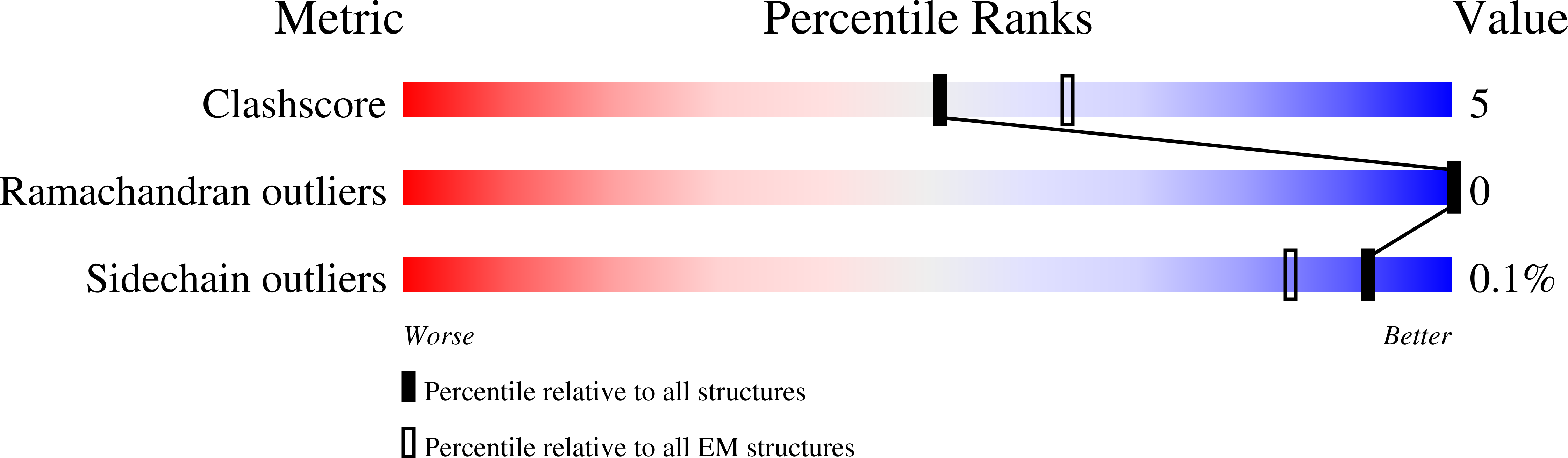
Deposition Date
2024-11-30
Release Date
2025-08-13
Last Version Date
2025-10-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9EJZ
Keywords:
Title:
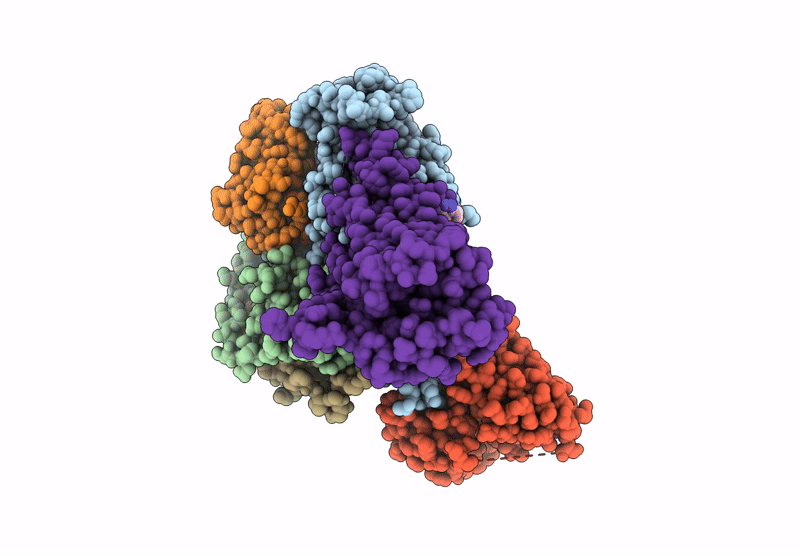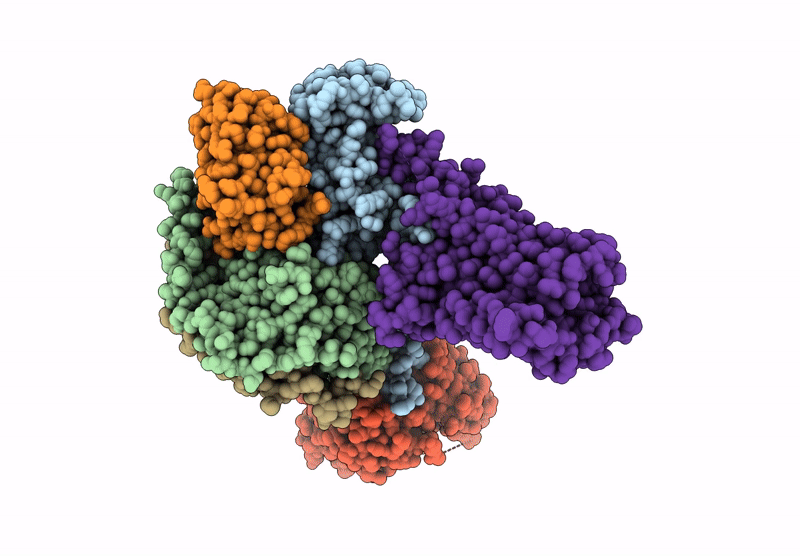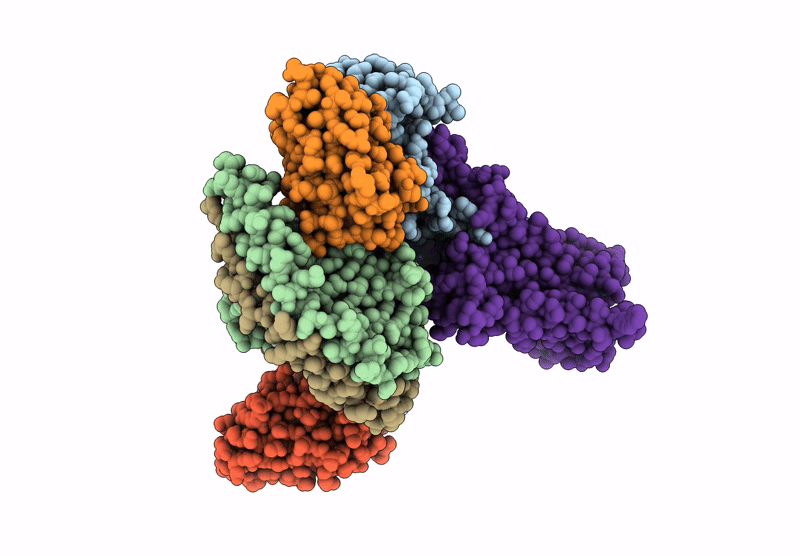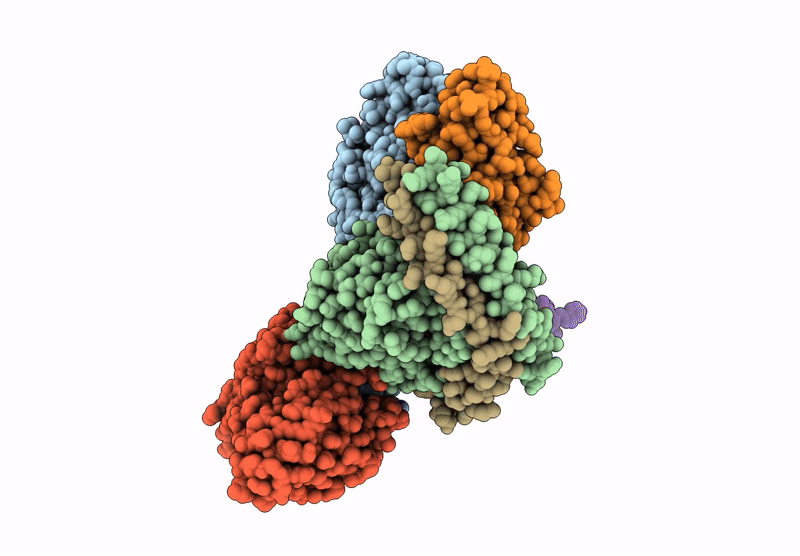
Human M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor complex with mini-Gq, agonist acetylcholine and positive allosteric modulator VU6007678
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.06 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE