Deposition Date
2023-06-12
Release Date
2023-12-06
Last Version Date
2025-07-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8PDR
Keywords:
Title:
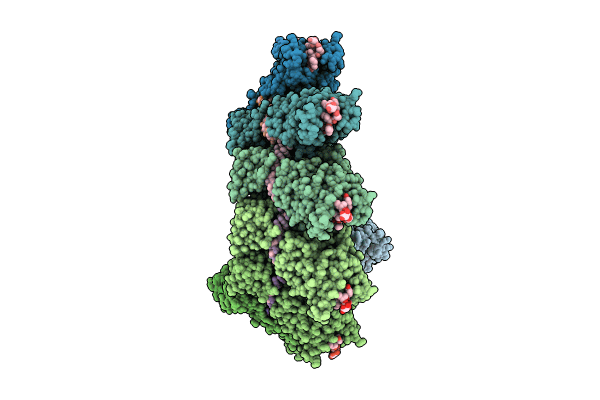
Rigid body fit of assembled HMPV N-RNA spiral bound to the C-terminal region of P
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Human metapneumovirus (strain CAN97-83) (Taxon ID: 694067)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
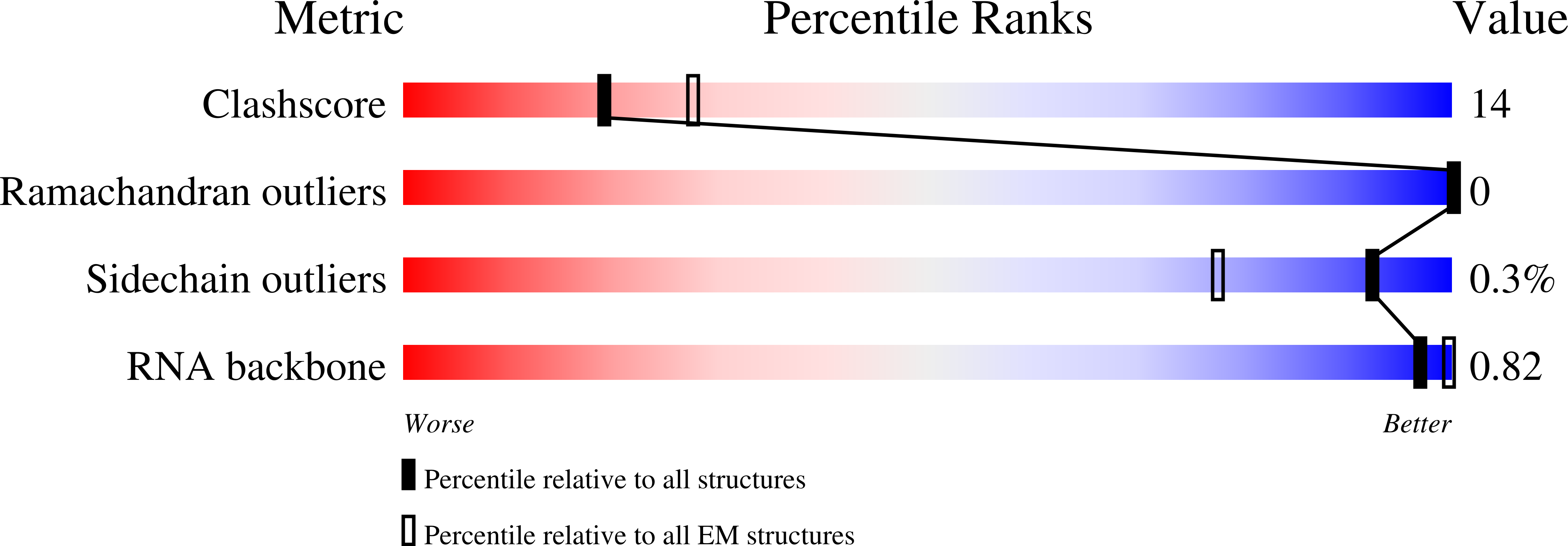
Resolution:
4.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE