Deposition Date
2023-12-26
Release Date
2024-07-31
Last Version Date
2025-06-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8XLP
Keywords:
Title:
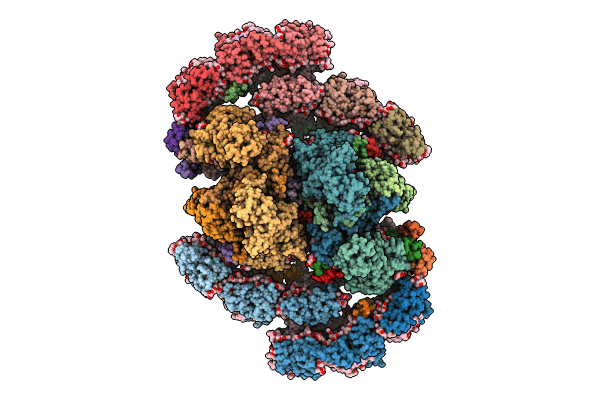
Structure of inactive Photosystem II associated with CAC antenna from Rhodomonas Salina
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rhodomonas salina (Taxon ID: 52970)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.57 Å
Aggregation State:
3D ARRAY
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE