Deposition Date
2024-05-13
Release Date
2025-02-26
Last Version Date
2025-07-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9BSN
Keywords:
Title:
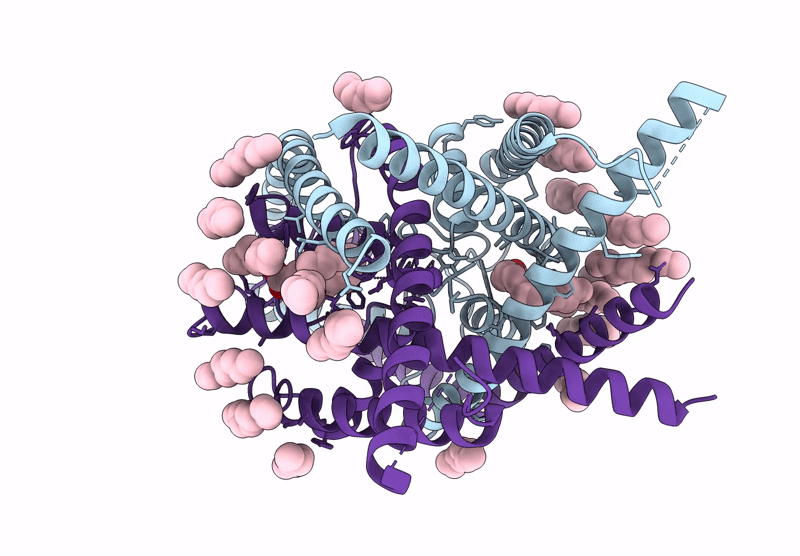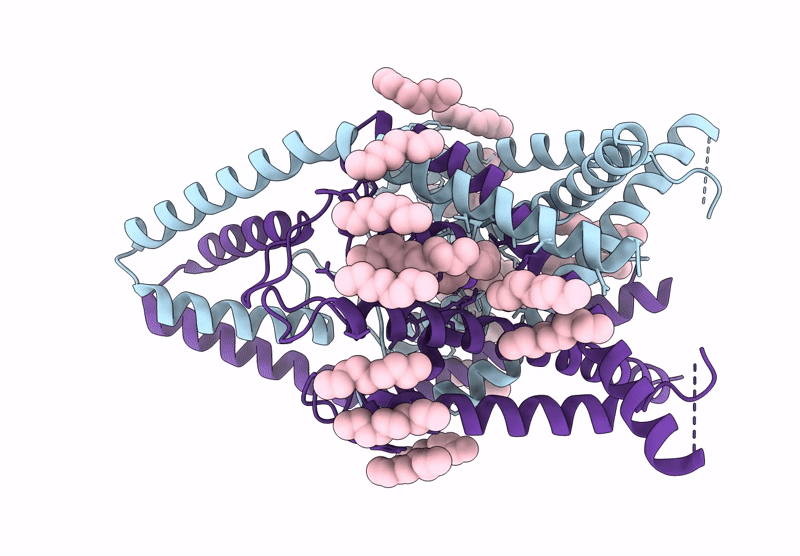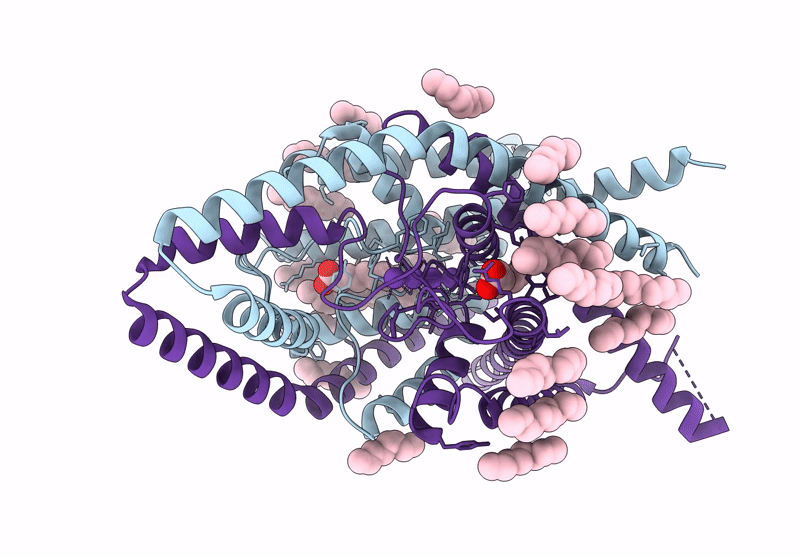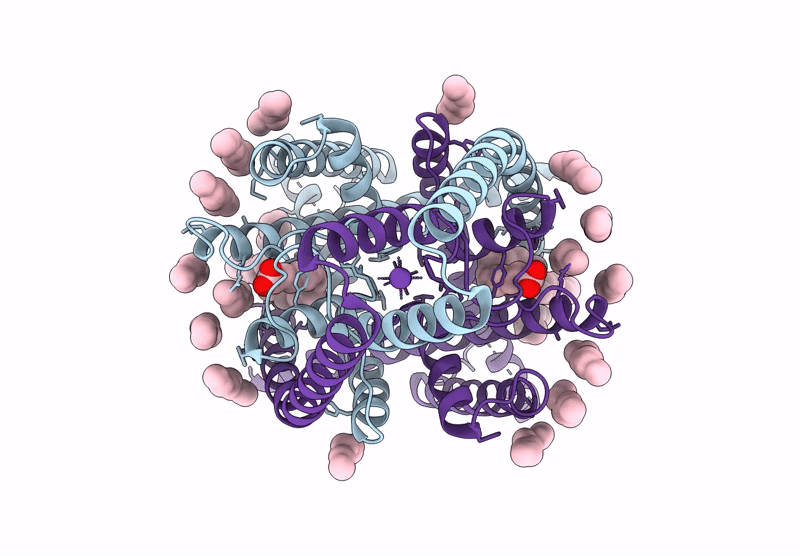
Structure of human K2P13.1 (THIK-1) in lipid nanodisc
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.70 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


