Deposition Date
2023-10-11
Release Date
2023-12-20
Last Version Date
2024-01-10
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8UJY
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of human WD repeat-containing protein 5 in complex with 4-(3,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-9-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-7-((2-imino-3-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-3,4-dihydrobenzo[f][1,4]oxazepin-5(2H)-one (compound 8)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
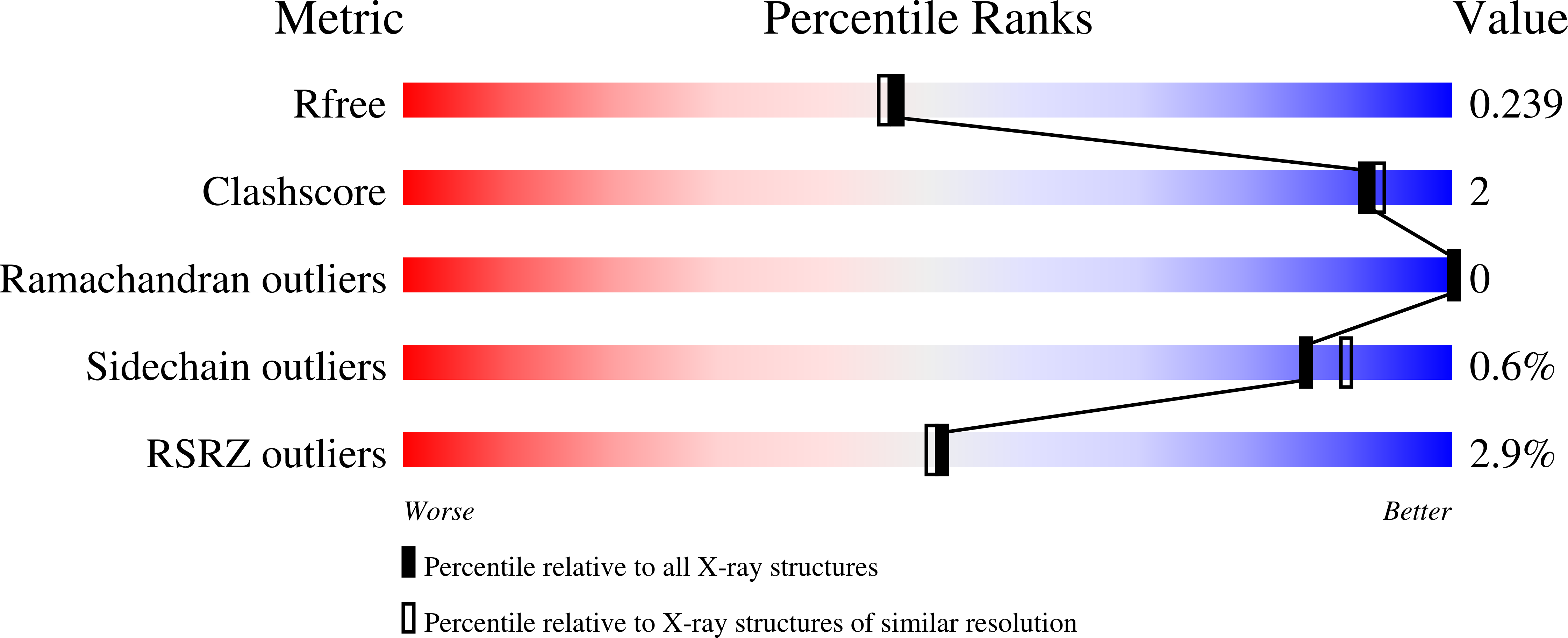
Resolution:
2.01 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.18
Space Group:
P 1