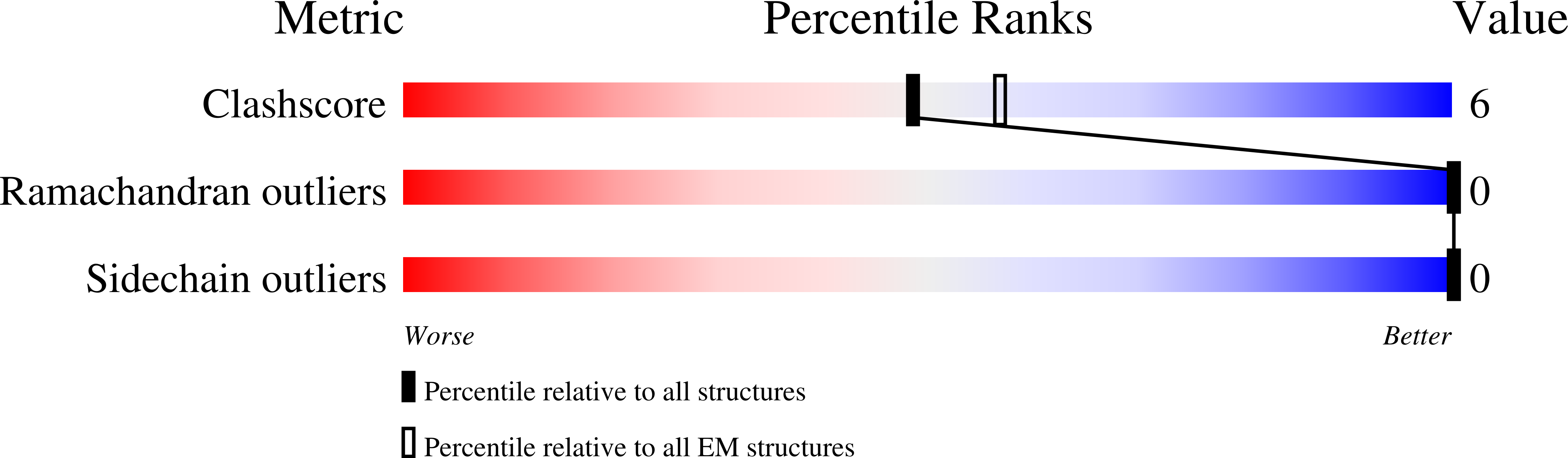
Deposition Date
2023-11-16
Release Date
2024-02-21
Last Version Date
2025-12-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8R5H
Keywords:
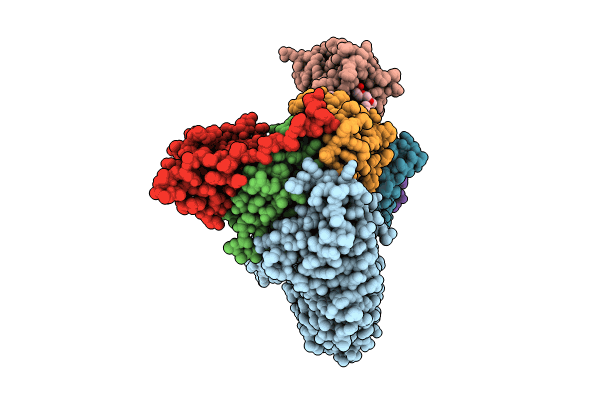
Title:
Ubiquitin ligation to neosubstrate by a cullin-RING E3 ligase & Cdc34: NEDD8-CUL2-RBX1-ELOB/C-VHL-MZ1 with trapped UBE2R2~donor UB-BRD4 BD2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.44 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE