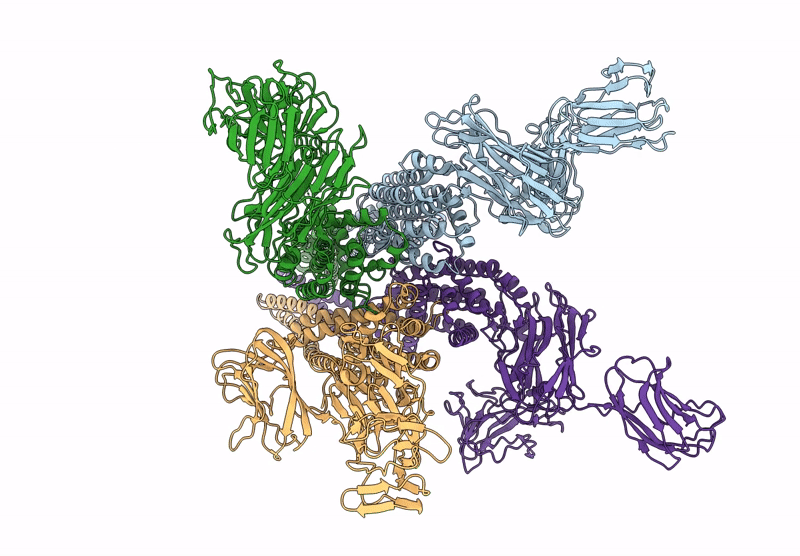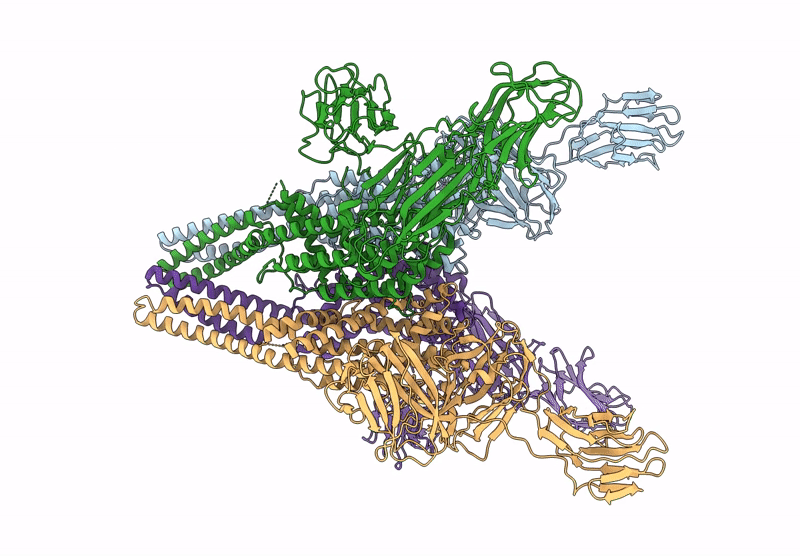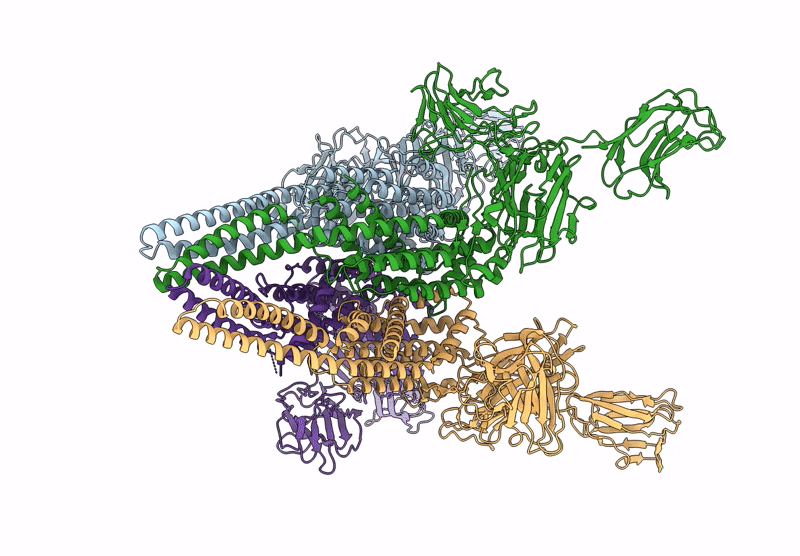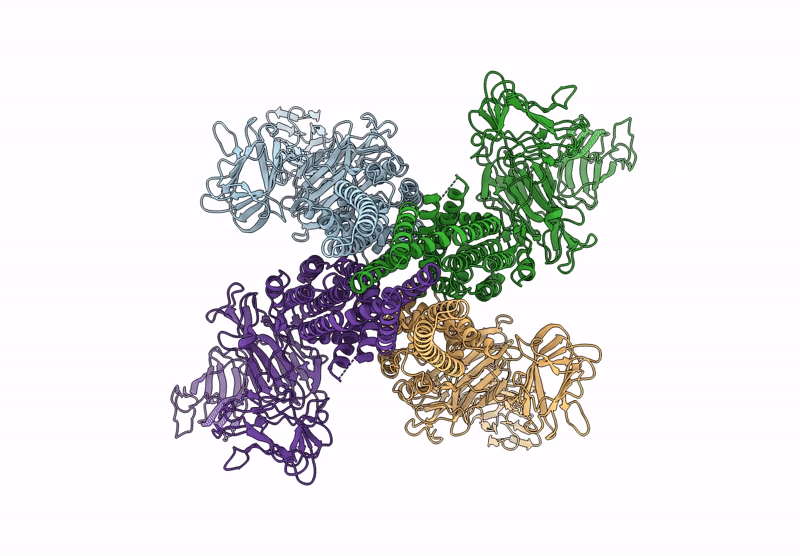
Abstact
New proteins are needed to control insects not controlled with Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) crops, and those evolving resistance to Bt crops. These proteins are increasingly being reported from non-Bt organisms to control Bt-resistant insects. However, these proteins mostly control the corn rootworm, Diabrotica spp. (Coleoptera), whereas most Bt-resistant insects are lepidopteran. We hypothesized that diversifying our search for proteins into non-Bt organisms, such as those related to Paenibacillus popilliae, used to control Japanese beetle Popillia japonica, could yield proteins with new insecticidal activities against Lepidoptera. Here, we identified Vip3Cb1 and Vip3Cc1 with broad lepidopteran activity, the first Vip3 proteins discovered from strains in the P. popilliae-containing clade. Vip3Cb1 protected plants against cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa zea and tobacco budworm, Chloridea virescens and H. zea, fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, and Southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella, in cotton and maize, respectively, like commercial Vip3Aa. Distinct from Vip3Aa, Vip3Cb1 also protected maize against European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis, the primary maize pest in the United States, with recent reports of resistance to Bt proteins. Consistent with previous reports, insects resistant to Vip3Aa were cross-resistant to Vip3Cb1. Cryo-electron microscopy demonstrated that Vip3Cb1 formed a pore-shaped tetramer upon proteolytic activation, in agreement with the pore-forming mechanism of action of Vip3Aa. Thus, diversifying the search beyond Bt has led to the discovery of the first Vip3 proteins from Paenibacillus spp. with different activity spectra from Vip3Aa, providing additional tools to control pests, including those currently resistant to Bt Cry proteins.IMPORTANCENew insecticidal proteins are needed for controlling insect pests that can devastate crop yield if left uncontrolled. Diversifying our search for new insecticidal proteins in Paenibacillus spp. resulted in the discovery of Vip3Cb1 and Vip3Cc1 insecticidal proteins active against lepidopteran crop pests. Structure and cross-resistance studies indicate overlap in the mechanism of action between Vip3Cb1 and commercial Vip3Aa. However, new activities, such as controlling European corn borer, make these proteins important new tools in the insect control toolbox.