Deposition Date
2023-07-10
Release Date
2023-12-20
Last Version Date
2025-07-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8PPU
Keywords:
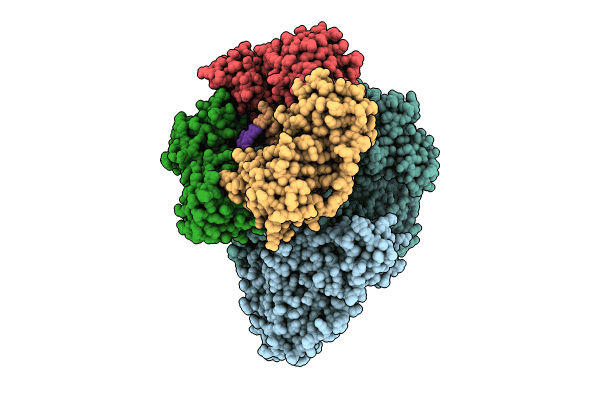
Title:
Pyrococcus abyssi DNA polymerase D (PolD) in its editing mode bound to a primer/template substrate containing three consecutive mismatches
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (Taxon ID: 272844)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.02 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


