Deposition Date
2023-08-31
Release Date
2023-10-18
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8QEC
Keywords:
Title:
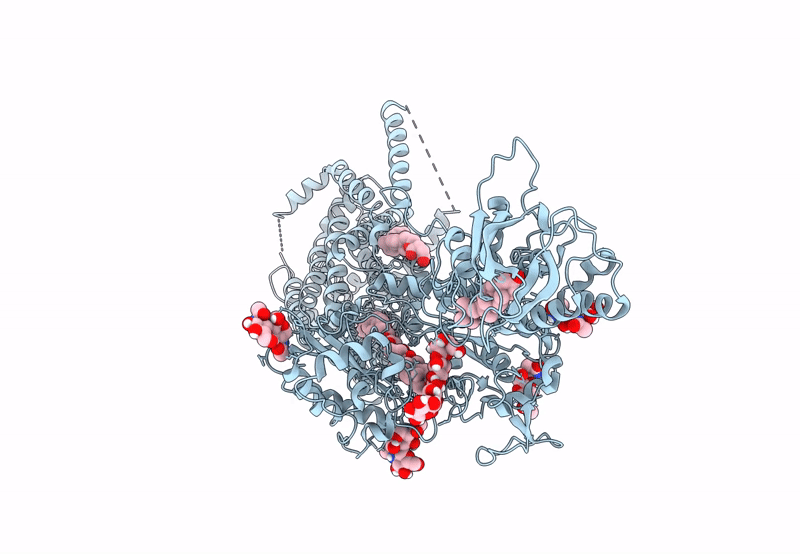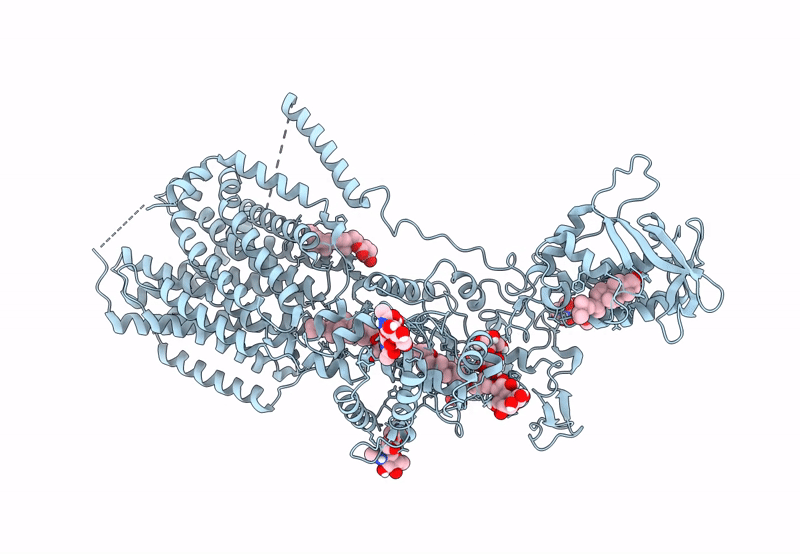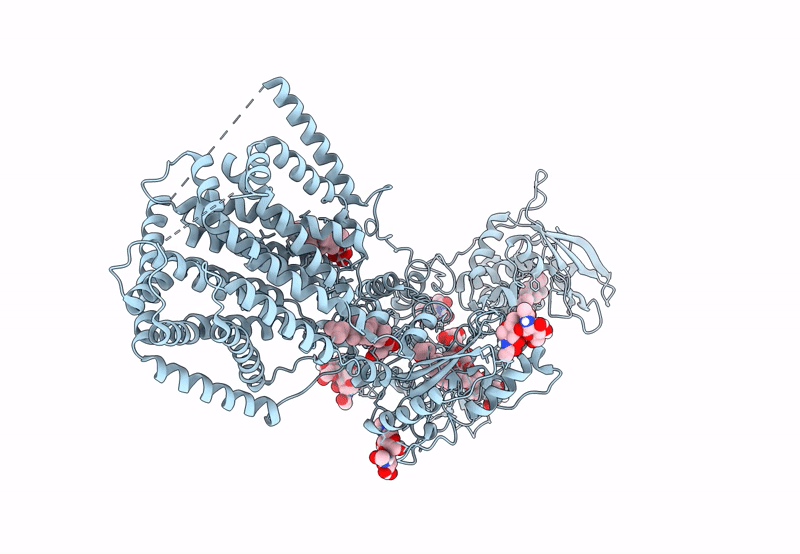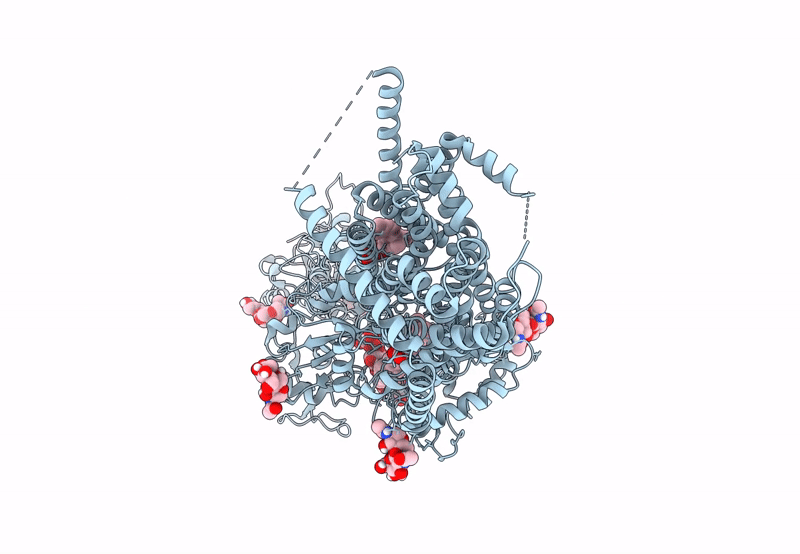
S. cerevisia Niemann-Pick type C protein NCR1 in GDN at pH 5.5
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.30 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


