Deposition Date
2023-12-15
Release Date
2024-02-14
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8XGC
Keywords:
Title:
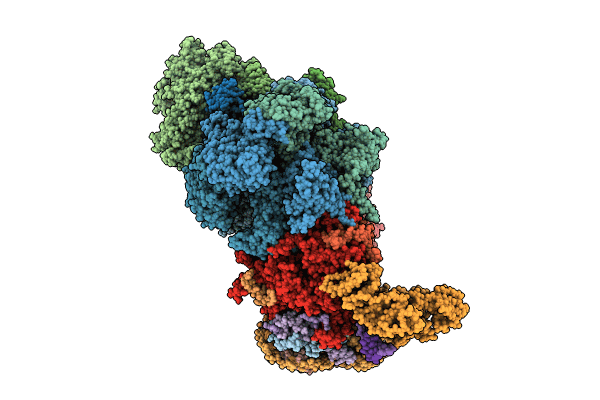
Structure of yeast replisome associated with FACT and histone hexamer, Composite map
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.70 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE