Deposition Date
2024-02-05
Release Date
2024-10-16
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8Y7Z
Keywords:
Title:
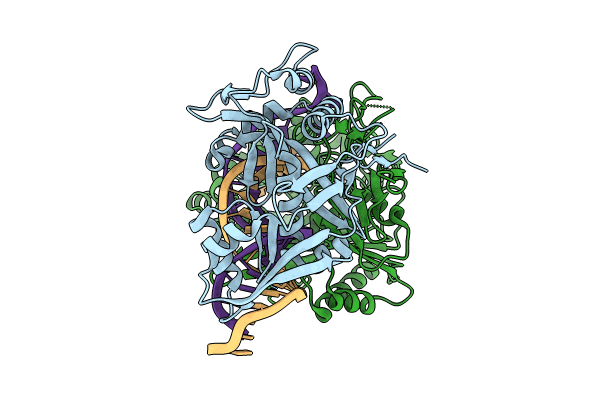
Cryo-EM structure of the monomeric SPARSA gRNA-ssDNA complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Geobacter sulfurreducens (Taxon ID: 35554)
Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (Taxon ID: 866768)
Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (Taxon ID: 866768)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
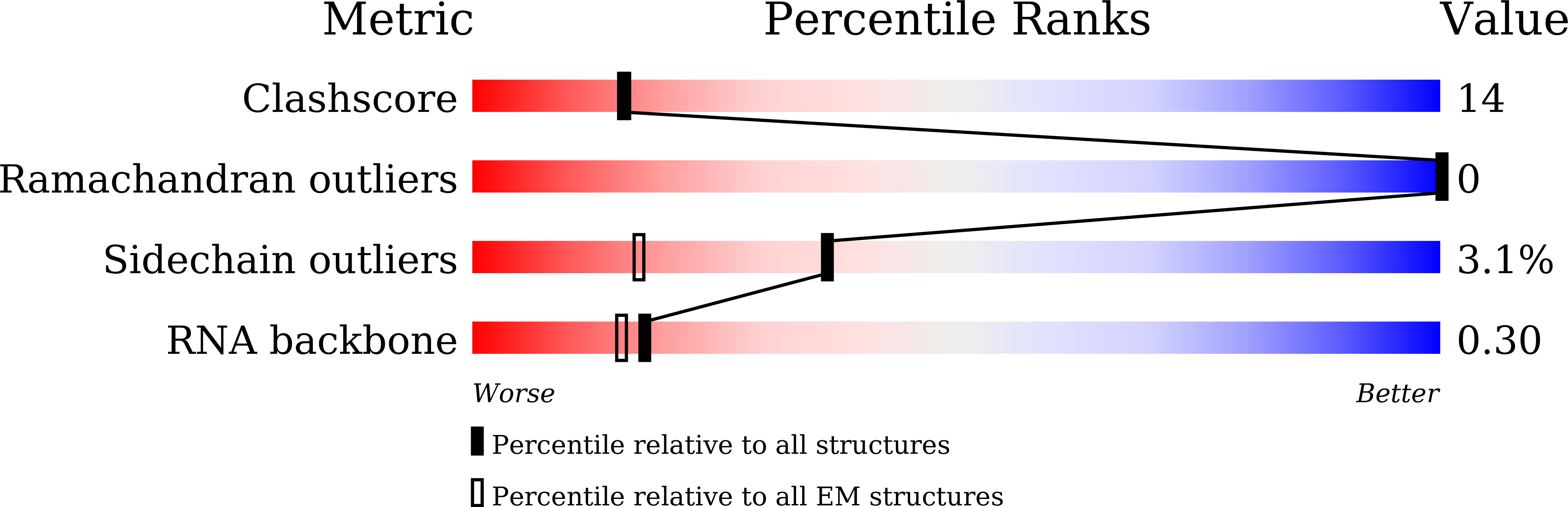
Resolution:
2.57 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE