Deposition Date
2023-05-25
Release Date
2023-08-30
Last Version Date
2025-05-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8SYF
Keywords:
Title:
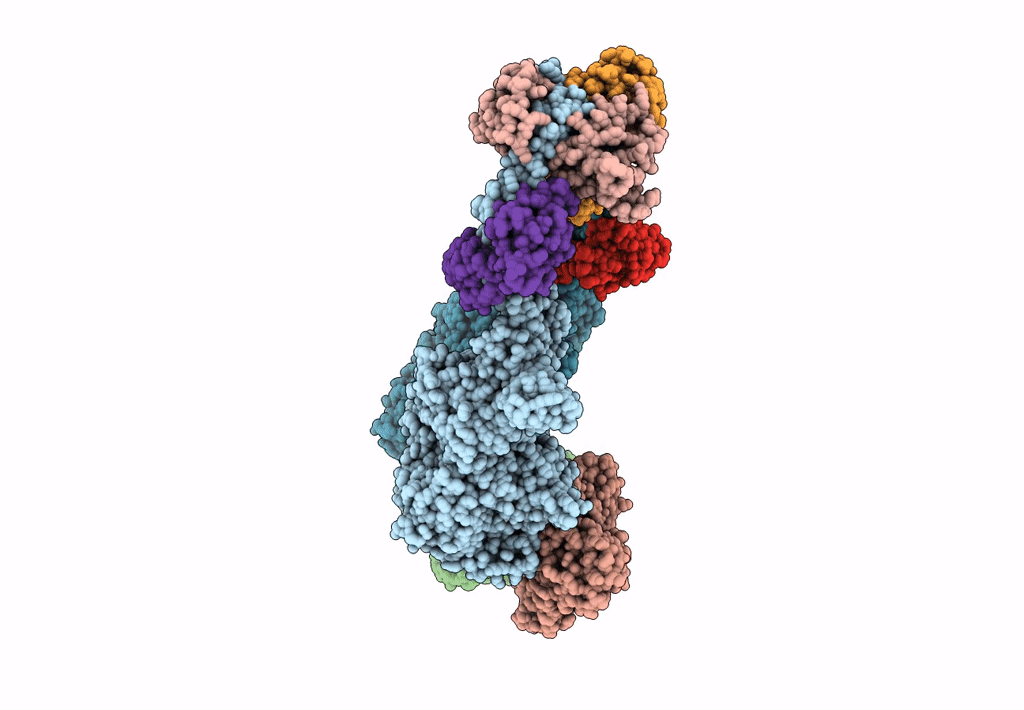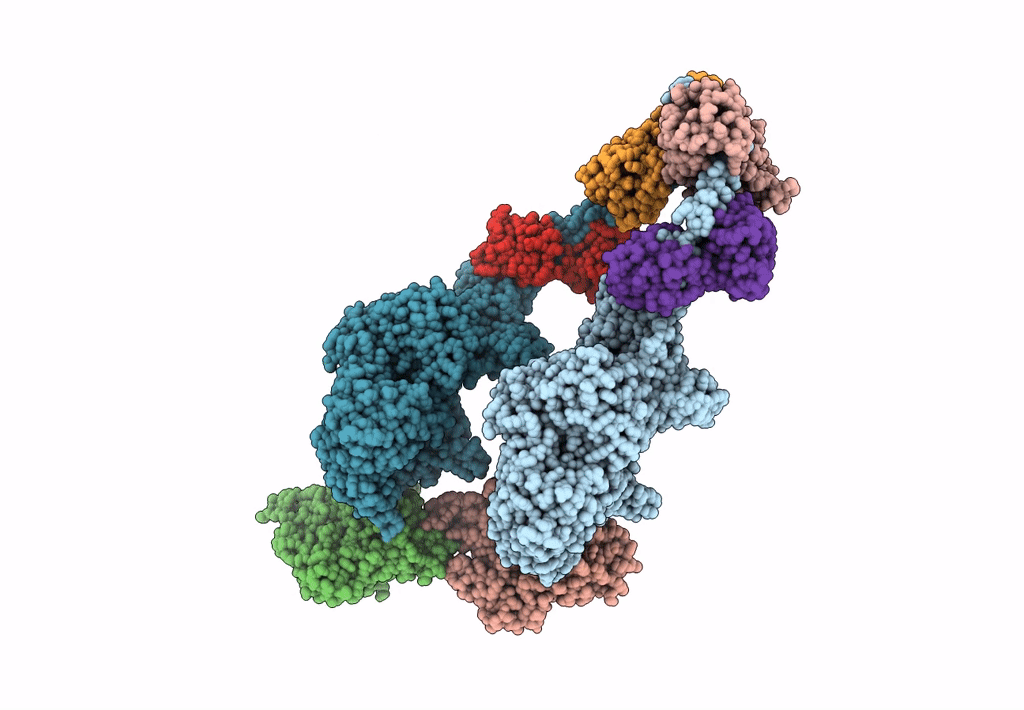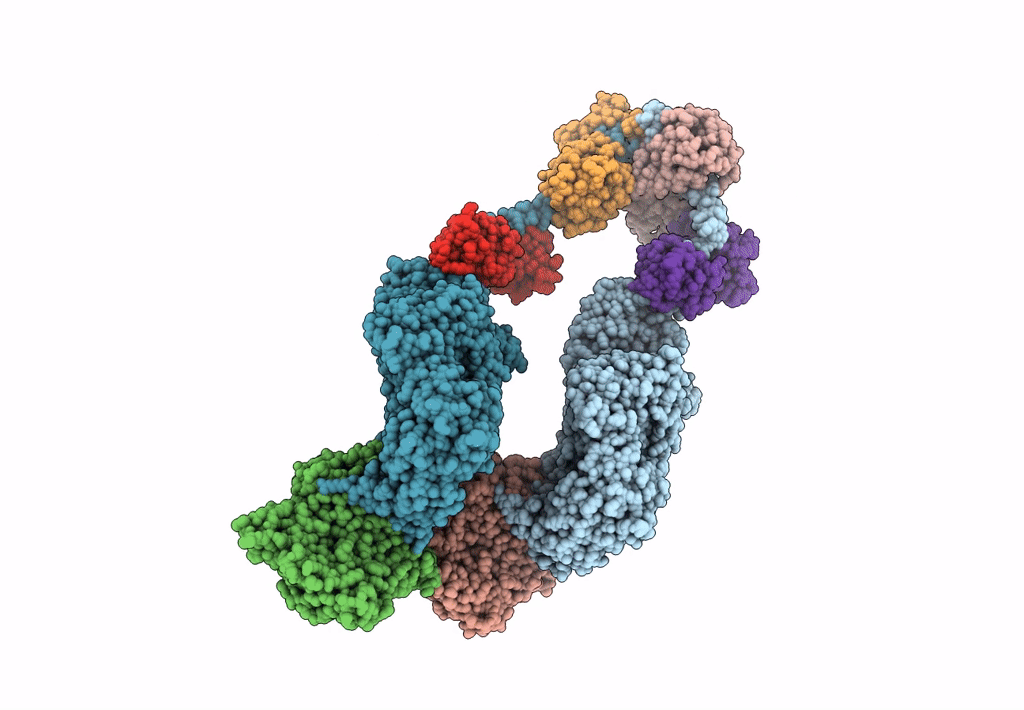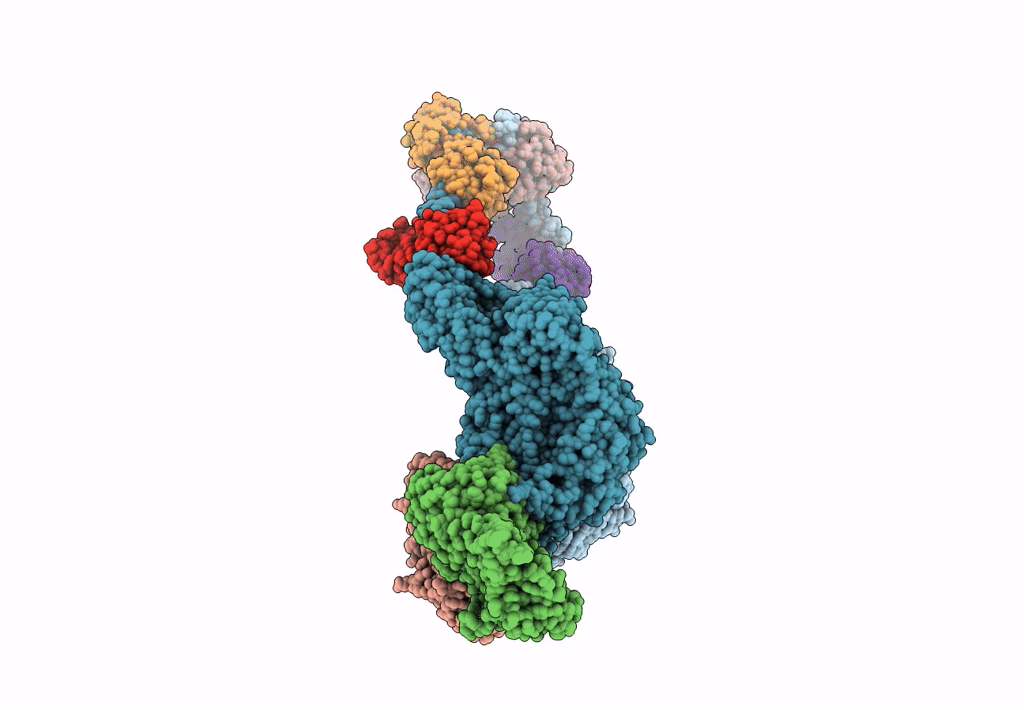
Homology model of Acto-HMM complex in ADP-state. Chicken smooth muscle HMM and chicken pectoralis actin
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Gallus gallus (Taxon ID: 9031)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
19.00 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


