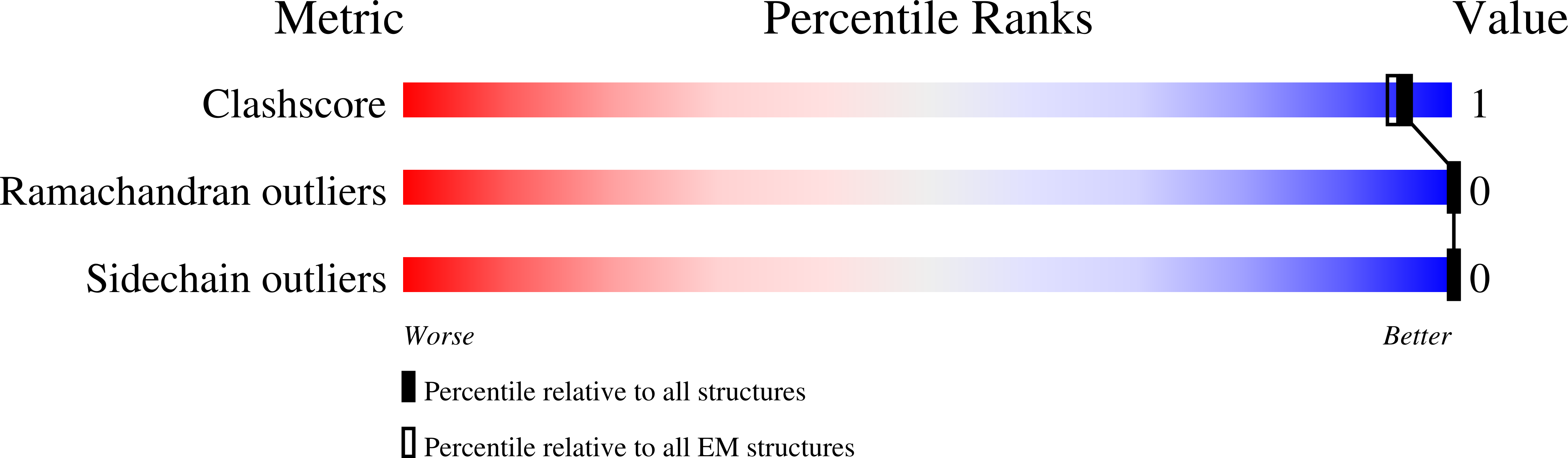
Deposition Date
2024-03-27
Release Date
2025-02-05
Last Version Date
2025-03-05
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
9B77
Keywords:
Title:
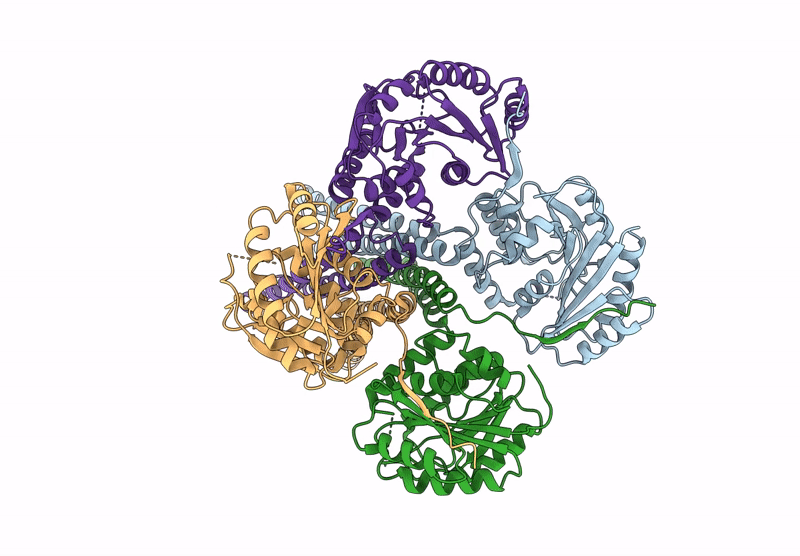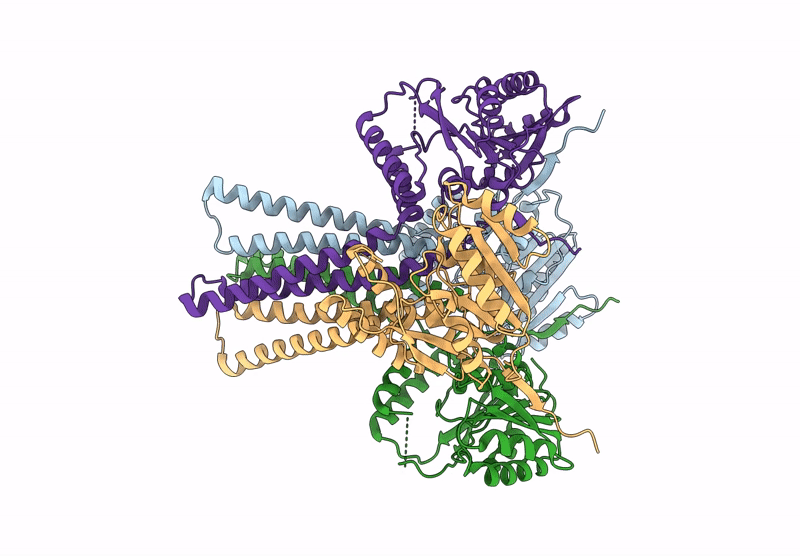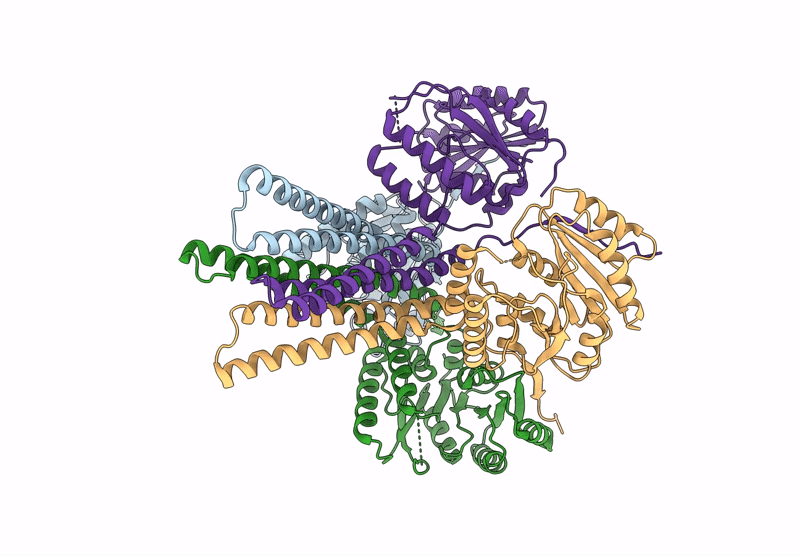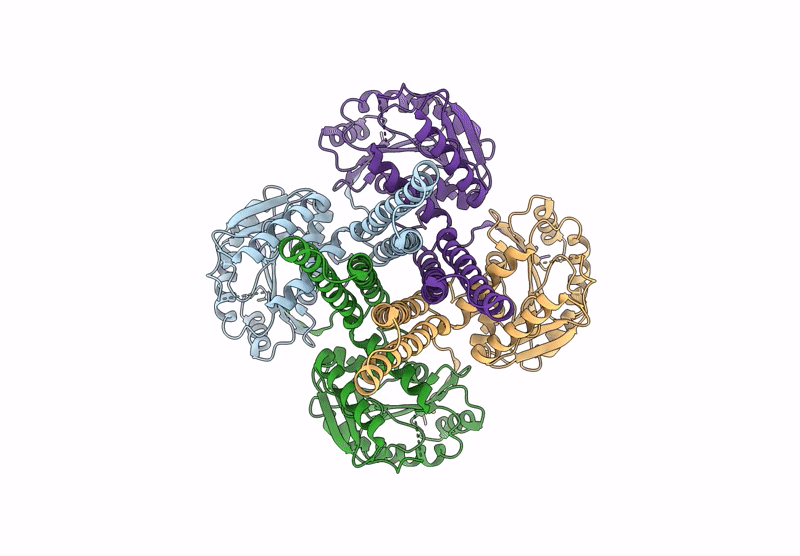
Cryo-EM Structure of the Glycosyltransferase ArnC from Salmonella enterica in the Apo State Determined on Krios microscope
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.74 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE