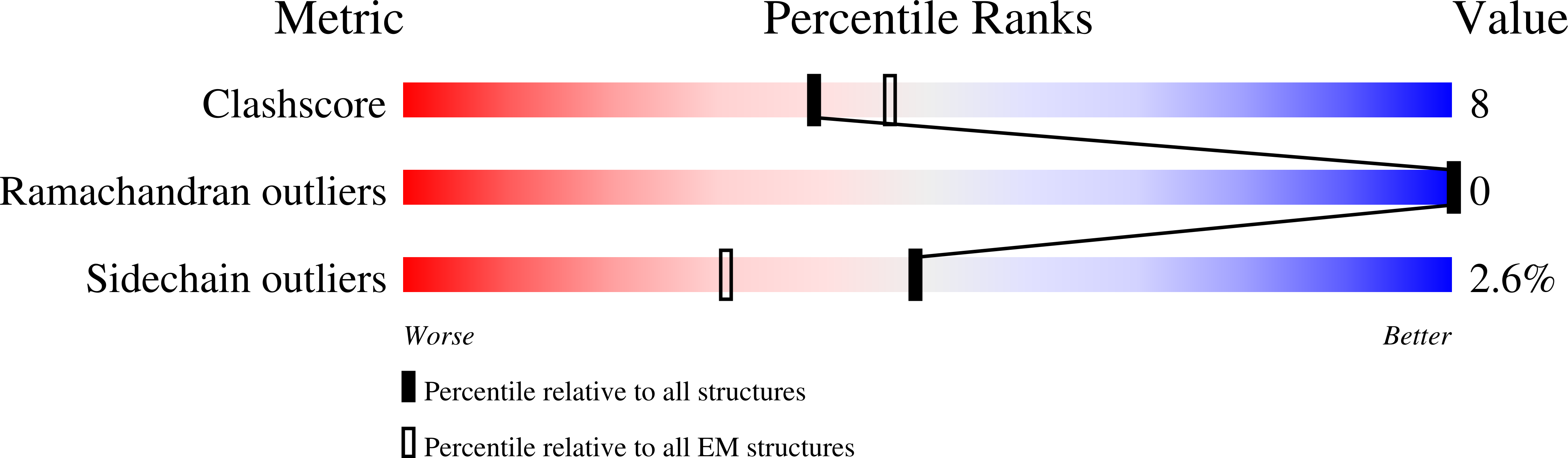
Deposition Date
2023-08-11
Release Date
2024-04-17
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8TSI
Keywords:
Title:
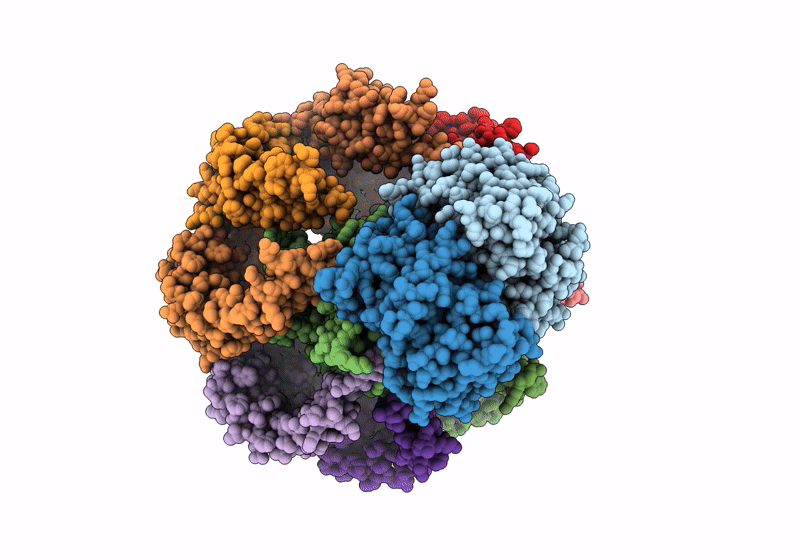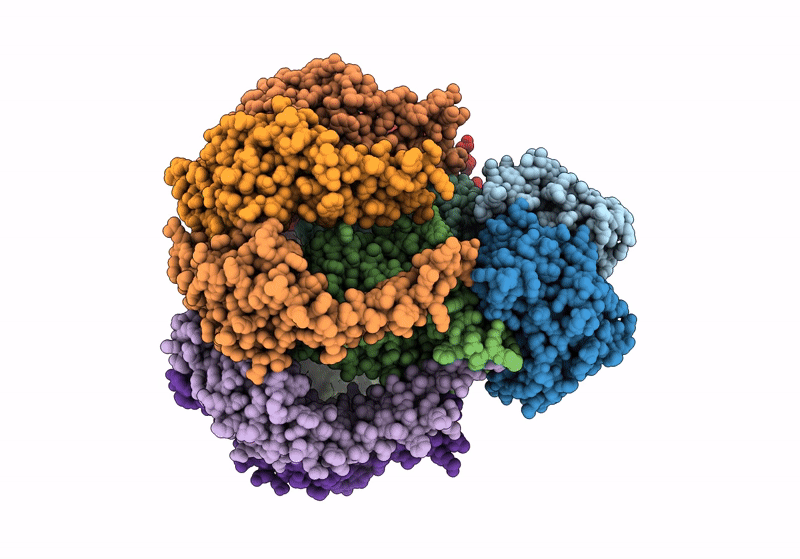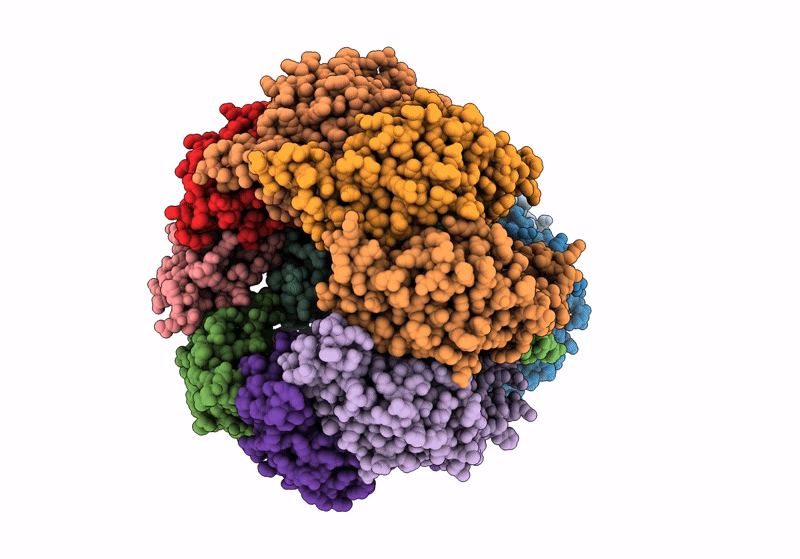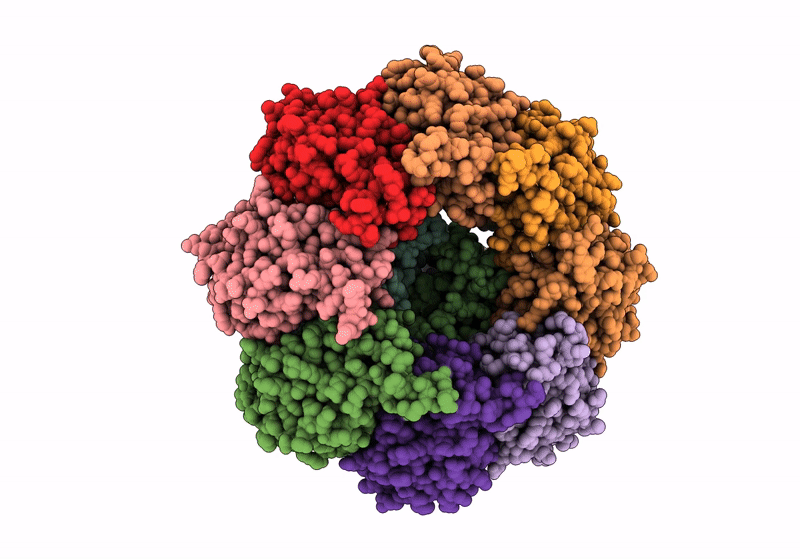
S. thermodepolymerans KpsMT-KpsE in complex with ADP:AlF4-
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Caldimonas thermodepolymerans (Taxon ID: 215580)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.40 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE