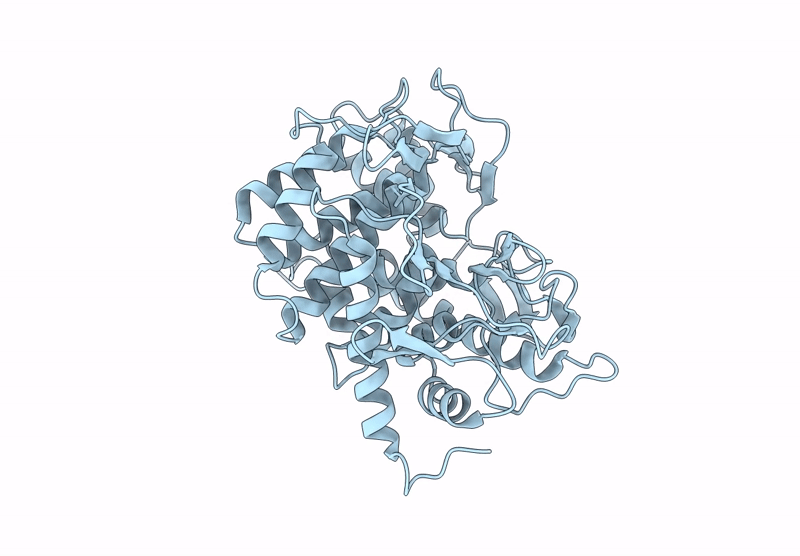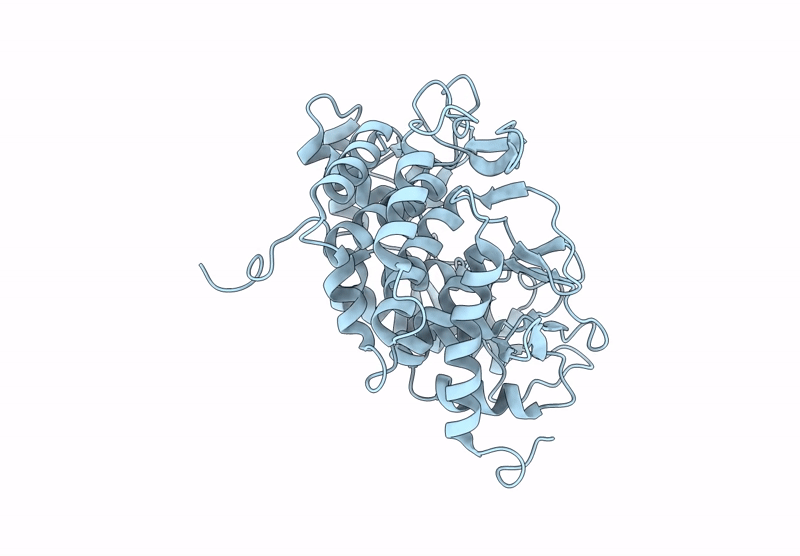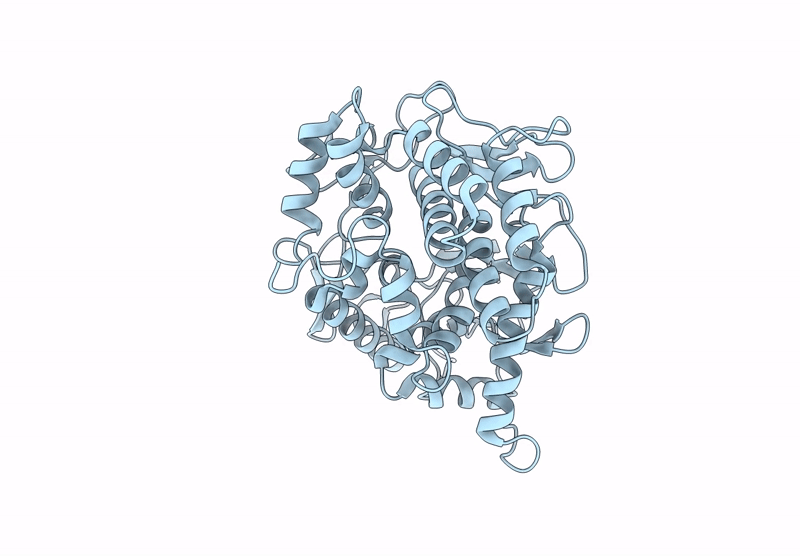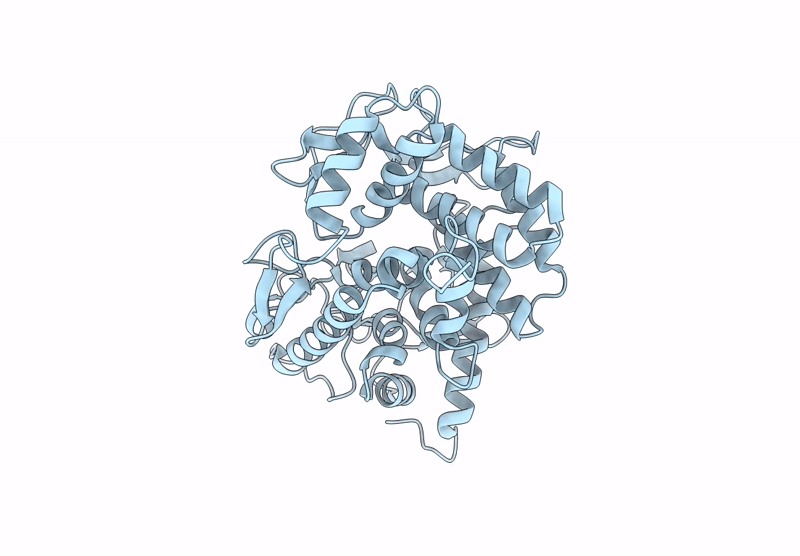
Abstact
β-1,2-Glucans are natural glucose polymers produced by bacteria and play important physiological roles, including as symbiotic or pathogenic factors and in osmoregulation. Glycoside hydrolase (GH) families related to β-1,2-glucan metabolism (GH144, GH162, and GH189) have recently been created by identification of two β-1,2-glucanases and a β-1,2-glucanotransferase, respectively. In this study, we further found four phylogenetically new groups with unknown functions (Groups 1-4) by sequence database analysis using enzymes from GH144 and GH162 as queries. Biochemical analysis of representative proteins in these groups revealed that the proteins in Groups 1-3 showed hydrolytic activity specific to β-1,2-glucan, while no substrate was found for the Group 4 protein. The kinetic parameters of the enzymes of Groups 1-3 were similar to GH144 and GH162 β-1,2-glucanases, indicating that these enzymes were β-1,2-glucanases. Optical rotation analysis revealed that the β-1,2-glucanases followed an anomer-inverting mechanism. Structural analysis of the proteins in Groups 1-4 revealed that they possess (α/α)6-barrel folds similar to those of GH144, GH162, and GH189 enzymes. Comparison of spatial positions of predicted acidic catalytic residues suggested that Groups 1-3 and GH144 had the same reaction mechanism. Overall, phylogenetic, biochemical, and structural analyses revealed that Groups 1-3 are new GH families, GH192, GH193, and GH194, respectively, and that the three families belong to clan GH-S (clan GH, classification based on structural similarity) as GH144 and GH162.