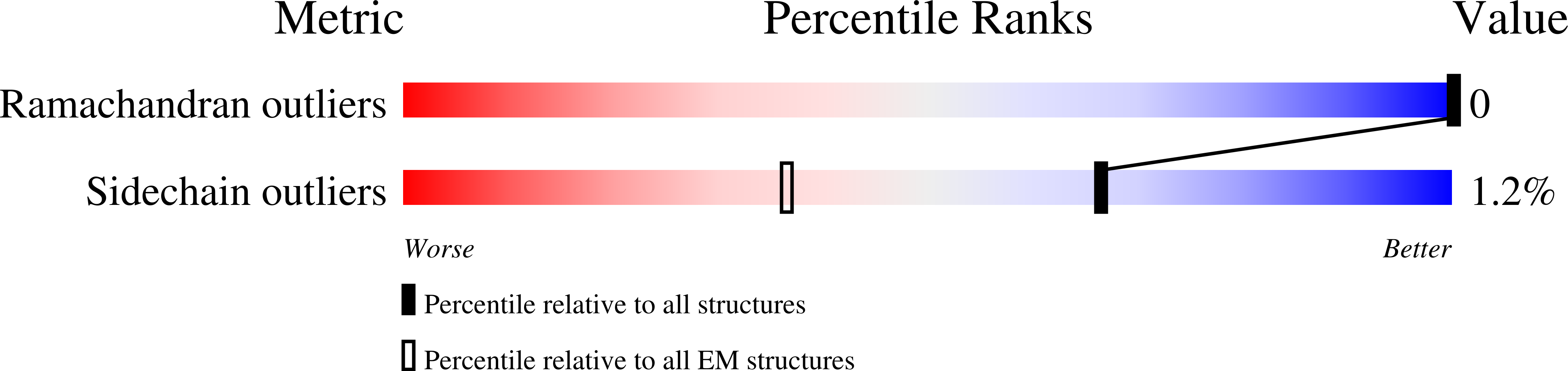
Deposition Date
2024-03-15
Release Date
2024-11-06
Last Version Date
2024-11-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9EOK
Keywords:
Title:
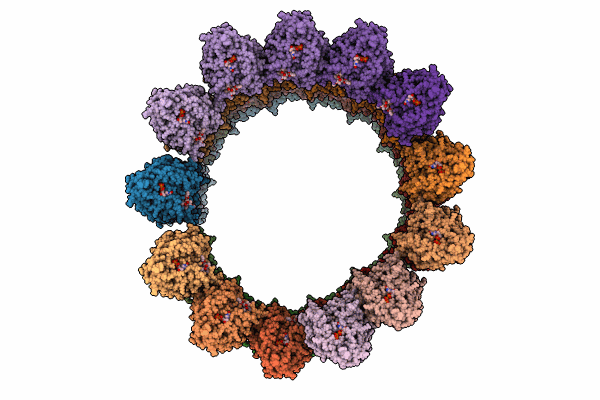
Minus end of the vertebrate gamma-tubulin ring complex-capped microtubule
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Xenopus laevis (Taxon ID: 8355)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
23.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE