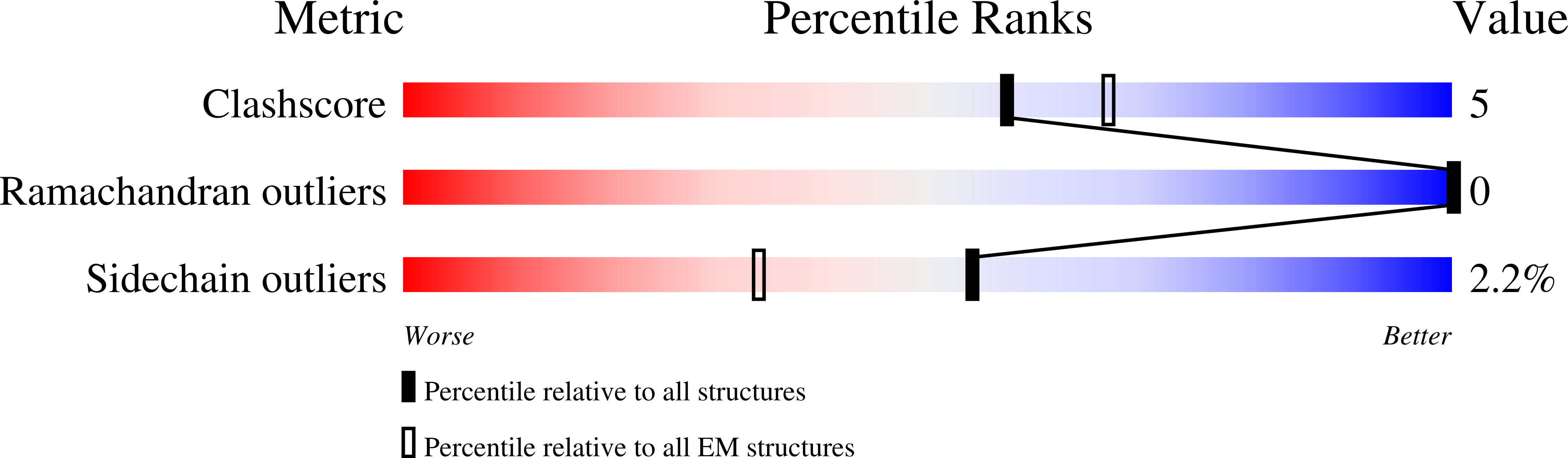
Deposition Date
2024-03-31
Release Date
2024-06-26
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9B8O
Keywords:
Title:
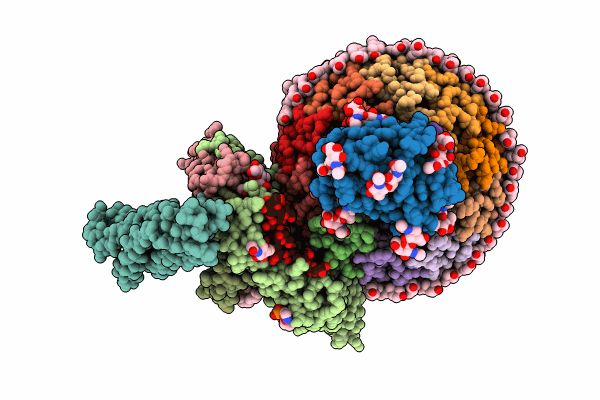
Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, Vo
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.20 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE