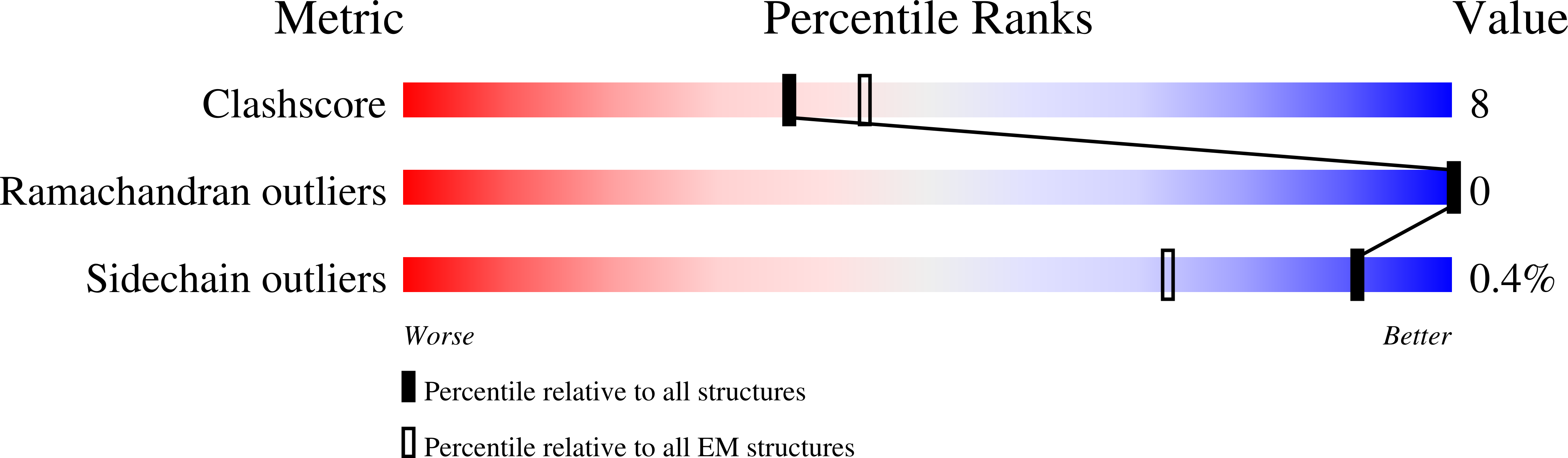Deposition Date
2024-01-08
Release Date
2024-02-07
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8VK4
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of mouse RyR1 in complex with S100A1 (high-Ca2+/CFF/ATP dataset)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.56 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE