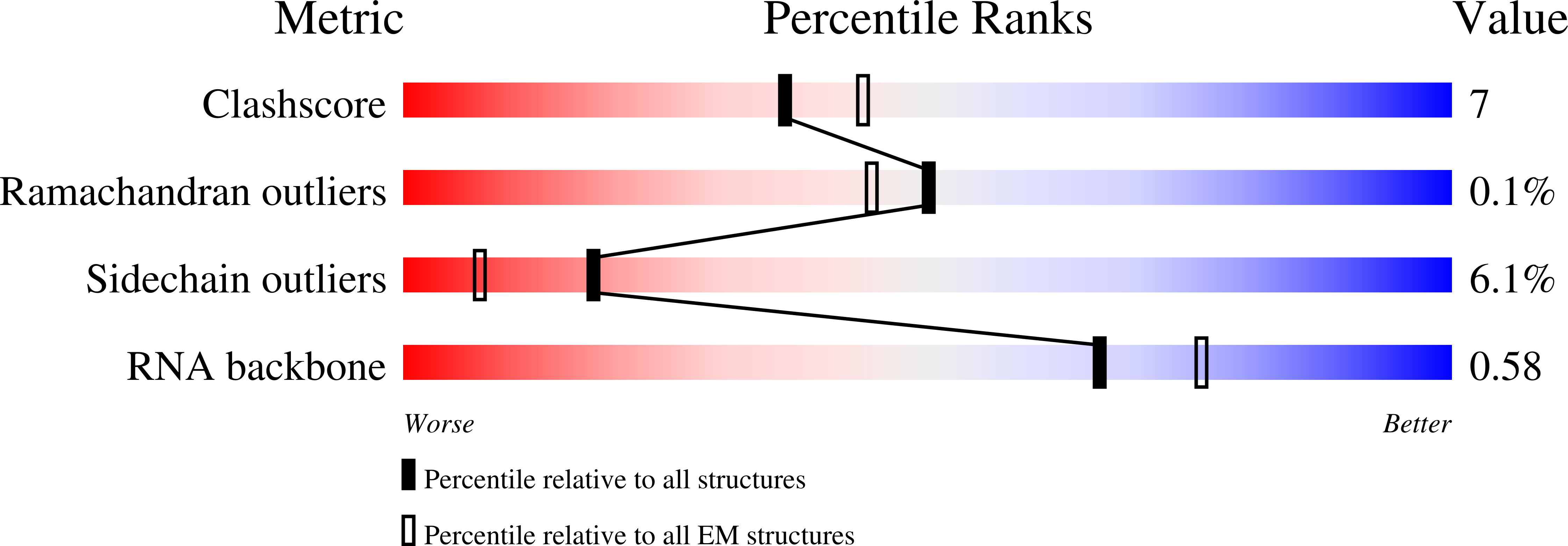
Deposition Date
2023-05-31
Release Date
2024-11-20
Last Version Date
2025-03-12
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8P8B
Keywords:
Title:
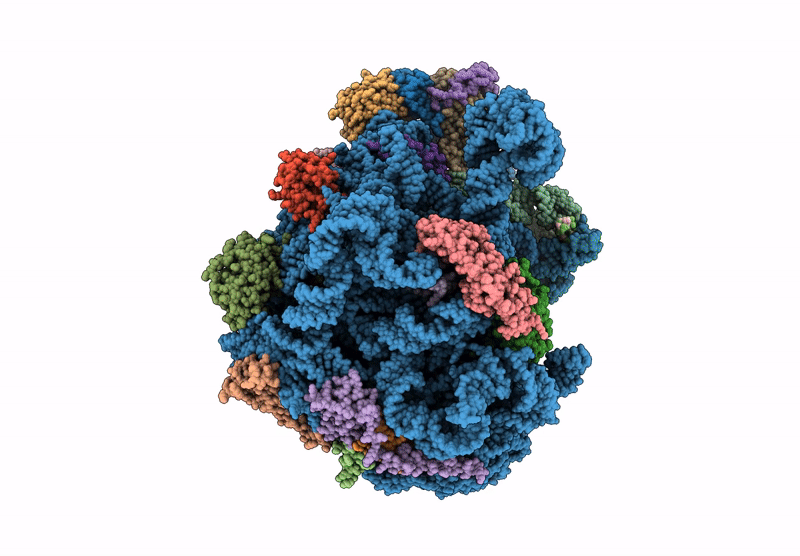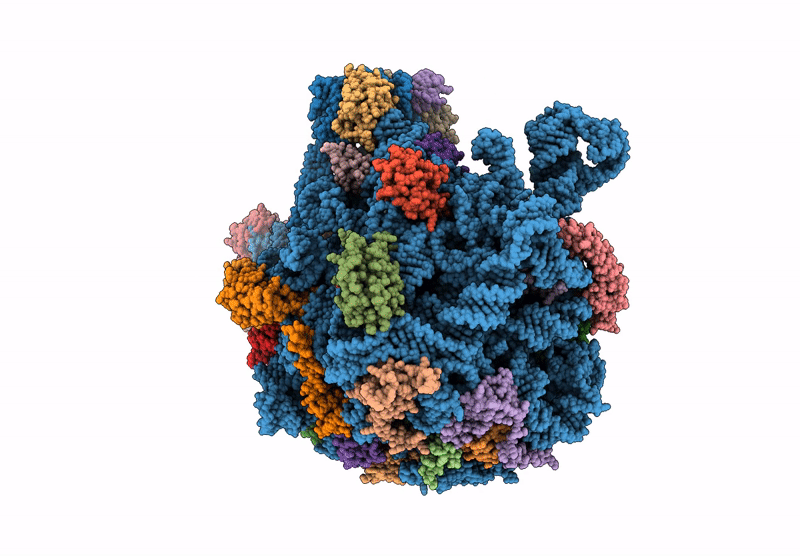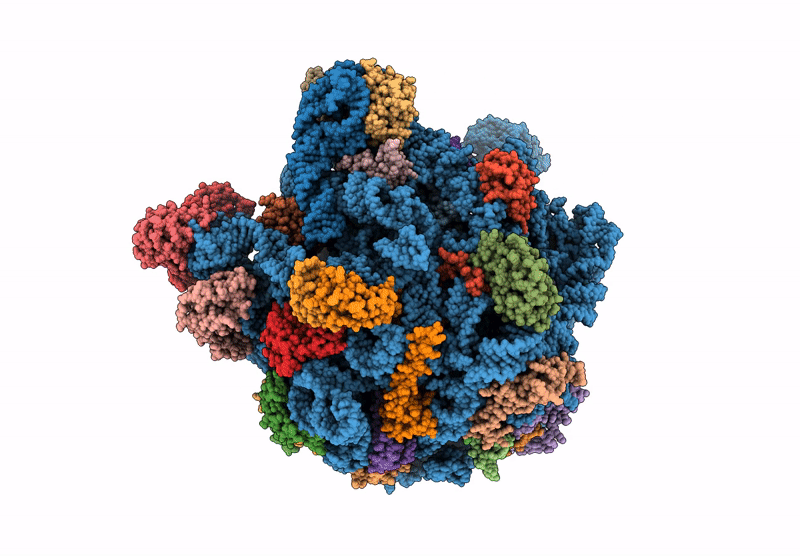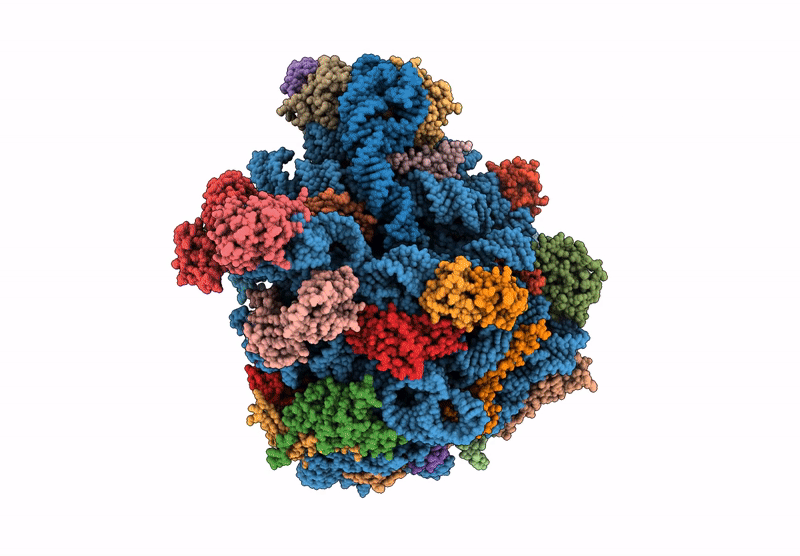
Mycoplasma pneumoniae large ribosomal subunit in chloramphenicol-treated cells
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (Taxon ID: 272634)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.90 Å
Aggregation State:
CELL
Reconstruction Method:
SUBTOMOGRAM AVERAGING