Deposition Date
2023-05-04
Release Date
2023-11-22
Last Version Date
2025-05-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8SQK
Keywords:
Title:
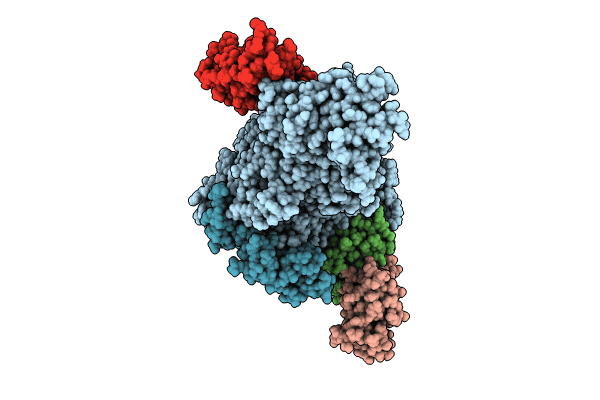
SARS-CoV-2 replication-transcription complex bound to RNA-nsp9 and GDP-betaS, as a pre-catalytic deRNAylation/mRNA capping intermediate
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
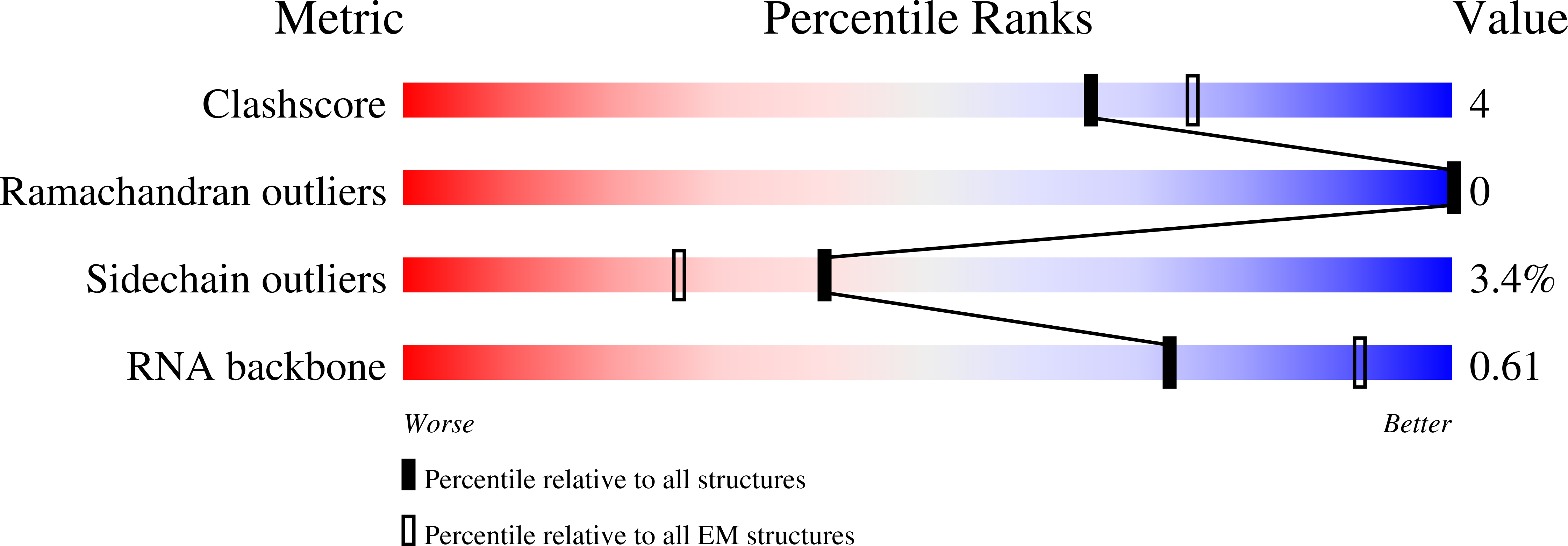
Resolution:
3.01 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE