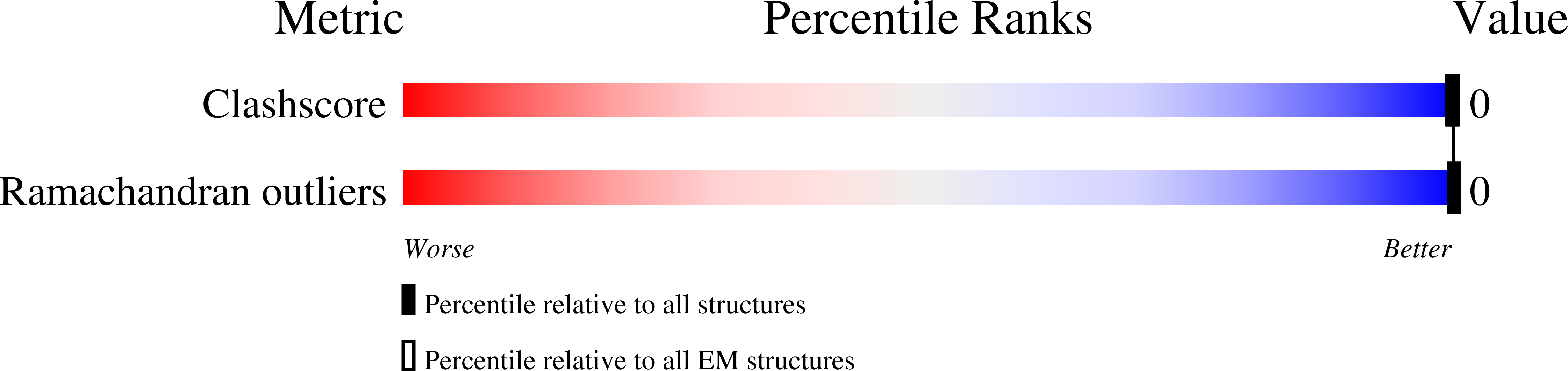
Deposition Date
2024-03-15
Release Date
2024-10-16
Last Version Date
2025-07-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9EON
Keywords:
Title:
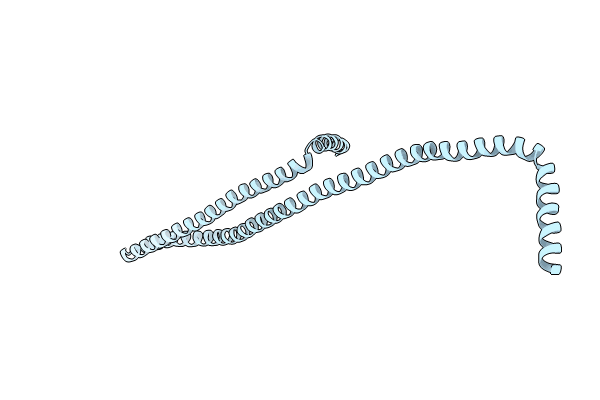
270A Vipp1 dL10Ala helical tubes in the presence of EPL
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (Taxon ID: 1148)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
6.40 Å
Aggregation State:
HELICAL ARRAY
Reconstruction Method:
HELICAL