Deposition Date
2024-02-19
Release Date
2024-11-06
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8S35
Keywords:
Title:
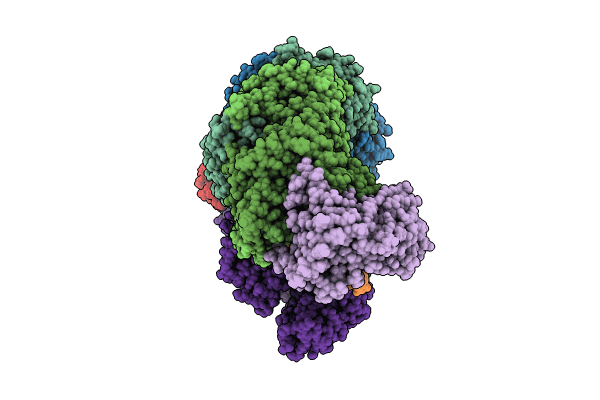
DNA-bound Type IV-A3 CRISPR effector in complex with DinG helicase from K. pneumoniae (state I)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Taxon ID: 573)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
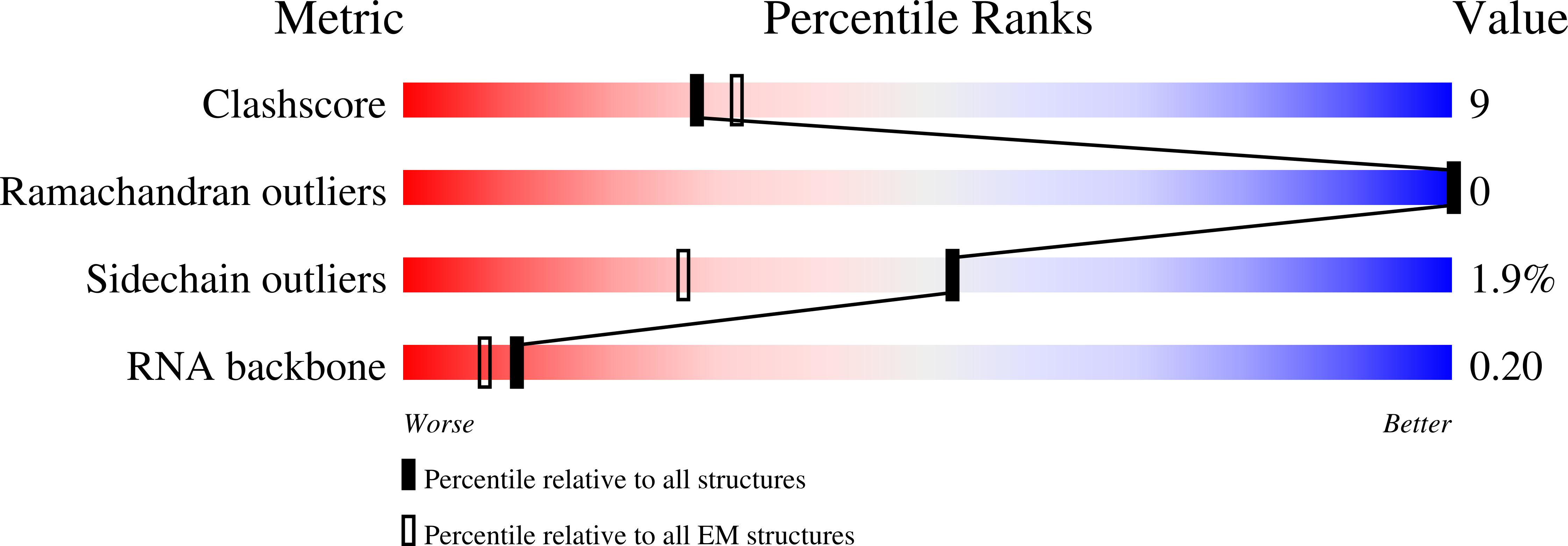
Resolution:
2.90 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE