Deposition Date
2023-11-23
Release Date
2024-04-24
Last Version Date
2024-06-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8R6W
Keywords:
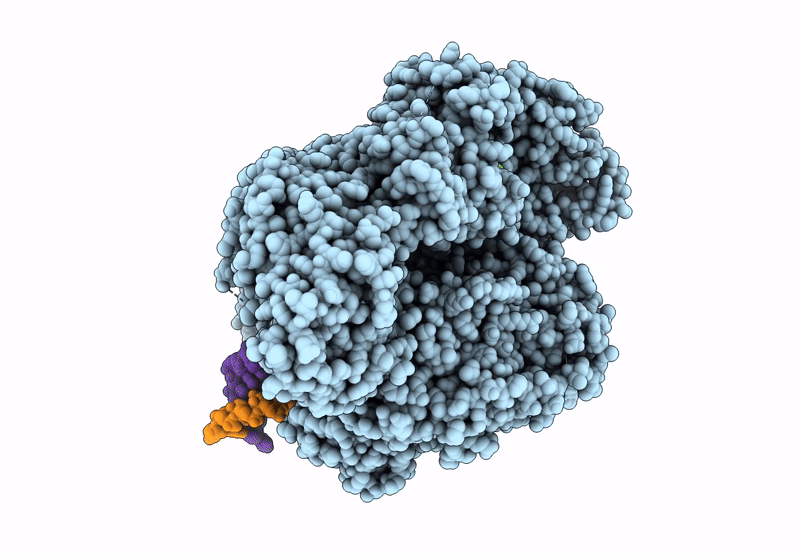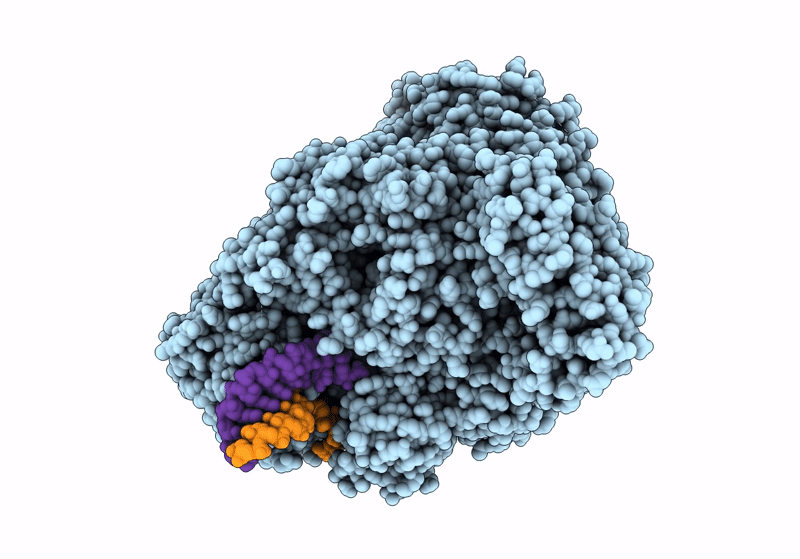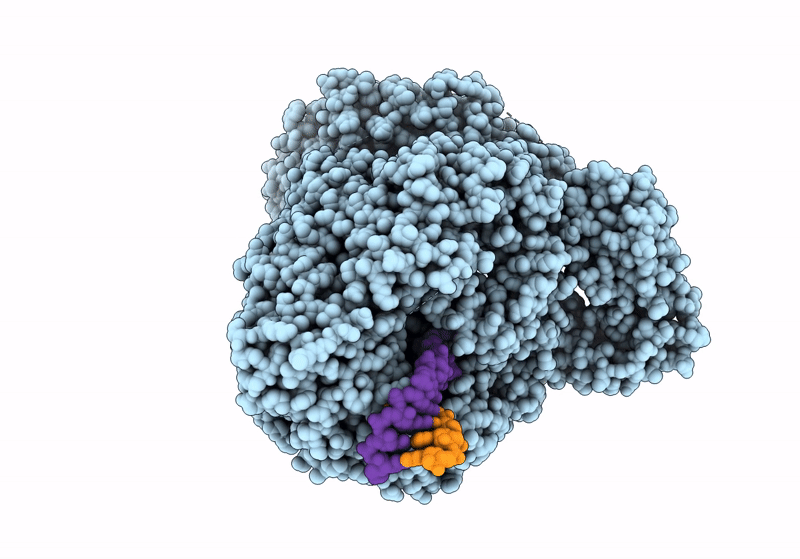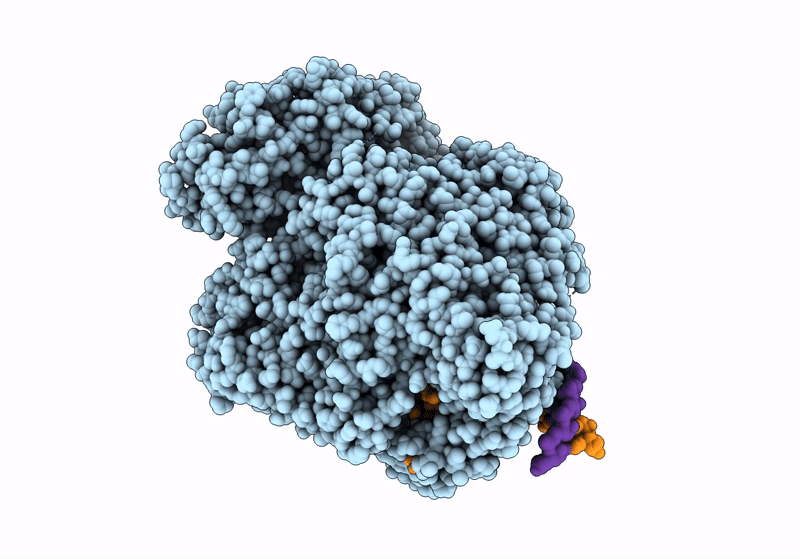
Title:
Structure of the SFTSV L protein in a transcription-priming state with bound capped RNA [TRANSCRIPTION-PRIMING]
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
SFTS virus AH12 (Taxon ID: 992210)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.35 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


