Deposition Date
2024-10-21
Release Date
2025-07-16
Last Version Date
2025-09-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9E1J
Keywords:
Title:
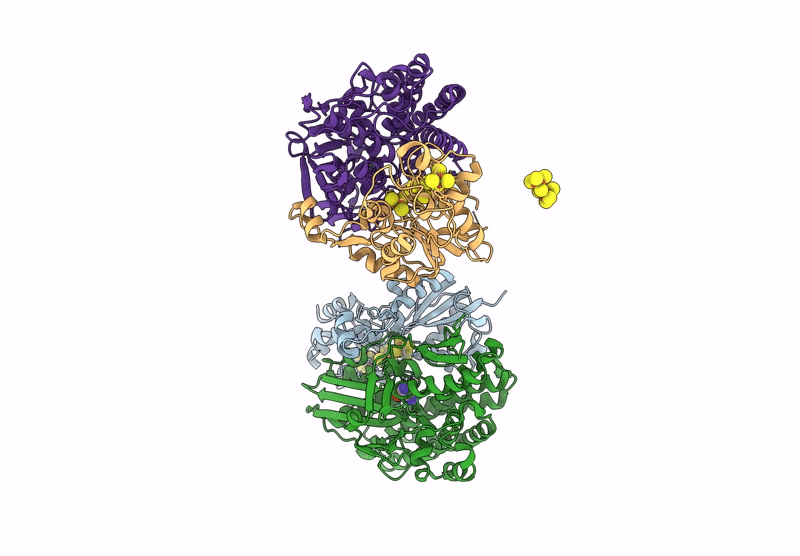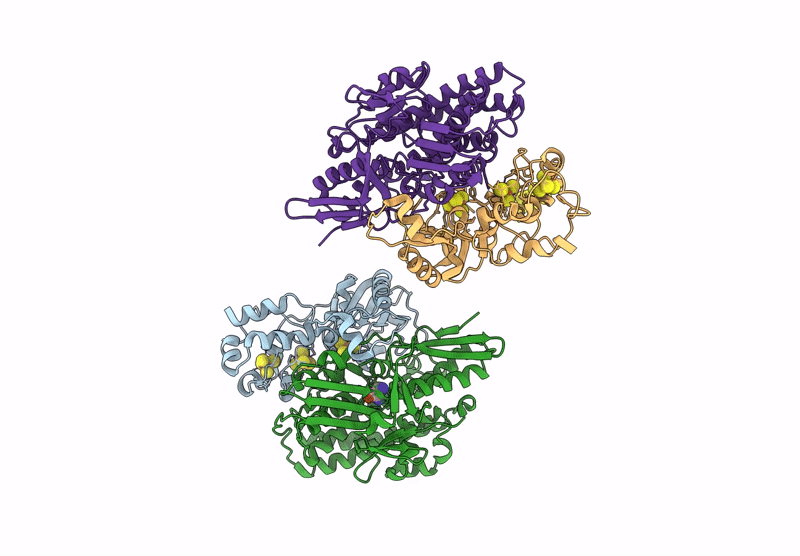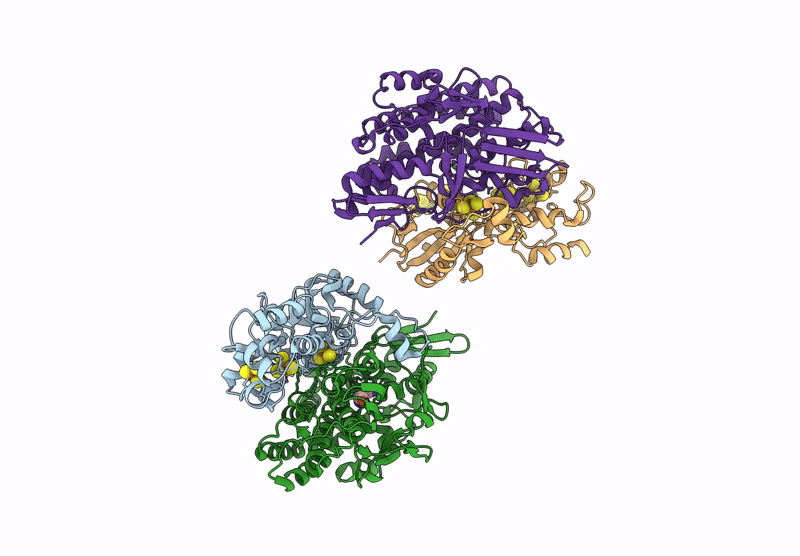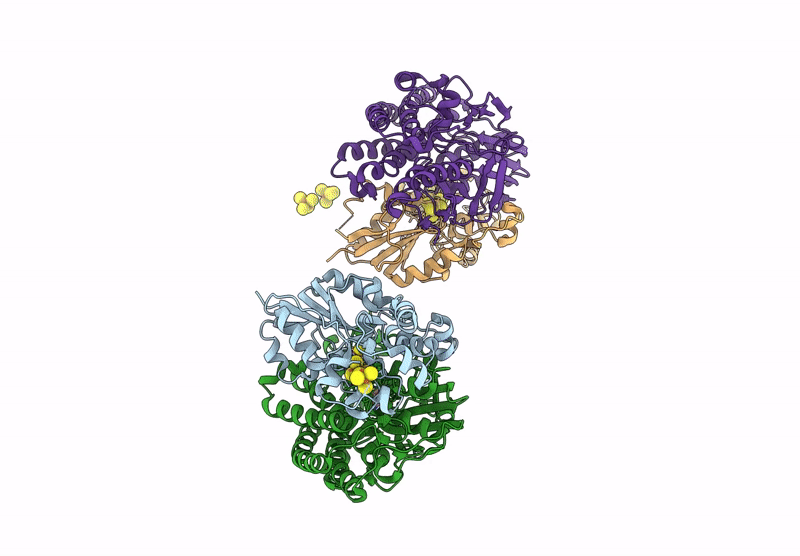
Alpha-Delta heterodimeric form of soluble hydrogenase I from Pyrococcus furiosus. Data processed and model refined in P21221
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Pyrococcus furiosus (Taxon ID: 2261)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.60 Å
R-Value Free:
0.31
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
P 21 2 21


