Deposition Date
2023-12-26
Release Date
2025-02-05
Last Version Date
2025-03-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8XLK
Keywords:
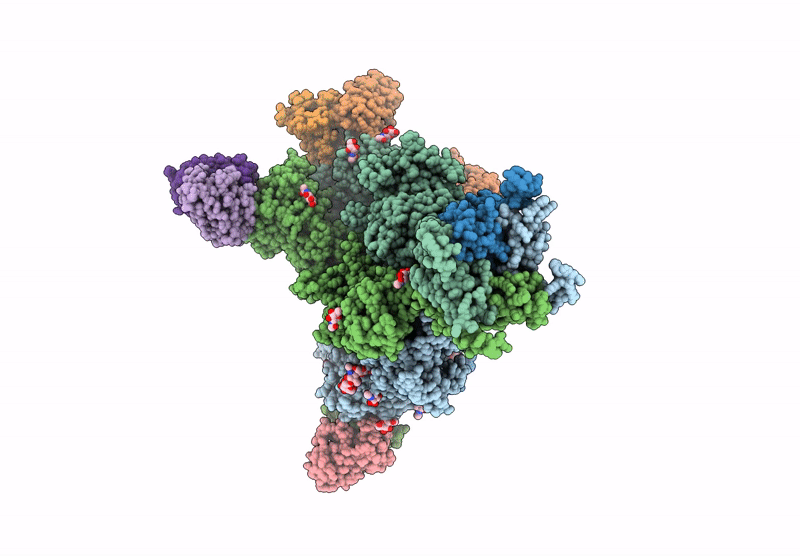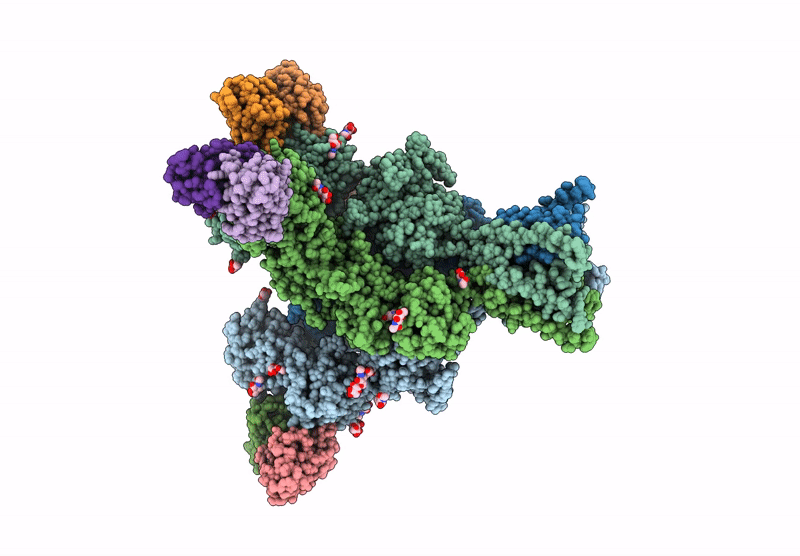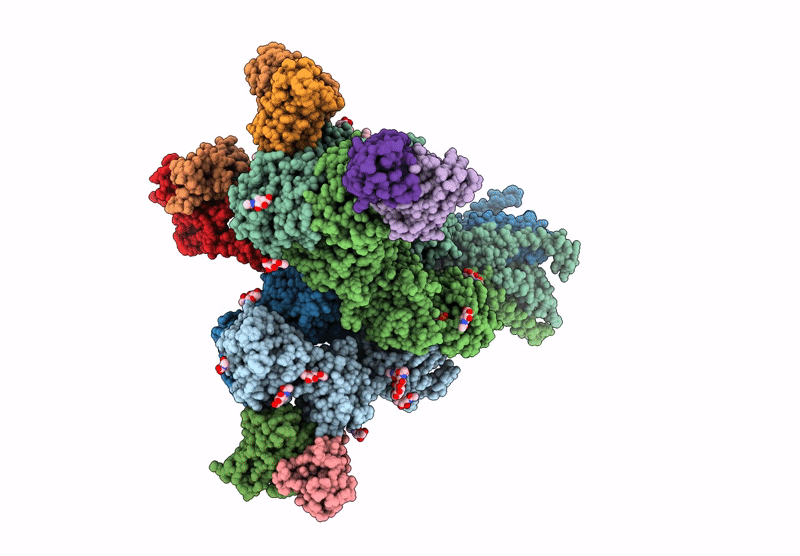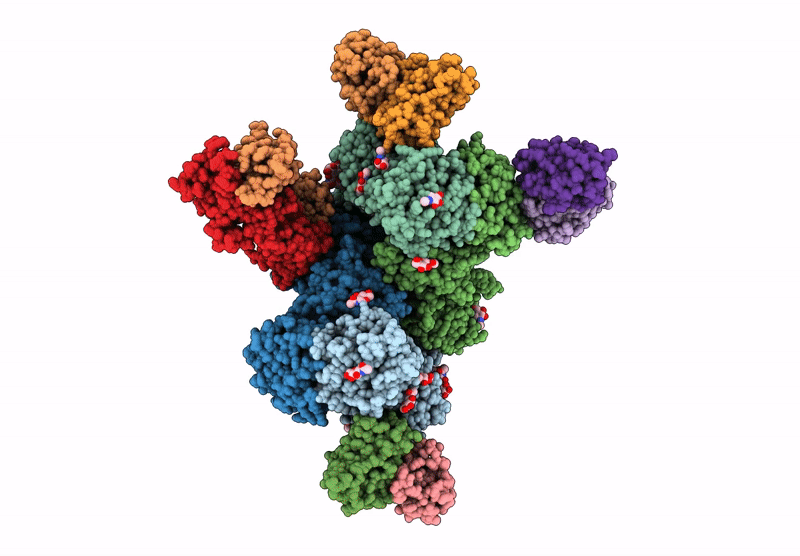
Title:
Structure of native tri-heteromeric GluN1-GluN2A-GluN2B NMDA receptor in rat cortex and hippocampus
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculoides (Taxon ID: 60742)
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.20 Å
Aggregation State:
TISSUE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


