Deposition Date
2024-02-20
Release Date
2025-03-05
Last Version Date
2025-09-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8S3M
Keywords:
Title:
LysTt72, a lytic endopeptidase from Thermus thermophilus MAT72 phage vB_Tt72
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermus phage Tt72 (Taxon ID: 2978976)
Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (Taxon ID: 469008)
Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (Taxon ID: 469008)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
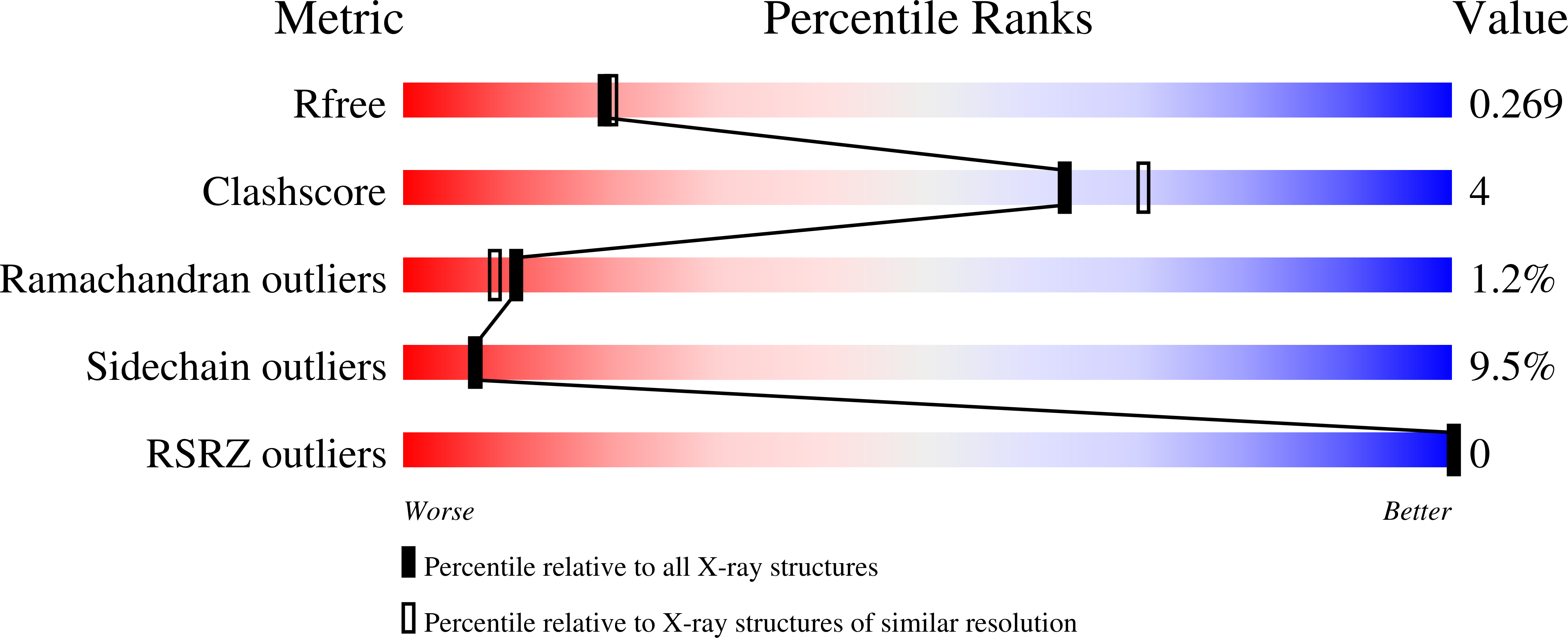
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.18
Space Group:
P 21 21 21