Abstact
BACKGROUND
The rapid emergence of highly transmissible and immune-evasive SARS-CoV-2 variants has required the reformulation of COVID-19 vaccines to target these evolving threats. Although previous infections and booster vaccinations can boost variant neutralisation, it remains uncertain whether monovalent vaccines-delivered via mRNA or protein-based platforms-can trigger novel B-cell responses specific to omicron XBB.1.5 variants. We sought to address this uncertainty by characterising the antibody repertoire of individuals receiving a monovalent booster vaccine.
METHODS
In this observational study, we analysed the genetic antibody repertoire of 603 individual plasmablasts from five individuals (recruited at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, from STUDY-16-01215/IRB-16-00971 and STUDY-20-00442/IRB-20-03374) vaccinated with a monovalent XBB.1.5 vaccine, either through mRNA (Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech; participants 1, 2, and 3) or adjuvanted protein (Novavax; participants 4 and 5) platforms. Before XBB.1.5 booster vaccination, all participants received mRNA-based priming and booster vaccine with ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and four of the five participants had a breakthrough omicron variant infection. We expressed 100 human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs; 50 from participants 1, 2, and 3, and 50 from participants 4 and 5) and evaluated their binding and neutralisation against various SARS-CoV-2 variants, including JN.1. We then selected four mAbs for in-vivo protection experiments by passive immunisation and viral challenge, and cryo-electron microscopy with two selected mAbs complexed with the XBB.1.5 spike (S) protein to determine their structures and binding interactions.
FINDINGS
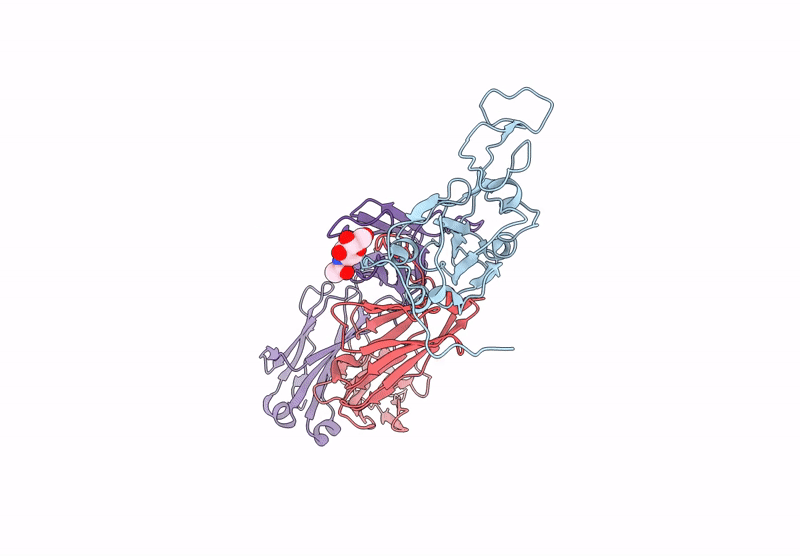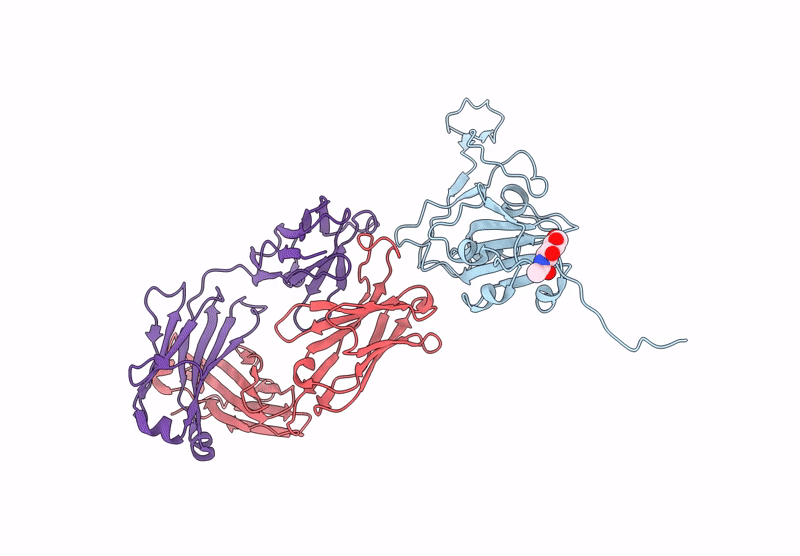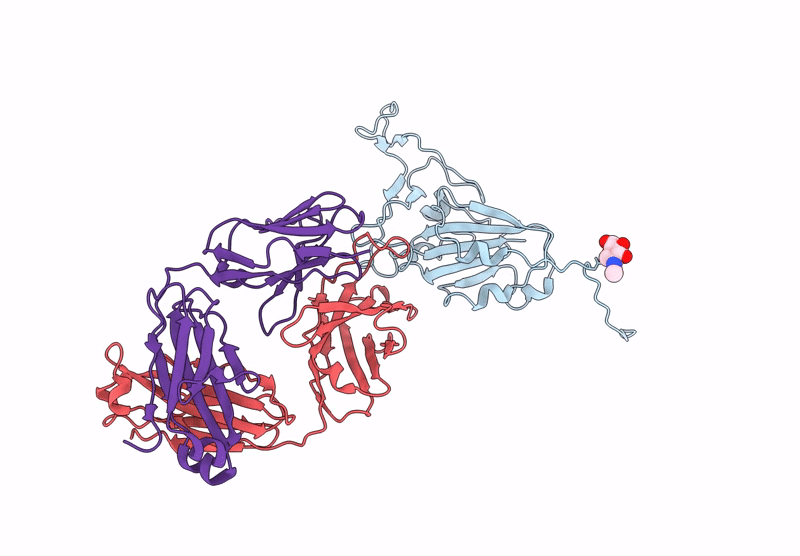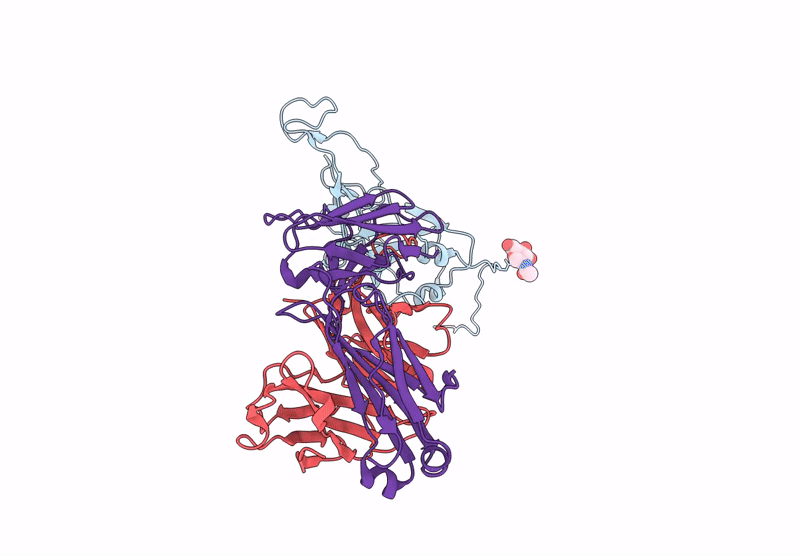
Between October and November, 2023, we enrolled three male and two female participants (mean age 46 years) all of whom were White. We identified 21 binding mAbs and tested their neutralisation capacity against ancestral SARS-CoV-2, XBB.1.5, and JN.1. From the six neutralising mAbs we characterised, we selected three (M2, M27, and M39) for in-vivo protection studies, along with one broadly binding antibody (M15), finding that three neutralising mAbs offered full protection against morbidity from XBB.1.5. M27 also displayed robust protection against the ancestral and JN.1 strains, and M39 offered partial protection from JN.1. Among these, we identified two standout antibodies: M2 and M39. M2 was uniquely specific to XBB.1.5, and M39 demonstrated the ability to bind and neutralise both XBB.1.5 and JN.1 strains. Using high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy, we mapped the binding sites of M2 and M39 on the XBB.1.5 S glycoprotein, uncovering the precise molecular interactions that dictate their specificity.
INTERPRETATION
Our findings offer key molecular insights into whether strain-specific boosters elicit sufficient protection against SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants. This knowledge can inform decisions on booster design and strategies to enhance preparedness to evolving viral threats.
FUNDING
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; National Institutes of Health (NIH) FIRST; Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center Support Grant; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; Human Immunology Project Consortium by NIH; the São Paulo Research Foundation; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the NIH; Irma T Hirschl and Monique Weill-Caulier Trust; and the Collaborative Influenza Vaccine Innovation Centers.