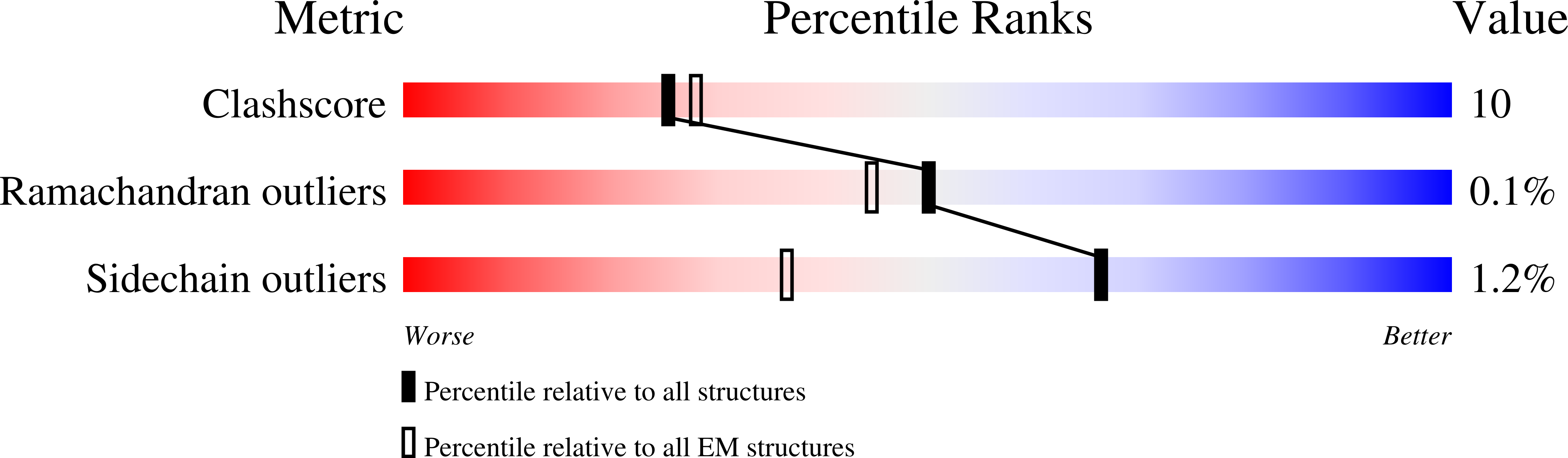
Deposition Date
2024-09-11
Release Date
2024-10-23
Last Version Date
2025-03-05
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9DM1
Keywords:
Title:
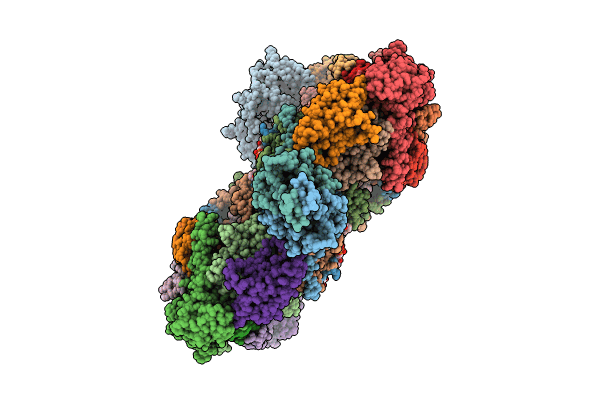
Mycobacterial supercomplex malate:quinone oxidoreductase assembly
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (Taxon ID: 246196)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.20 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE