Deposition Date
2023-08-25
Release Date
2024-02-07
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
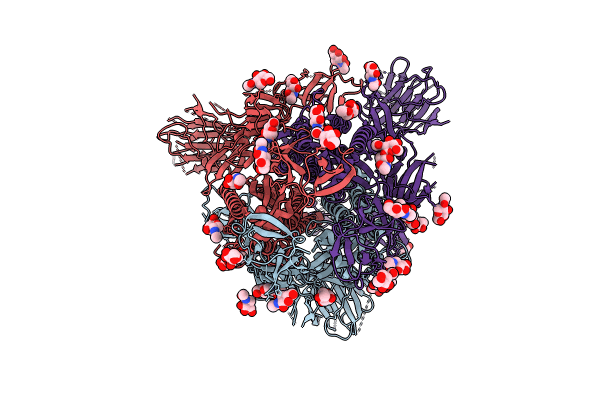
PDB ID:
8TYO
Keywords:
Title:
Structural and biochemical rationale for Beta variant protein booster vaccine broad cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.75 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


