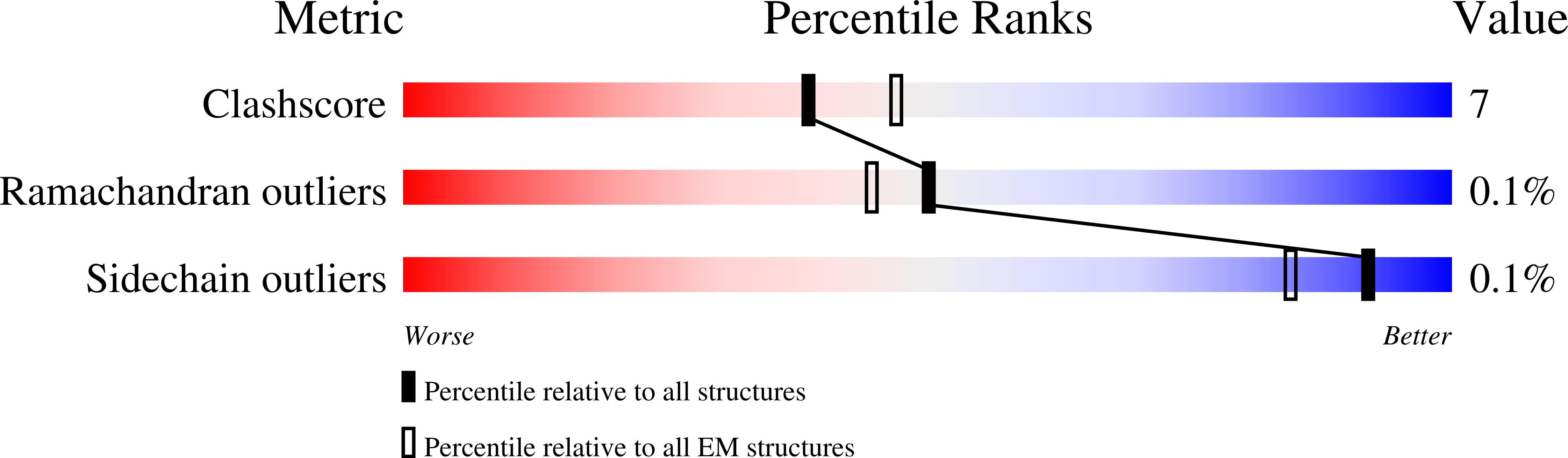
Deposition Date
2023-11-13
Release Date
2024-11-27
Last Version Date
2025-10-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8UY8
Keywords:
Title:
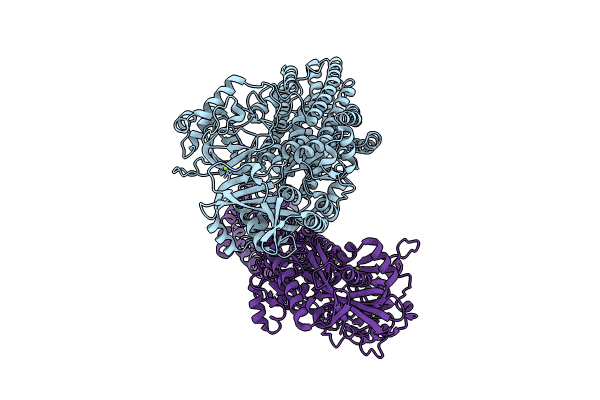
Magnesium transporter MgtA dimer from E. coli in 5 mM MgCl2 in C1
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 83333)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.03 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE